一、哈希表:快速访问的艺术
1.1 哈希表的基本概念
哈希表(Hash Table)是一种通过键(Key)直接访问值(Value)的数据结构,它通过哈希函数将键映射到数组中的特定位置,从而实现平均时间复杂度为O(1)的快速查找、插入和删除操作。
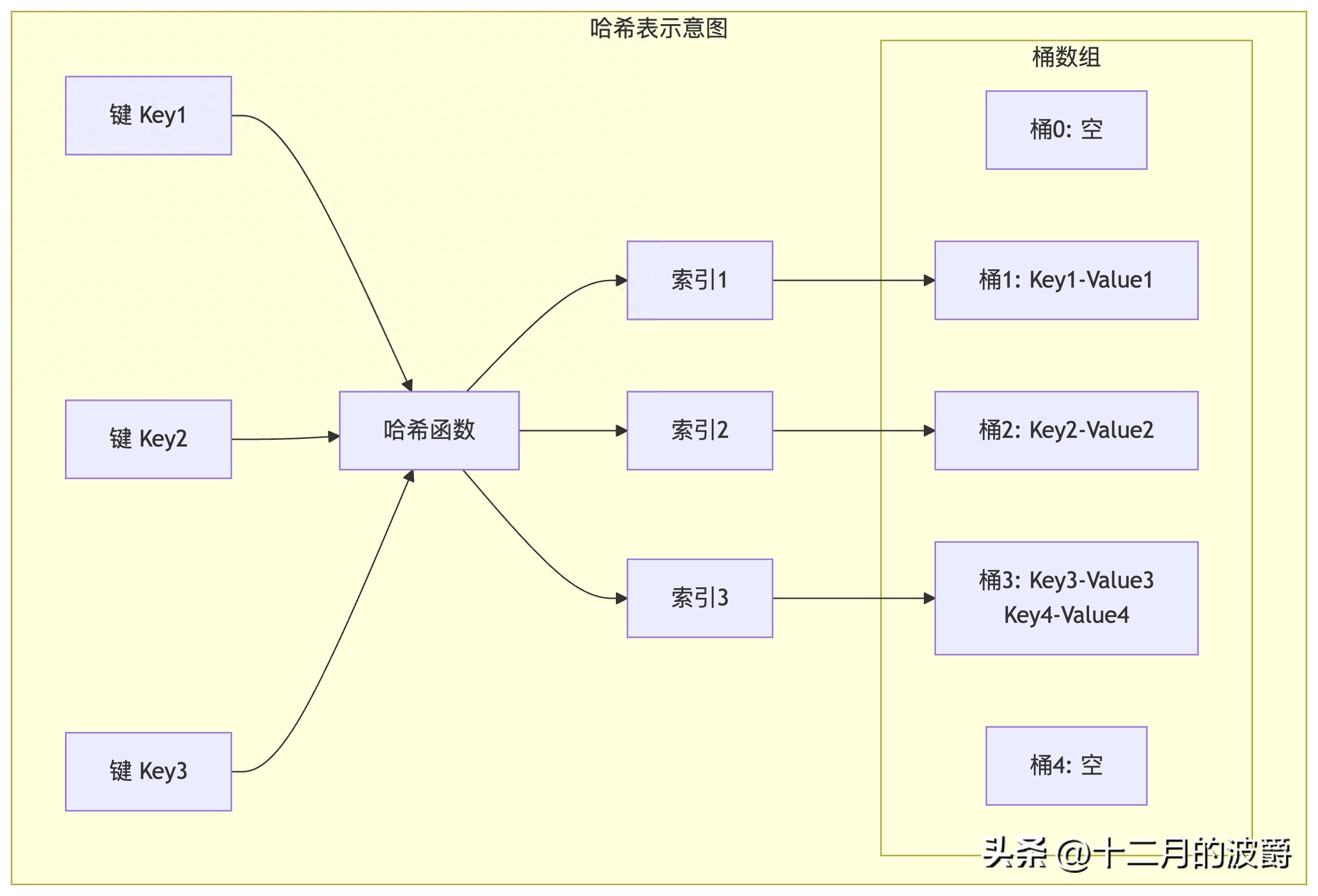
核心概念:
- 哈希函数:将任意大小的数据映射到固定大小值的函数
- 哈希值:哈希函数计算的结果
- 桶(Bucket):存储键值对的数组元素
- 冲突(Collision):不同键映射到相同哈希值的情况
- 负载因子(Load Factor):元素数量与桶数量的比率,决定何时扩容
二、HashMap的实现原理
2.1 Java 8+中的HashMap结构
Java 8中的HashMap采用"数组+链表+红黑树"的混合结构:
// HashMap的核心内部结构
public class HashMap<K, V> {
// 哈希表数组
transient Node<K, V>[] table;
// 链表节点定义
static class Node<K, V> {
final int hash; // 哈希值
final K key; // 键
V value; // 值
Node<K, V> next; // 下一个节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
// 红黑树节点定义(当链表过长时转换为树节点)
static final class TreeNode<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K, V> {
TreeNode<K, V> parent;
TreeNode<K, V> left;
TreeNode<K, V> right;
TreeNode<K, V> prev;
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K, V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
}
// 其他重要字段
transient int size; // 键值对数量
int threshold; // 扩容阈值(容量*负载因子)
final float loadFactor; // 负载因子(默认0.75)
}
2.2 哈希函数的设计
Java HashMap使用精心设计的哈希函数来减少冲突:
// HashMap中的哈希函数实现
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
// 1. 获取key的hashCode
// 2. 高16位与低16位进行异或运算,增加低位的随机性
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
// 确定元素在数组中的位置
int index = (table.length - 1) & hash; // 相当于 hash % table.length
这种设计的好处:
- 使用高半位和低半位异或,充分利用哈希码的所有信息
- 与(length-1)进行与运算,比取模运算更高效
- 对null键有特殊处理(放在第0个桶)
三、哈希冲突的解决方案
3.1 拉链法(Separate Chaining)
HashMap使用拉链法解决冲突,即每个数组元素是一个链表(或树)的头节点:
// HashMap的put方法核心逻辑(简化版)
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 计算哈希值
int hash = hash(key);
int index = (table.length - 1) & hash;
// 检查是否已存在该键
Node<K, V> first = table[index];
for (Node<K, V> node = first; node != null; node = node.next) {
if (node.hash == hash &&
(node.key == key || (key != null && key.equals(node.key)))) {
V oldValue = node.value;
node.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// 创建新节点并添加到链表头部
table[index] = new Node<>(hash, key, value, first);
size++;
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (size > threshold)
resize();
return null;
}
3.2 树化优化(Treeify)
当链表过长时,Java 8会将链表转换为红黑树,提高查询效率:
// 树化阈值
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 树化逻辑
final void treeifyBin(Node<K, V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index;
Node<K, V> e;
// 只有当数组长度达到64时才会树化,否则优先扩容
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 将链表转换为红黑树
TreeNode<K, V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K, V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
四、扩容与重新哈希
4.1 扩容机制
HashMap在元素数量达到阈值时进行扩容,通常扩大为原来的2倍:
// resize方法核心逻辑
final Node<K, V>[] resize() {
Node<K, V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
// 计算新容量和新阈值
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // 双倍阈值
}
// 初始化情况处理...
threshold = newThr;
// 创建新数组
Node<K, V>[] newTab = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
// 重新哈希:将旧数组元素转移到新数组
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K, V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null) {
// 单个节点直接重新计算位置
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
}
else if (e instanceof TreeNode) {
// 树节点拆分
((TreeNode<K, V>) e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
}
else {
// 链表拆分:保持相对顺序
Node<K, V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K, V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K, V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
// 判断节点在新数组中的位置
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
// 位置不变(低位链表)
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
// 位置改变(高位链表)
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
// 将低位链表放到原索引位置
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
// 将高位链表放到新索引位置
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
4.2 重新哈希的优化
Java HashMap的重新哈希过程有一个巧妙优化:由于容量总是2的幂,元素在新数组中的位置要么保持不变,要么原位置+旧容量:
旧容量: 16 (二进制: 10000) 新容量: 32 (二进制: 100000) 计算索引: hash & (capacity - 1) 对于hash值: - 如果第5位为0: 新位置 = 原位置 - 如果第5位为1: 新位置 = 原位置 + 16
这种设计避免了重新计算哈希值,提高了扩容效率。
五、线程安全的哈希实现
5.1 ConcurrentHashMap
对于多线程环境,Java提供了线程安全的ConcurrentHashMap:
// ConcurrentHashMap的基本使用
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> concurrentMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 线程安全的操作方法
concurrentMap.put("key", 1);
Integer value = concurrentMap.get("key");
concurrentMap.remove("key");
// 原子操作
concurrentMap.putIfAbsent("key", 2); // 键不存在时插入
concurrentMap.computeIfPresent("key", (k, v) -> v + 1); // 键存在时计算新值
5.2 ConcurrentHashMap的实现原理
Java 8的ConcurrentHashMap使用分段锁+CAS操作:
// ConcurrentHashMap的核心结构
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> {
// 使用Node数组存储,volatile保证可见性
transient volatile Node<K, V>[] table;
// 使用CAS操作保证原子性
static final <K, V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K, V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K, V> c, Node<K, V> v) {
return U.compareAndSetReference(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
// 分段锁策略(Java 8优化为更细粒度的锁)
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K, V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K, V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// 使用CAS尝试无锁插入
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break;
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
// 对链表头节点加锁
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 链表或树操作...
}
}
}
}
// 检查是否需要树化...
return null;
}
}
六、哈希表的应用场景
6.1 缓存实现
// 基于HashMap的简单LRU缓存实现
public class LRUCache<K, V> {
private final int capacity;
private final HashMap<K, Node> map;
private final DoublyLinkedList list;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.map = new HashMap<>();
this.list = new DoublyLinkedList();
}
public V get(K key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
return null;
}
Node node = map.get(key);
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
} else {
if (map.size() >= capacity) {
Node last = list.removeLast();
map.remove(last.key);
}
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
list.addFirst(newNode);
}
}
// 双向链表节点
class Node {
K key;
V value;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
// 双向链表
class DoublyLinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
void addFirst(Node node) {
// 实现添加到头部的逻辑
}
void remove(Node node) {
// 实现移除节点的逻辑
}
Node removeLast() {
// 实现移除尾部节点的逻辑
return tail;
}
}
}
6.2 频率统计
// 使用HashMap进行词频统计
public class WordFrequencyCounter {
public Map<String, Integer> countWords(String text) {
Map<String, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap<>();
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return frequencyMap;
}
// 分割文本为单词
String[] words = text.toLowerCase().split("\\W+");
for (String word : words) {
if (word.isEmpty()) continue;
// 使用merge方法简化计数
frequencyMap.merge(word, 1, Integer::sum);
// 等价于:
// frequencyMap.put(word, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
return frequencyMap;
}
// 找出出现频率最高的单词
public String mostFrequentWord(String text) {
Map<String, Integer> frequencyMap = countWords(text);
return frequencyMap.entrySet().stream()
.max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.orElse(null);
}
}
6.3 数据索引
// 使用HashMap构建多字段索引
public class MultiIndexDatabase<K, E> {
private final Map<K, E> primaryIndex = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Map<Object, Set<E>>> secondaryIndices = new HashMap<>();
// 添加对象到数据库
public void add(K key, E entity) {
primaryIndex.put(key, entity);
updateSecondaryIndices(entity, true);
}
// 更新二级索引
private void updateSecondaryIndices(E entity, boolean add) {
for (Field field : entity.getClass().getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Indexed.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
Object value = field.get(entity);
String fieldName = field.getName();
secondaryIndices
.computeIfAbsent(fieldName, k -> new HashMap<>())
.computeIfAbsent(value, k -> new HashSet<>());
if (add) {
secondaryIndices.get(fieldName).get(value).add(entity);
} else {
secondaryIndices.get(fieldName).get(value).remove(entity);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// 处理异常
}
}
}
}
// 通过二级索引查询
public Set<E> queryByField(String fieldName, Object value) {
return secondaryIndices.getOrDefault(fieldName, Collections.emptyMap())
.getOrDefault(value, Collections.emptySet());
}
}
// 索引注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@interface Indexed {
}
七、性能优化与最佳实践
7.1 HashMap性能调优
- 初始容量设置:
// 预估元素数量,避免频繁扩容 int expectedSize = 1000; float loadFactor = 0.75f; int initialCapacity = (int) (expectedSize / loadFactor) + 1; Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
- 键对象设计:
// 自定义对象作为键时,正确实现hashCode和equals方法
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age); // 使用Objects.hash简化实现
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) return true;
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;
Person other = (Person) obj;
return age == other.age && Objects.equals(name, other.name);
}
}
7.2 选择正确的Map实现
| 实现类 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
| HashMap | 快速查找,非线程安全 | 大多数单线程场景 |
| LinkedHashMap | 保持插入顺序 | 需要顺序遍历的场景 |
| TreeMap | 按键排序,红黑树实现 | 需要有序映射的场景 |
| ConcurrentHashMap | 线程安全,高并发性能 | 多线程环境 |
| Hashtable | 线程安全,性能较差 | 遗留系统(不推荐新项目使用) |
7.3 避免常见陷阱
// 1. 并发修改异常
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 1);
map.put("b", 2);
// 错误:在迭代时修改集合
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
if ("a".equals(key)) {
map.remove(key); // 抛出ConcurrentModificationException
}
}
// 正确:使用迭代器的remove方法
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
if ("a".equals(entry.getKey())) {
iterator.remove(); // 安全删除
}
}
// 2. 可变对象作为键
Map<List<String>, Integer> mutableKeyMap = new HashMap<>();
List<String> key = new ArrayList<>();
key.add("hello");
mutableKeyMap.put(key, 1);
key.add("world"); // 修改键对象
Integer value = mutableKeyMap.get(key); // 可能返回null,因为哈希值改变了
总结
HashMap是Java中最重要和最常用的数据结构之一,其精妙的设计和实现体现了计算机科学的深度:
核心要点:
- HashMap基于"数组+链表+红黑树"的混合结构,在时间和空间效率间取得平衡
- 优秀的哈希函数设计和冲突解决策略是高效性的关键
- 动态扩容和重新哈希机制保证了性能的稳定性
- 线程安全场景应选择ConcurrentHashMap而非Hashtable
最佳实践:
- 根据预估元素数量合理设置初始容量和负载因子
- 作为键的对象必须正确实现hashCode()和equals()方法
- 避免在迭代过程中直接修改集合
- 不要使用可变对象作为HashMap的键
HashMap不仅是Java集合框架的核心组件,其设计思想也广泛应用于各种系统设计中。深入理解HashMap的工作原理,对于编写高效、可靠的Java程序至关重要。






















 983
983

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










