一、SIFT特征原理描述
- 尺度空间极值检测:搜索所有尺度上的图像位置。通过高斯微分函数来识别潜在的对于尺度和旋转不变的兴趣点。(采用不同参数的高斯模板进行不同尺度的模糊,对图像进行下采样进行图像金字塔,同层的上下两层相减得到高斯差分图像进行极值点检测DOG。)
- 关键点定位:在每个候选的位置上,通过一个拟合精细的模型(三维二次函数)来确定位置和尺度。关键点的选择依据于它们的稳定程度。
- 方向确定:基于图像局部的梯度方向,分配给每个关键点位置一个或多个方向。所有后面的对图像数据的操作都相对于关键点的方向、尺度和位置进行变换,从而提供对于这些变换的不变性。旋转不变性,利用梯度的方法求取局部结构的稳定性。
- 关键点描述(128维):在每个关键点周围的邻域内,在选定的尺度上测量图像局部的梯度。这些梯度被变换成一种表示,这种表示允许比较大的局部形状的变形和光照变化。描述子是关键点领域高斯图像梯度统计结果的一种表示,通过对关键点周围图像区域分块,计算块内梯度直方图,生成具有独特性的向量。
二、对两张图片进行SIFT特征匹配处理
在过去的十年间,最成功的图像局部描述子之一是尺度不变特征变换(SIFT),它是由David Lowe发明的。SIFT在2004年由Lowe完善并经受住了时间的考验。

from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
# im1f = '../data/sf_view1.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/sf_view2.jpg'
im1f = '../data/crans_1_small.jpg'
im2f = '../data/crans_2_small.jpg'
# im1f = '../data/climbing_1_small.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/climbing_2_small.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print '{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0]))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
三、对两张图片进行Harris角点检测处理
Harris角点检测器可以给出图像中检测到兴趣点,但它并没有提供在图像间对兴趣点进行比较的方法,我们需要在每个角点添加描述子,以及对这些描述子进行比较。
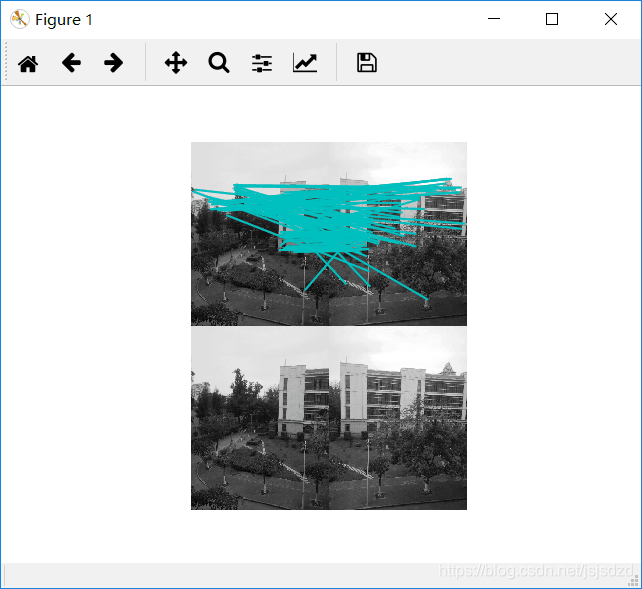
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
from PCV.tools.imtools import imresize
"""
This is the Harris point matching example in Figure 2-2.
"""
# Figure 2-2上面的图
#im1 = array(Image.open("../data/crans_1_small.jpg").convert("L"))
#im2= array(Image.open("../data/crans_2_small.jpg").convert("L"))
# Figure 2-2下面的图
im1 = array(Image.open("../data/sf_view1.jpg").convert("L"))
im2 = array(Image.open("../data/sf_view2.jpg").convert("L"))
# resize加快匹配速度
im1 = imresize(im1, (im1.shape[1]/2, im1.shape[0]/2))
im2 = imresize(im2, (im2.shape[1]/2, im2.shape[0]/2))
wid = 5
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d1 = harris.get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d2 = harris.get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
print 'starting matching'
matches = harris.match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
harris.plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
四、对从不同视点拍摄的图片做地理标记图像匹配
1.从集美大学拍摄15张图片
2. 用局部描述子进行匹配
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print 'comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j]
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print 'number of matches = ', nbr_matches
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print "The match scores is: \n", matchscores
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
3.可视化接连的图片
我们对上面匹配后的图像进行连接可视化,要做到这样,我们需要在一个图中用边线表示它们之间是相连的。我们采用pydot工具包,它提供了GraphViz graphing库的Python接口。
import pydot
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph')
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(0), fontcolor='transparent'))
for i in range(5):
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i + 1)))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(0), str(i + 1)))
for j in range(5):
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j + 1) + '0' + str(i + 1)))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(j + 1) + '0' + str(i + 1), str(j + 1)))
g.write_png('../images/ch02/ch02_fig2-9_graph.png', prog='neato')
同样将匹配后对其进行可视化,为了是得到的可视化结果比较好看,我们对每幅图像用100*100的缩略图缩放它们。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print 'comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j]
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print 'number of matches = ', nbr_matches
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print "The match scores is: \n", matchscores
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('whitehouse.png')




 本文介绍了SIFT特征的原理,包括尺度空间极值检测、关键点定位、方向确定和关键点描述。接着,讨论了使用SIFT特征进行图像匹配的过程。此外,还涉及了Harris角点检测,并指出其需要添加描述子以进行图像间的比较。最后,阐述了如何对不同视点拍摄的图片进行地理标记图像匹配的步骤和可视化方法。
本文介绍了SIFT特征的原理,包括尺度空间极值检测、关键点定位、方向确定和关键点描述。接着,讨论了使用SIFT特征进行图像匹配的过程。此外,还涉及了Harris角点检测,并指出其需要添加描述子以进行图像间的比较。最后,阐述了如何对不同视点拍摄的图片进行地理标记图像匹配的步骤和可视化方法。
















 14万+
14万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








