12.29 ~ 12.30 复习期末累了 刷会算法题吧 1400 ~ 1500是我能做但是有时候会卡的题 关键是对题目信息的挖掘与转化
1670C. Where is the Pizza?(并查集)
题目大意:给定俩个数组A,B再给一个数组D D数组中元素要么为A中元素 要么为B中元素 0表示任选 求能形成多少个从1~n的排列
例:
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2 3 1 7 6 5 4
2 0 1 0 0 0 0
思路 对于第4个位置和第7个位置 这俩个位置 可以4 7 也可以7 4 第一次遇到4 7把他们加到一个集合当中 第二次遇到4 7判断一下他们是否在一个集合当中 若在 则ans*2(只在当前位置给的值是0的情况下操作)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010,mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long LL;
int a[N],b[N],p[N];
int n;
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cin >> b[i];
LL ans = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
if(!x && a[i] != b[i])//如果x是0 并且 俩个数字不相同
{
int pa = find(a[i]),pb = find(b[i]);
if(pa == pb) ans = (ans * 2LL) % mod;//如果之前俩个数已经在一个集合当中 那么ans * 2
else p[pa] = pb;//否则将俩个数合并到一个集合
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
1644C. Increase Subarray Sums(前缀和 + 线性DP)

题目大意:k从0到n 所以连续子序列(长度为len) 每次加上min(k,len) * x 的最大值
思路:先求出长度从1 到 n的连续子序列和的最大值f[1~n]
再对于k从0 ~ n求max(f[len] + min(len,k) * x)(len: 1~n);
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5050;
int presum[N];
int f[N];
void solve()
{
int n,p;
cin >> n >> p;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> presum[i];
presum[i] += presum[i-1];//前缀和
}
for(int len = 1;len <= n;len ++)//枚举区间长度
{
f[len] = -2e9;//初始化为负无穷
for(int l = 1;l <= n - len + 1;l++)//枚举左端点
{
int r = l + len - 1;
f[len] = max(f[len],presum[r] - presum[l-1]);//计算该区间对于的和
}
}
for(int k = 0;k <= n;k++)
{
int maxv = 0;
for(int len = 0;len <= n;len++)
{
maxv = max(maxv,f[len] + min(k,len) * p);
}
cout << maxv <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1634B. Fortune Telling(思维+奇偶性)
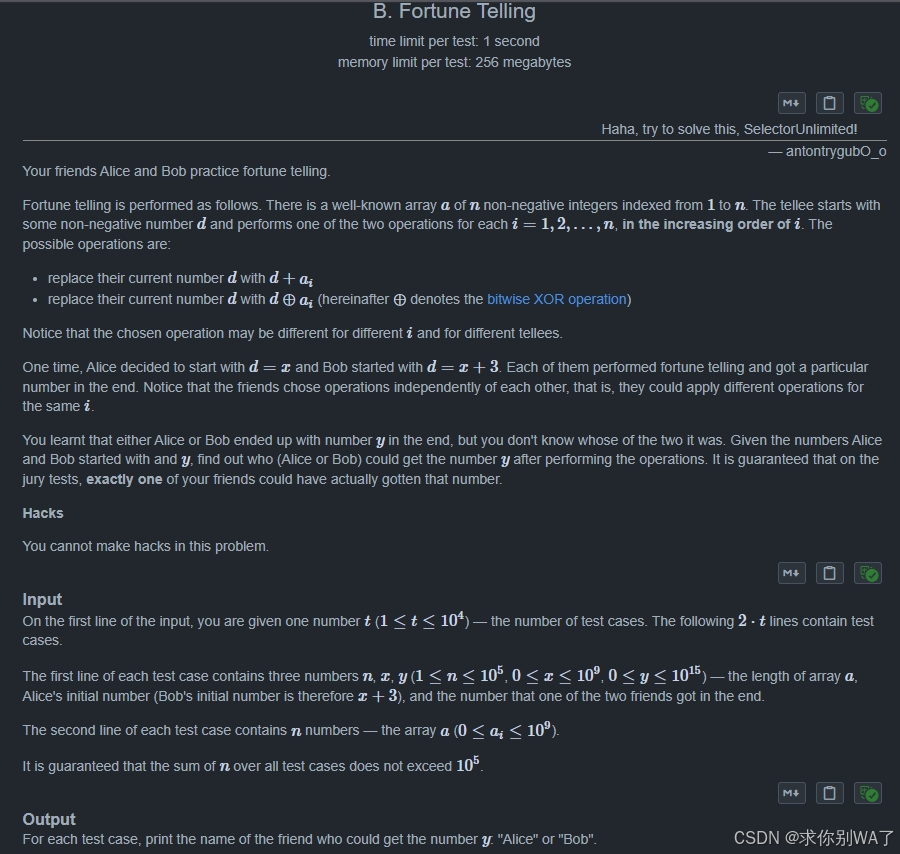
题目大意:给定初始值 x,a[i] A从x开始 B从x+3开始 每次可以对a[i]进行加法或者异或(0<i<n)
再给定最终的结果 判断是A变化而成 还是B变化而成
思路:1.看到只能加法或者异或 -----他们在二进制下(对于奇偶性)是等价的
2.为什么是x 和 x+3 ----- 两者奇偶性不同
3.数据范围超LL ------ 不能枚举加法和异或
4.我们只要判断一下 ans 和 初始值的奇偶性是否相同 在判断一下 a[i]的所有值 是否能改变奇偶性
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void solve()
{
LL n,st,ed;
cin >> n >> st >> ed;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
LL a;
cin >> a;
res ^= a;
}
if(res % 2 == (st ^ ed) % 2) cout << "Alice" << endl;
//如果结果奇偶性改变(不改变)但是a[i]不改变(能改变)那么是bob得出的结果
else cout << "Bob" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1679C. Rooks Defenders(树状数组)
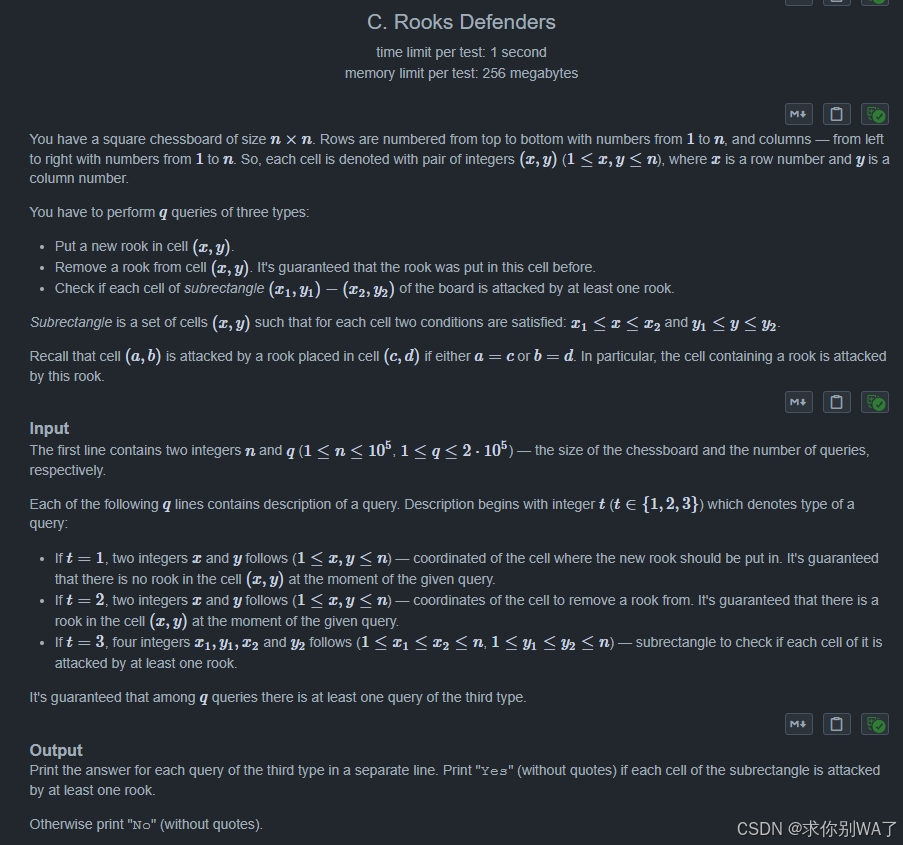
题目大意 :每次放一辆车 可以对当前行 和 当前列造成伤害 每次查询一个矩形 判断矩形里面是否全部受到伤害
思路:前缀和 但是每次修改都要重新做一遍前缀和 时间复杂度为O(n^2)会TLE
于是用树状数组 修改和查询都是O(logn) 总时间复杂度是O(nlogn)可以过
不过要注意 一个点只能加一次 需要额外开2个数组 记录加减的次数 当次数为0且需要增加时 或者当次数为1 且要减少时 才对树状数组进行修改操作
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int row[N],col[N];
int r[N],cl[N];
int n,q;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & -x;
}
void add(int x,int c,int tr[])
{
for(int i = x;i <= n;i += lowbit(i)) tr[i] += c;
}
int ask(int x,int tr[])
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = x;i > 0;i -= lowbit(i))
{
res += tr[i];
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> q;
while(q--)
{
int t,x1,x2,y1,y2;
cin >> t >> x1 >> y1;
if(t == 1)
{
if(r[x1]==0) add(x1,1,row),r[x1]++;
else r[x1] ++;
if(cl[y1]==0) add(y1,1,col),cl[y1]++;
else cl[y1] ++;
}
else if(t == 2)
{
if(r[x1] == 1) add(x1,-1,row),r[x1] --;
else r[x1] --;
if(cl[y1] == 1) add(y1,-1,col),cl[y1] --;
else cl[y1] --;
}
else
{
cin >> x2 >> y2;
int cntrow = ask(x2,row) - ask(x1-1,row);
int cntcol = ask(y2,col) - ask(y1-1,col);
if(cntrow >= x2 - x1 + 1 || cntcol >= y2 - y1 + 1) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
1682C. LIS or Reverse LIS?(思维)
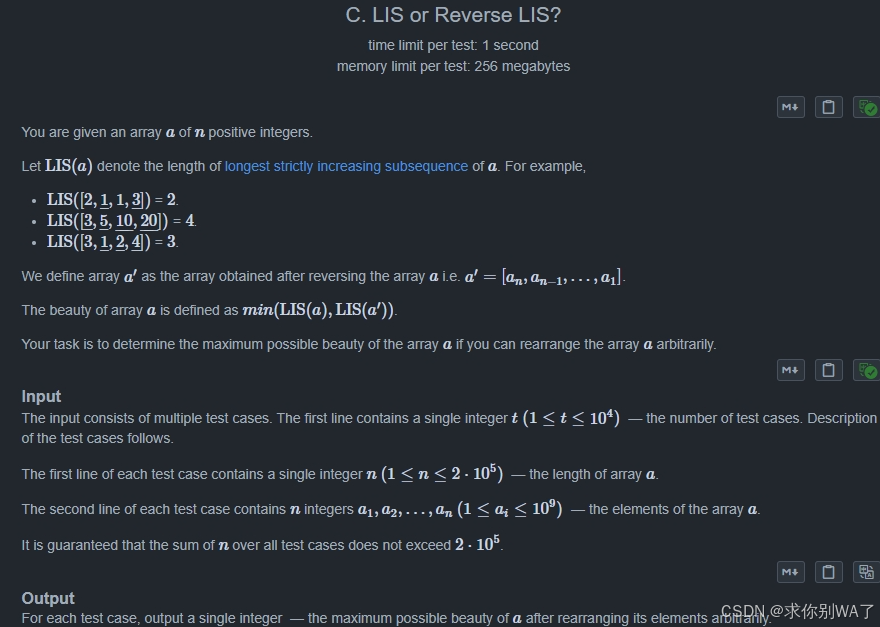
题目大意:一个数组可以任意排列 求 min(从左到右最长上升子序列,从右到左最长上升子序列)
思路:对于一个数 出现2次那么 从左到右 从右到左各一次 其余出现次数(不为1)都是没用的
对于一个数出现1次 可以放中间 或者是一边
记录cnt对于次数小于等于2的 ++,结果就是cnt/2上取整
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
map<int,int> alls;
void solve()
{
alls.clear();
int n;
cin >> n;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
if(!alls.count(x)) alls[x] = 1,ans ++;
else if(alls.count(x))
{
alls[x]++;
if(alls[x] <= 2) ans ++;
}
}
cout << (ans+1) / 2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
580B. Kefa and Company(前缀和+ 结构体排序+二分)

题目大意:kefa有很多财富值不同的好友 每个好友的好感度不同 但是又不能叫他们都来 因为如果财富值相差m有好友就要伤心 求能过达到的总的好感度的最大值(不让所有人伤心的前提)
思路:对于好友的财富值排序 从左到右遍历一遍 找到能够满足财富值差值的区间 对于每一个这样的区间 求好感度 取max
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100010;
struct info
{
int w,v;
//习惯在结构体内部重载小于号
bool operator <(const info&t)const
{
return w < t.w;//按照好友财富值排序
}
}fri[N];
int n,m;
LL s[N];
bool check(int u,int mid)
{
if(fri[mid].w - fri[u].w < m) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
int w,v;
cin >> w >> v;
fri[i] = {w,v};
}
sort(fri+1,fri+n+1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) s[i] = s[i-1] + (LL)fri[i].v;
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)//wi 要找到最右边一个 wj - wi < m的位置
{
int l = i,r = n;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if(check(i,mid)) l = mid;//找出最右边的一个
else r = mid - 1;
}
ans = max(ans,s[r] - s[i-1]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
580C. Kefa and Pdfs)
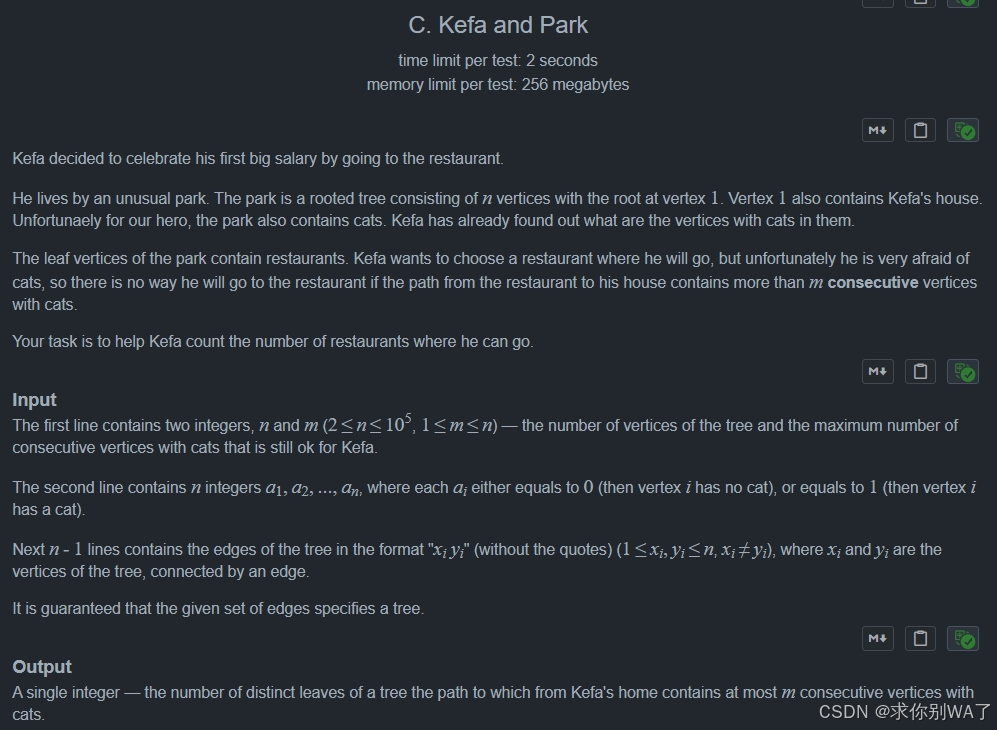
题目大意:从家走到餐厅需要路过公园 kefa选择性恐猫症(不能连续遇到m只猫猫)餐厅在叶子节点,求到餐厅的个数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N],e[N*2],w[N*2],ne[N*2],idx;
int n,m;
int ans;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx++;
}
void dfs(int u,int cnt,int fa)//cnt表示连续猫猫数量
{
if(cnt > m) return;//如果这条路连续猫猫数量超过m 那么不符合直接return
bool isleaf = true;//判断是否走到餐厅
for(int i = h[u]; ~i;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(j == fa) continue;//由于建立双向边 只能往下搜 不能往上搜 不然死循环
isleaf = false;//如果有儿子 表示不是叶子节点
if(w[j] == 1) dfs(j,cnt+1,u);//如果该点是猫猫 那么cnt+1
else dfs(j,0,u);//如果不是猫猫 那么猫猫数量清0(因为要的是连续猫猫)
}
if(isleaf) ans++;//如果到餐厅了 答案++
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) cin >> w[i];//每个节点的猫猫存在情况 1表示存在
for(int i = 0;i < n-1;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);//建立双向边
}
dfs(1,w[1],-2);//从根节点开始dfs
cout << ans << endl;
}
690C1. Brain Network (easy)(dfs判断环)
题目大意:一副无向图 判断图中所有点是否能到并且不存在环(也就是多余边)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int h[N],e[N * 2],ne[N * 2],idx;
bool st[N];
int ans;
int n,m;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx++;
}
bool dfs(int u,int fa)
{
st[u] = true;
ans ++;//统计能到达的节点数量
for(int i = h[u];~i;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(j == fa) continue;
if(st[j]) //如果儿子之前已经找过了 那么表示形成环了
{
return false;//形成环直接返回false
}
if(!dfs(j,u)) return false;//如果儿子的儿子形成环 也返回false
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
if(dfs(1,-1) && ans == n) puts("yes");//如果没有环 并且 每个点都能到达 那么满足题意
else puts("no");
}
690C2. Brain Network (medium)(dfs+树的直径-->任意俩点距离最大值)
题目大意:找树当中任意俩点距离的最大值
思路:每个点有很多儿子 找出最长的一个儿子 和次长的儿子 相加就是距离最大值
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N],e[N * 2],ne[N * 2],idx;
int n,m;
int ans;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx++;
}
int dfs(int u,int fa)//返回以u为根的最长子路
{
//d1表示最长儿子 d2表示次长儿子
int d1 = 0,d2 = 0;
for(int i = h[u];~i;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(j == fa) continue;
int d = dfs(j,u) + 1;//d表示每个儿子的长度
//更新最长与次长
if(d > d1) d2 = d1,d1 = d;
else if(d > d2) d2 = d;
}
ans = max(ans,d1 + d2);//每次更新一遍全局最大值
return d1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
dfs(1,-1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
977E. Cyclic Components(dfs)

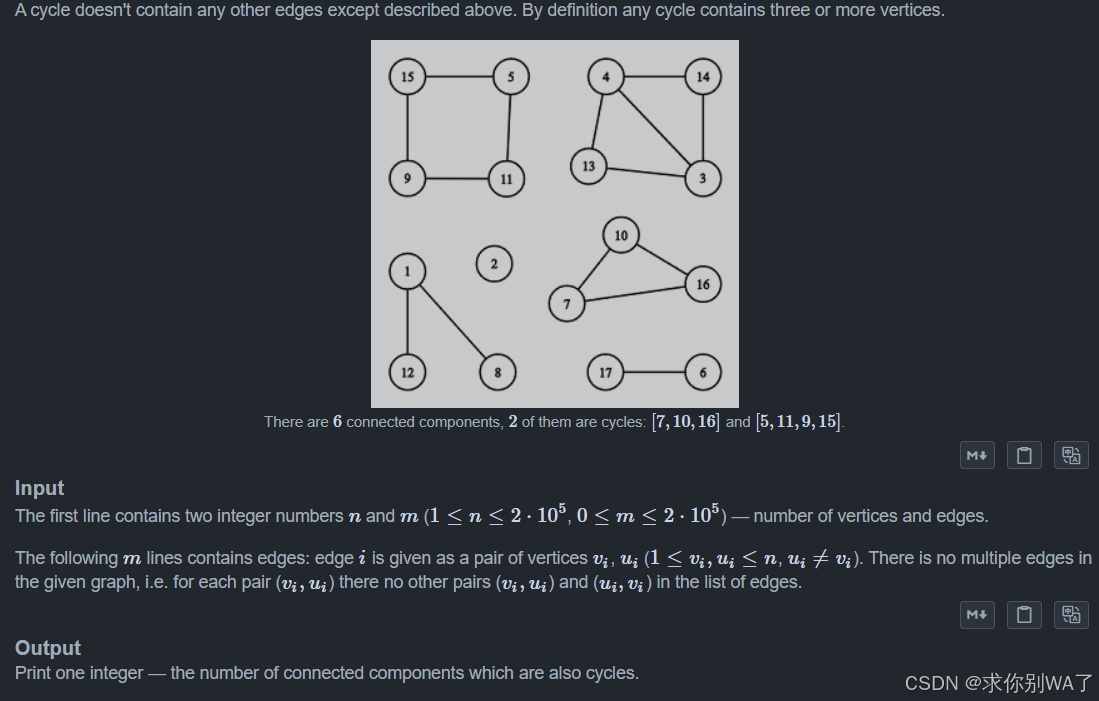
题目大意:求所有连通块当中 满足所有点度数为2 的联通块个数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
bool st[N],flag;
int h[N],e[N * 2],ne[N * 2],idx;
int d[N];
int n,m;
int ans;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx++;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
st[u] = true;
if(d[u] != 2) flag = false;
for(int i = h[u];~i;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(st[j]) continue;
dfs(j);
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
d[a] ++,d[b]++;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
flag = true;
if(!st[i])
{
dfs(i);
if(flag) ans ++;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
982C. Cut 'em all!(dfs求节点数)

题目大意:在去掉尽可能多的边的条件下 满足剩下连通块点的数量相同
思路:对于点数为奇数的 显然无解
对于点数为偶数 记录只要以u为根的节点数为偶数 (那么中间一定可以砍一刀)那么ans++
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N],e[N * 2],ne[N * 2],idx;
int n,ans;
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx++;
}
int dfs(int u)//返回以u为根的节点数量
{
st[u] = true;
int s = 1;
for(int i = h[u];~i;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(st[j]) continue;
s += dfs(j);
}
if(s % 2 == 0) ans ++;//如果以u为根的节点数量为偶数ans++
//从叶子节点往上算
return s;
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin >> n ;
for(int i = 0;i < n - 1;i++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
if(n % 2 == 1) cout << "-1";
else
{
dfs(1);
cout << ans - 1 << endl;//答案减一原因是算上了一刀不砍的偶数情况
}
return 0;
}





















 2292
2292

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








