队列(Queue)
一、基本概念
队列是一种线性数据结构;
相比数组,队列对应的操作也是数组的子集;
只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素;
图解:队列就相当于排队
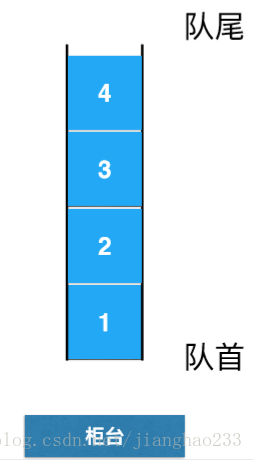
由上图知,队列是先进先出的数据结构(First In First Out [FIFO]);
二、队列的实现
数组队列:
队列的基本操作:
Queue<E>
void enqueue(E) --- 【入队】向队列中添加元素 时间复杂度:O(1)
E dequeue() ---【出队】从队列中拿出队首元素 时间复杂度:O(n)【队首后面的所有的元素都要移动一下】
E getFornt() ---查看队首元素 时间复杂度:O(1)
int getSize() ---查看队列中总共有多少个元素 时间复杂度:O(1)
boolean isEmpty() ---判断队列是否为空 时间复杂度:O(1)
示例代码:
Array.java(复用上章数组的代码)
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
Queue.java
public interface Queue<E> {
int getSize(); //查看队列中总共有多少个元素
boolean isEmpty();//判断队列是否为空
void enqueue(E e);//【入队】向队列中添加元素
E dequeue(); //【出队】从队列中拿出栈顶元素
E getFront(); //查看队首元素
}
ArrayQueue.java
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private Array<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){ //构造函数,传入数组容量
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue(){
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){ //查看静态数组容量
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
array.addLast(e); //增
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
return array.removeFirst(); //拿出队首
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
return array.getFirst(); //查看队首
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: ");
res.append("front ["); //数组左侧是队首
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.getSize() ; i ++){
res.append(array.get(i)); //将队列的每个元素都放到 res 中
if(i != array.getSize() - 1) //如果 i 不是array 的最后一个元素
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail"); //数组右侧是队尾
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i); //添加元素
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue); //取出元素
}
}
}
}
输出:

2.数组队列的问题
删除队首元素(左侧队首)
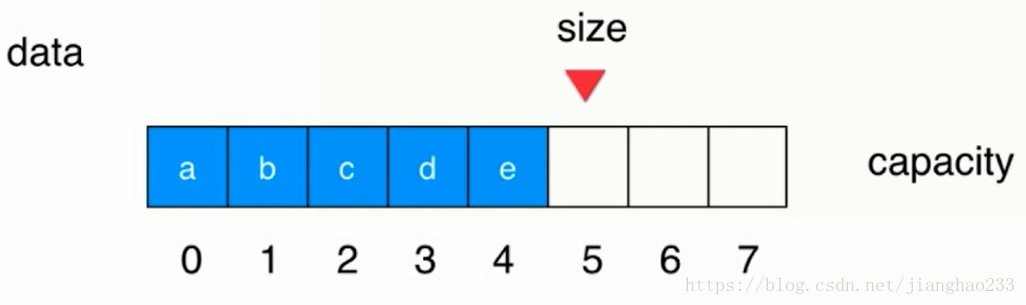
a 移除队列,后面的移动一个单位,size -1;得图
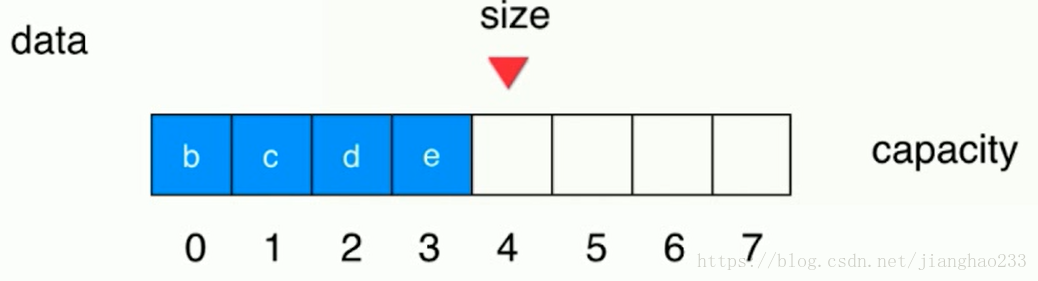
但如果 a移除队列后,后面的不移动,记录目前的队首位置为 front,队尾为 tail,只要维护 front 的指向即可(front++),不需要所有的元素移动一个单位,即可得到循环队列这种实现方式。
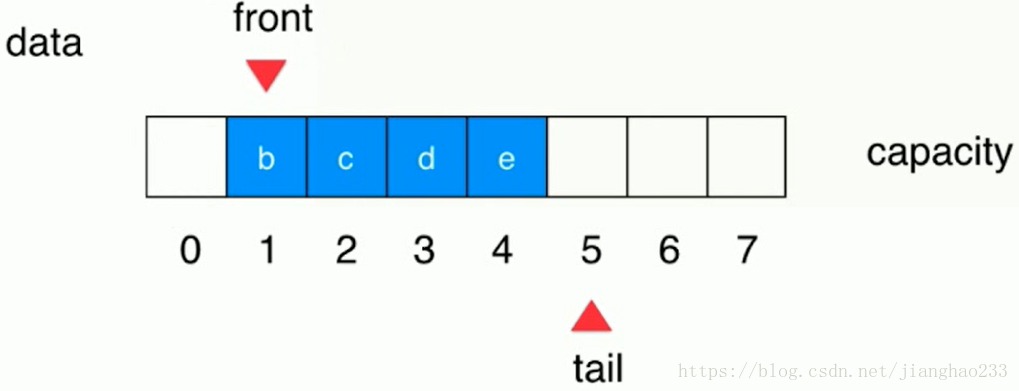
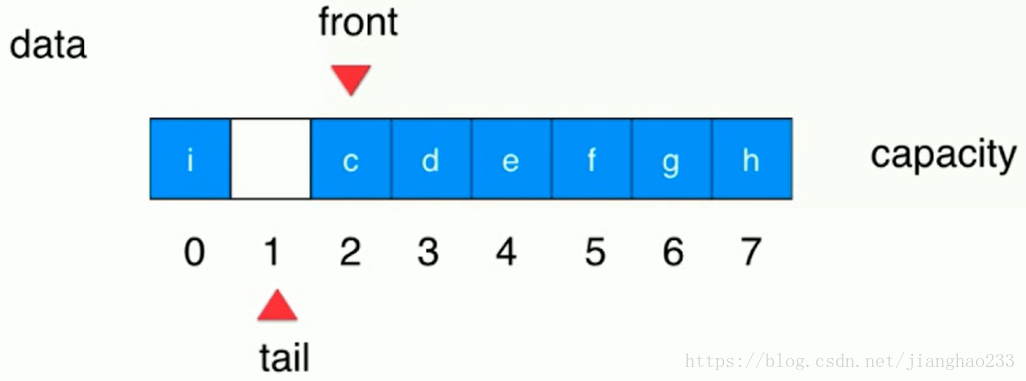
3.循环队列
front == tail --- 队列为空时【起始状态如下图所示】
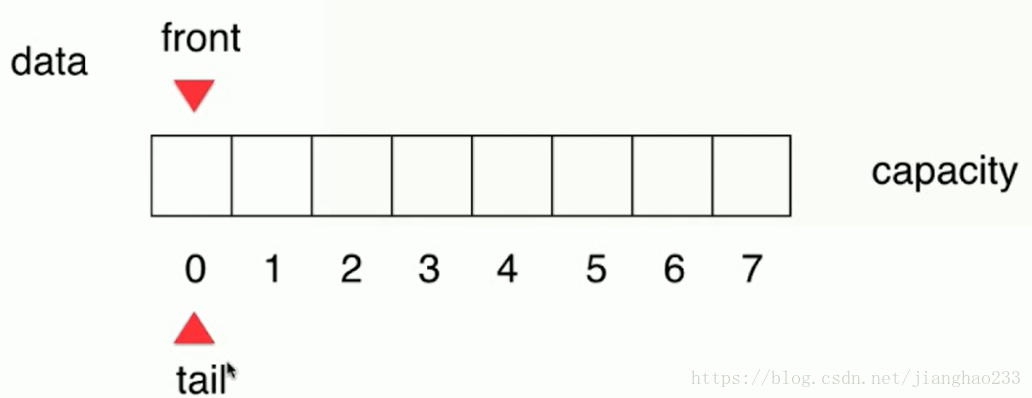
队列进入5个元素后【front不变,tail 右移即可(tail++)】
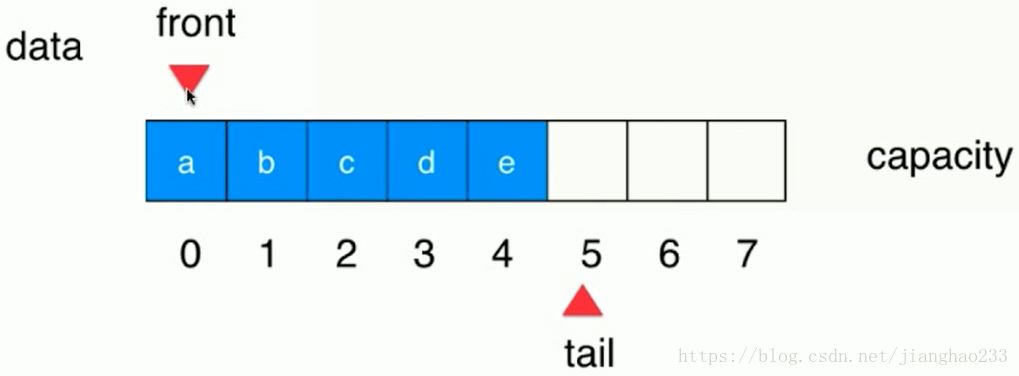
将 a 移除队列,【tail不变,front 右移即可(front++)】其余元素不必移动
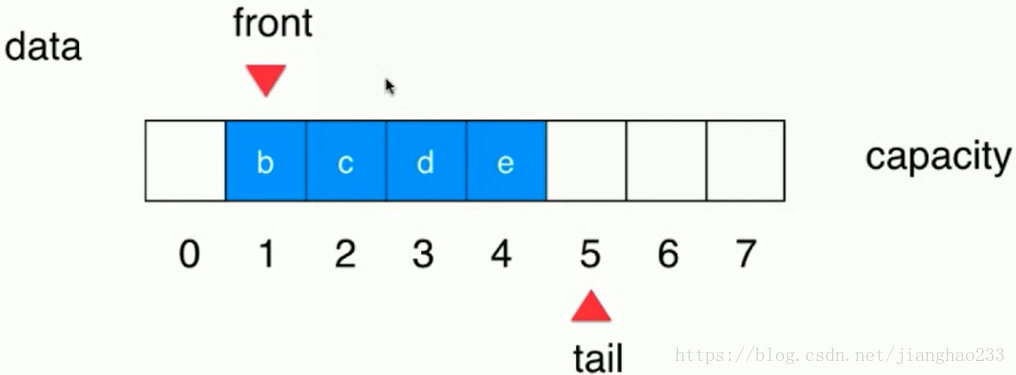
继续加入元素到队列中,装满后面的空间,前面还有空着的空间,tail 就会移动到前面 0 的位置【环形结构】
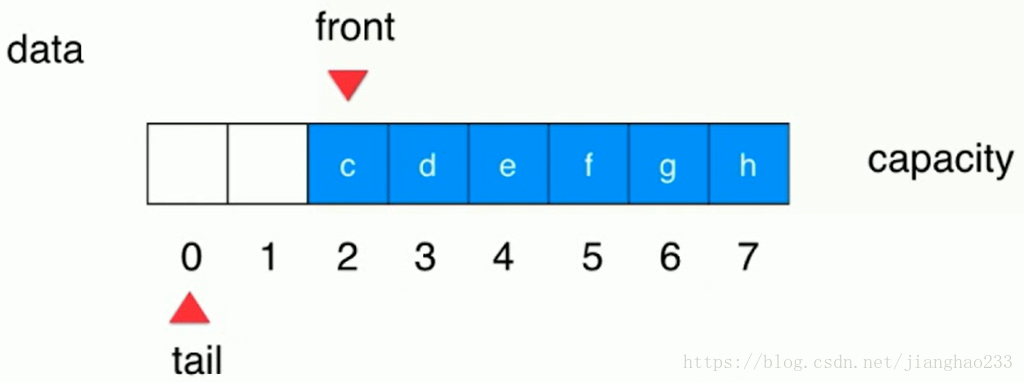
(tail+1)%c == front ---队列满时 ,效果如图【capacity 中有意识的浪费一个空间】
队列的基本操作:
Queue<E>
void enqueue(E) --- 【入队】向队列中添加元素 时间复杂度:O(1)【均摊】
E dequeue() ---【出队】从队列中拿出队首元素 时间复杂度:O(1)【均摊】
E getFornt() ---查看队首元素 时间复杂度:O(1)
int getSize() ---查看队列中总共有多少个元素 时间复杂度:O(1)
boolean isEmpty() ---判断队列是否为空 时间复杂度:O(1)
循环队列的实现
示例代码:
Queue.java
public interface Queue<E> {
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
void enqueue(E e);
E dequeue();
E getFront();
}
LoopQueue.java
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front, tail;
private int size; // 有兴趣的同学,在完成这一章后,可以思考一下:
// LoopQueue中不声明size,如何完成所有的逻辑?
// 这个问题可能会比大家想象的要难一点点:)
public LoopQueue(int capacity){ //定义数组容积capacity
data = (E[])new Object[capacity + 1]; //循环数组中有意识的浪费一个空间
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue(){ //无参数的构造函数
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity(){ //循环队列中最多装载的元素数量
return data.length - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == tail;
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
@Override //(新增代码)
public void enqueue(E e){ //循环队列入队
if((tail + 1) % data.length == front) //判断队列是否“满”
resize(getCapacity() * 2); //队列扩容
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size ++;
}
@Override //(新增代码)
public E dequeue(){ //循环队列出队
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
E ret = data[front]; //出队的元素是队首元素
data[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
size --;
if(size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0) //队列容量要自动缩减
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
return ret;
}
@Override //(新增代码)
public E getFront(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
return data[front];
}
private void resize(int newCapacity){ ////(新增代码)定义扩展数组的方法
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity + 1]; //数组特意浪费一个空间
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++) //遍历方式一
newData[i] = data[(i + front) % data.length]; //将data中的size个元素放到了newData中的[0,size-1]的位置
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
@Override//(新增代码)
public String toString(){ //打印输出
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Queue: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, getCapacity()));
res.append("front ["); //队列左侧是队首
for(int i = front ; i != tail ; i = (i + 1) % data.length){ //遍历方式二
res.append(data[i]);
if((i + 1) % data.length != tail) //判断当前索引不是最后一个元素
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail"); //队列右侧是队尾
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){//(新增代码)
LoopQueue<Integer> queue = new LoopQueue<>(); //添加测试用例
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i); //将0-9这10个数字存放到 queue 中
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue(); //每隔三个数字执行出队操作
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
输出:


三、数组队列和循环队列的比较(执行效率)
示例代码:Main.java
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
// 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueueu和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount){ //测试所花的时间
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); //记录时间(开始)
Random random = new Random(); //声明随机数
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); //入队
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.dequeue(); //出队
long endTime = System.nanoTime(); //记录时间(结束)
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0; //将纳秒转化为秒
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000; //操作数量
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>(); //数组队列输出时间
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>(); //循环队列输出时间
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s");
}
}
输出:

数组队列执行10万个队列入队出队所需的时间远远大于循环队列所需的时间
主要的差距在出队的过程中,数组队列 每一次出队后面所有的元素都要向前挪动一个位置,时间复杂度为O(n),则对于testQueue来说是O(n2);循环队列 则无需挪动位置,时间复杂度为O(n),对于testQueue来说是O(n).







 本文介绍了队列的基本概念,包括其作为先进先出(FIFO)数据结构的特性。接着详细阐述了数组队列的实现,包括入队、出队、获取队首元素等操作的时间复杂度,并指出了数组队列在出队时的效率问题。然后,文章重点讨论了循环队列的实现,解释了如何通过维护front和tail指针来避免元素移动,从而提高出队操作的效率。最后,通过比较数组队列和循环队列在执行效率上的差异,强调了循环队列在处理大量操作时的优势。
本文介绍了队列的基本概念,包括其作为先进先出(FIFO)数据结构的特性。接着详细阐述了数组队列的实现,包括入队、出队、获取队首元素等操作的时间复杂度,并指出了数组队列在出队时的效率问题。然后,文章重点讨论了循环队列的实现,解释了如何通过维护front和tail指针来避免元素移动,从而提高出队操作的效率。最后,通过比较数组队列和循环队列在执行效率上的差异,强调了循环队列在处理大量操作时的优势。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








