一.STL
1.stl(standard template library) 包含一些常用数据结构与算法的模板的C++软件库。其包含四个组件----算法,容器,仿函数,迭代器。
2.重要容器及其用法
1.Vector
1.用来替换普通数组

2.要提前指定长度(如果长度确定)
因为vector额外内存耗尽后的重分配是有时间开销
3.离散化操作
int find(int x)
{
return lower_bound(alls.begin(),alls.end(),x) - alls.begin();
}
alls.push_back(把需要用到的数值存到alls当中)
alls.sort(alls.begin(),alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(),alls.end()),alls.end());
通过find函数找离散化后的值
//关于sort
1.升序sort(alls.begin(),alls.end());
2.降序1 sort(alls.begin(),alls.end(),greater<int>());
3.降序2 sort(alls.begin(),alls.end()); reverse(alls.begin(),alls.end());
2.Stack
1.先进后出 不可遍历元素
2.
例题.A - Plug-in

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
char ans[N];
stack <char> st1;
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0;i < str.size();i++)
{
//如果栈不空 并且 栈顶元素 与遍历到的元素 相等 意味着可以消去
if(!st1.empty() && st1.top() == str[i]) st1.pop();
else st1.push(str[i]);//否则进栈
}
int idx = 0;
//输出栈中内容
while(!st1.empty())
{
auto t = st1.top();
st1.pop();
ans[idx++] = t;
}
for(int i = idx-1;i >= 0;i--) cout << ans[i];
}
3.Queue
1.q.push() q.pop() q.front() q.back()
2.不可直接访问内部元素
3.优先队列
优先队列
priority_queue<int> heap; //大根堆 heap.top() 为最大值
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> heap; //小根堆 heap.top() 为最小值
4.时间复杂度
插入之后快速排序 O(nlogn)
例题 Heap Operations

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000100;
int idx;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
/*
简单模拟题
题目描述三种操作
1.insert --- heap.push()
2.removeMin --- heap.pop() 要注意当堆为空 需要先加一个元素 在进行pop操作
3.getMin --- heap.top()
*/
string moving[3] = {"insert","removeMin","getMin"};
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> heap;
PII ans[N];
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--)
{
string op;
int x;
cin >> op ;
if(op == "insert")
{
cin >> x;
ans[idx++] = {0,x};
heap.push(x);
}
else if(op == "removeMin")
{
//当堆为空却要去掉最小值
//手动加一个0 然后pop()
if(heap.empty())
{
ans[idx++] = {0,0};
heap.push(0);
}
ans[idx++] = {1,-1};
heap.pop();
}
else
{
cin >> x;
//当堆顶元素 小于x 则弹出
while(!heap.empty() && heap.top() < x)
{
ans[idx++] = {1,-1};
heap.pop();
}
//如果堆空 或者堆顶元素 大于 x 那么可以直接 push(x)
if(heap.empty() || heap.top() > x)
{
ans[idx++] ={0,x};
heap.push(x);
ans[idx++] = {2,x};
}
//如果刚好堆顶元素为 x 那么不用push
else if(heap.top() == x)
{
ans[idx++] = {2,x};
}
}
}
cout << idx << endl;
for(int i = 0;i < idx;i++)
{
int t = ans[i].first;
if(t == 1) cout << moving[t] << endl;
else cout << moving[t] << " " << ans[i].second << endl;
}
}
例题 Potions (Hard Version)

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> heap;
int ans;
//遇到正数直接吃
//负数先吃下去 然后放在小根堆当中
//如果这一次吃下去 变成负数了 那么将之前吃过的最小的那个负数 吐出来
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
LL hp = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
hp += (LL)x;
ans ++;
if(x < 0) heap.push(x);
if(hp < 0)
{
hp -= (LL)heap.top();
ans --;
heap.pop();
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
4.Map
1.遍历方式
for(auto item : mp)
{
cout << item.first << " " << item.second << endl;
}
for(auto [key,val] : mp)
{
cout << key << " " << val << endl;
}
2.mp.count() 判断元素是否存在
3.统计字符串出现个数
例题 Knitpicking

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
//存储不同袜子的三种状态:left right any
/*
1.把所有袜子的max(left,right)拿完
2.再每个只有any的袜子拿一个(如果拿完之后发现全部袜子拿过了 意味着 没有袜子能匹配)
3.之后拿的一个 一定能跟之前凑成一对
*/
map<string,array<int,3>> socks;
int n,sum;
//sum 用来记录袜子总数
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
string color,type;
int cnt;
cin >> color >> type >> cnt;
sum += cnt;
if(type == "left") socks[color][0] += cnt;
else if(type == "right") socks[color][1] += cnt;
else socks[color][2] += cnt;
}
int ans = 0;
for(auto item : socks)
{
string a = item.first;
int l = socks[a][0];
int r = socks[a][1];
//如果袜子只有 状态 any 那么ans ++
if(l == 0 && r == 0 && socks[a][2] > 0) ans ++;
//如果袜子有左或者右或者都有 那么取最多的一边
else ans += max(l,r);
}
//如果ans == sum 也就意味着所有袜子都选完了还没有匹配 那么返回无解
//否则一定能再找到一只袜子 与之前选过的匹配 于是袜子数再加1
if(ans != sum)
{
ans ++;
cout << ans << endl;
}
else cout << "impossible";
}
5.Set
1。提供对数时间的插入删除查找 st.insert() st.erase() set.find() st.count() (均为O(logn))
2.每个元素再set当中只出现一次 并且按照升序或者降序排列 (无下标)
set<int> st1; 从小到大
set<int,greater<int>> st2;从大到小
例题 Cutting Woods

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
/*
初始元素只有0 和 L
每次将截断位置x插入set当中
查询位置x 只需将离x最近的左右俩边相减 就是对应的长度(题目保证 查询位置一定没有被砍)
*/
set<int> alls;
int main()
{
int L,Q;
cin >> L >> Q;
alls.insert(L);
alls.insert(0);
while(Q--)
{
int op,x;
cin >> op >> x;
if(op == 1) alls.insert(x);
else
{
auto r = alls.lower_bound(x);
cout << (*r) - *(--r) << endl;
}
}
}
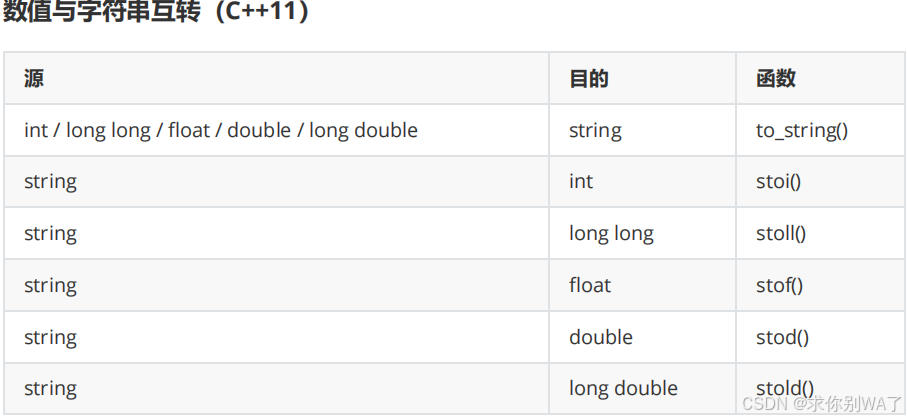
6.String
1.基本操作
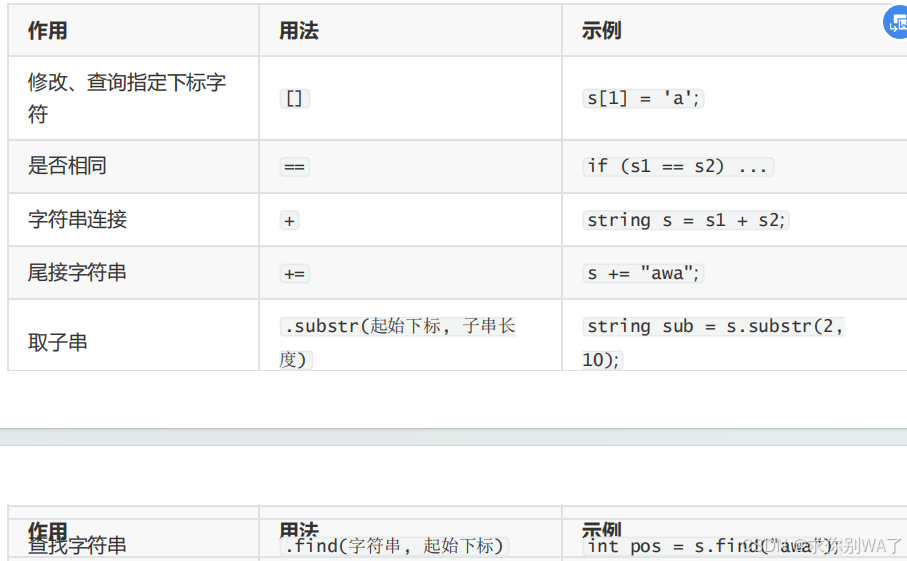
 注意事项
注意事项
1.string 的 += 会在原字符串尾巴直接接上 而 s = s + 'a',会生成一个临时变量 再复制给string 在字符串长度很长的时候会TLE
2.str.substr(子串起点下标,子串长度)
3.find() 时间复杂度为O(n^2)
综合题 Social Media

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
/*
思考答案来源:1.俩个新朋友没有发过消息
2.俩个发过消息的新朋友
记录 用户a ---- 用户 b
1.当其中一个已经是朋友 则另一个的价值加一
2.俩个都不是朋友 计算 若选择这俩人 价值总和是多少
3.俩个已经都是朋友 ans++;
4.单个价值当中 寻找价值最高前俩名(注意讨论只有1人的情况)
*/
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
bool fri[N];
void solve()
{
memset(fri,0,sizeof fri);
int n,m,k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector<int> val(k + 1);//存放只选择当前人的价值
map<pair<int,int>,int> cnt;//存放互相发过消息的俩人价值
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
int c;
cin >> c;
fri[c] = true;
}
int res1 = 0;
int res2 = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
if(fri[a] && fri[b]) res1 ++;//俩人已经是朋友
else if(fri[a]) val[b] ++;
else if(fri[b]) val[a] ++;
else//俩人都不是朋友
{
if(a > b) swap(a,b);
if(a == b) val[a] ++;
else
{
cnt[{a,b}] ++;
}
}
}
for(auto [p,c] : cnt)
{
auto [a,b] = p;
res2 = max(val[a] + val[b] + c,res2);
}
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 1;i <= k;i++)
{
if(!fri[i])
{
tmp.push_back(val[i]);
}
}
sort(tmp.begin(),tmp.end(),greater<int>());
if(tmp.size() >= 2)
{
res2 = max(res2,tmp[0] + tmp[1]);
}
else if(tmp.size() == 1) res2 = max(res2,tmp[0]);
cout << res1 + res2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
7.ST表 (RMQ)
st表就是通过一种倍增的思想可以多而不可以少的覆盖一段区间
也就是需要满足自身和自身操作不会有变化的时候可以使用st表
例题 acwing1273. 天才的记忆

#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010,M = 18;
int w[N];
int f[N][M];
int n,m;
void init()
{
for(int j = 0;j < M;j++)
{
for(int i = 1;i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n;i++)
{
if(!j) f[i][j] = w[i];
else f[i][j] = max(f[i][j-1],f[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
}
}
}
int quiry(int l,int r)
{
int len = r - l + 1;
int k = log(len)/log(2);
return max(f[l][k],f[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cin >> w[i];
init();
cin >> m;
while(m--)
{
int l,r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << quiry(l,r) << endl;
}
}




















 4338
4338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








