map用法总结
参考资料:
1、C++ map用法总结
2、map的基本操作
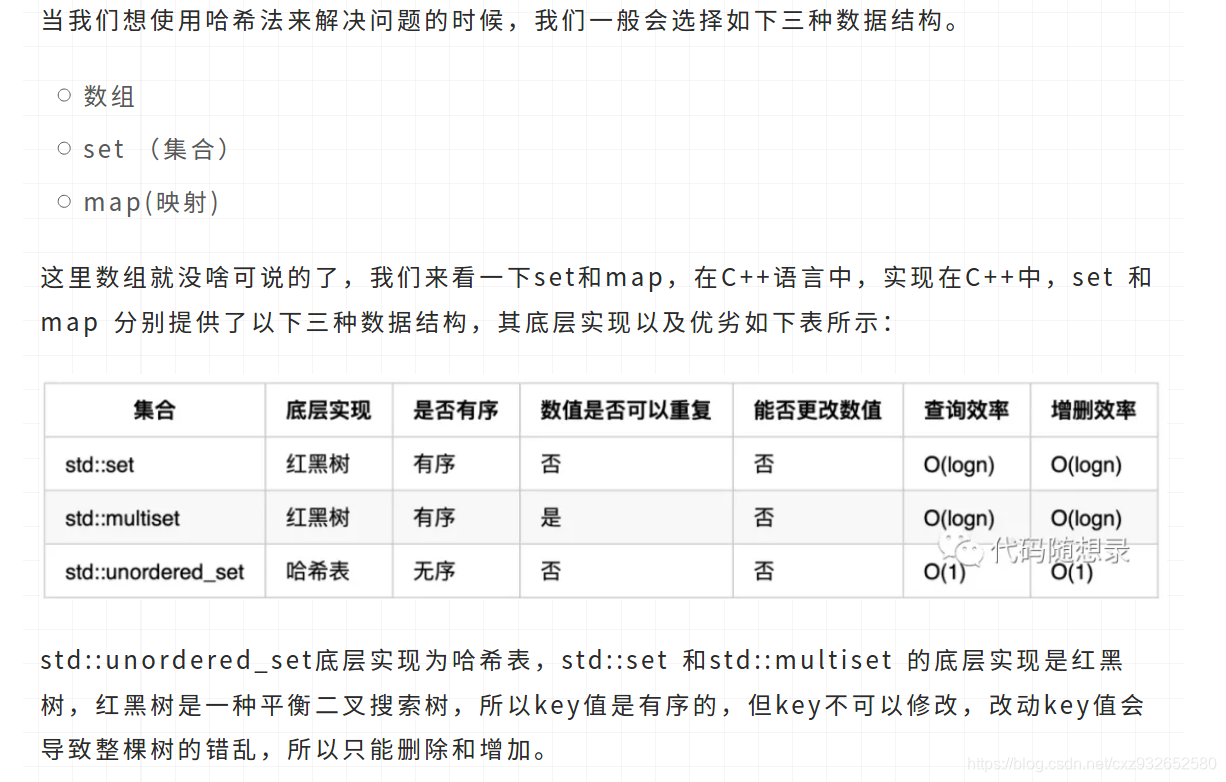
3、关于哈希表,你该了解这些
1 map简介
map 是STL的一个关联容器,提供一对一的hash
1.1 第一个可以称为关键字(key),每个关键字只能在map中出现一次;
1.2 第二个可以称为该关键字的值(value);
1.3 参考代码随想录中对哈希表的介绍

2 map功能
2.1 自动建立key - value 的对应,key 和value 可以是任意需要的类型,包括自定义类型。
2.2 map是有序的,会按照关键字从小到大进行排序,如果关键字是字符串,会按照第一个字符的大小进行排序,从A到Z(a 到 z); 可运行3.1的代码进行理解。
3 使用map
3.1 向map添加元素
一共有四种方式
mmap.insert(pair<string,int>("fsdfads", 43));//第一种插入方式
mmap.insert(map<string, int>::value_type("fsdf", 5));//第二种
mmap["fsdff"] = 3;//第三种
mmap.insert({ "fsd",4 });//第四种
注意从hash表里取值是随机的?
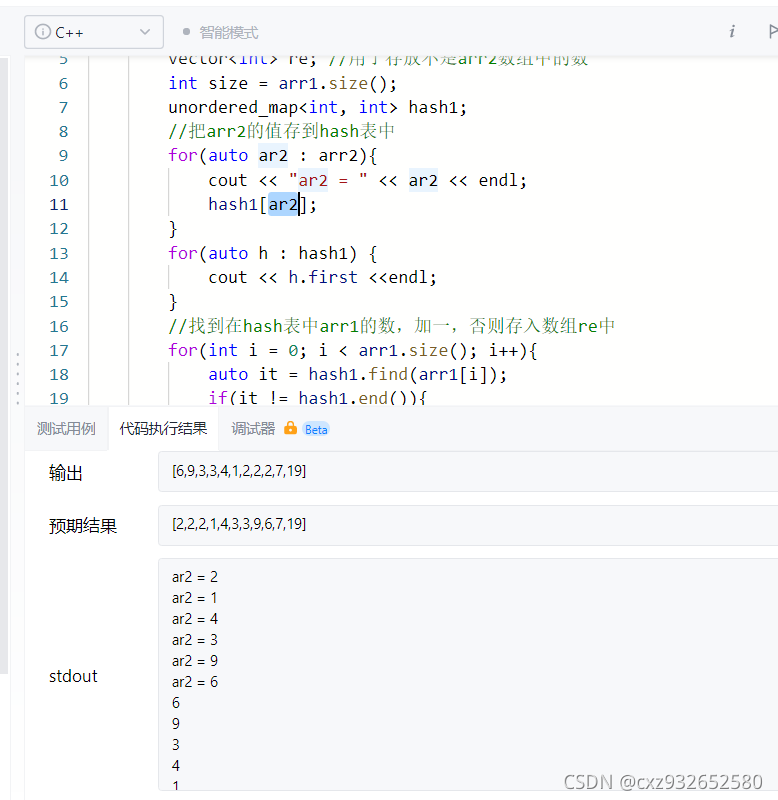
后面用的是第四种方式进行介绍
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> Mmap;
Mmap.insert({ "yi", 2 });
Mmap.insert({ "er", 3 });
Mmap.insert({ "yi", 4 });
Mmap.insert({ "er", 5 });
for (auto it : Mmap) {
cout << it.first << " " << it.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
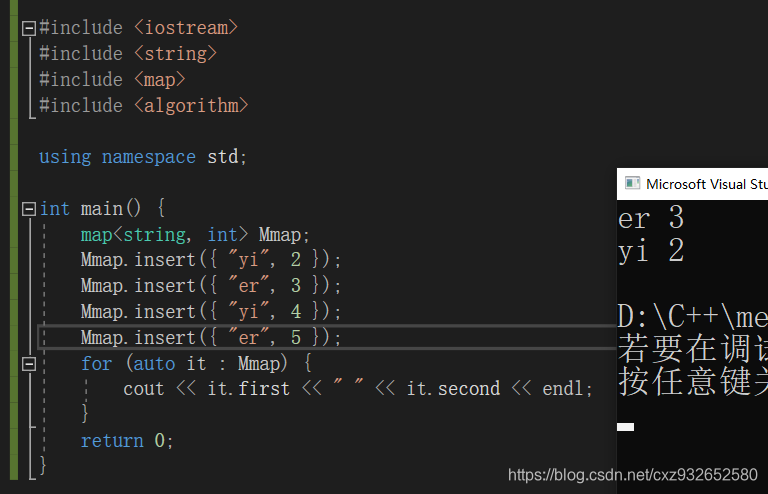
3.1.1 不会重复插入相同key
从3.1的运行结果我们可以知道,Mmap的第三条和第四条插入语句时没法插入成功的,因为前面已经对相同键值做过了插入操作,后面就不会再插入了。
3.1.2 重复插入相同key,原key对应的value值不变
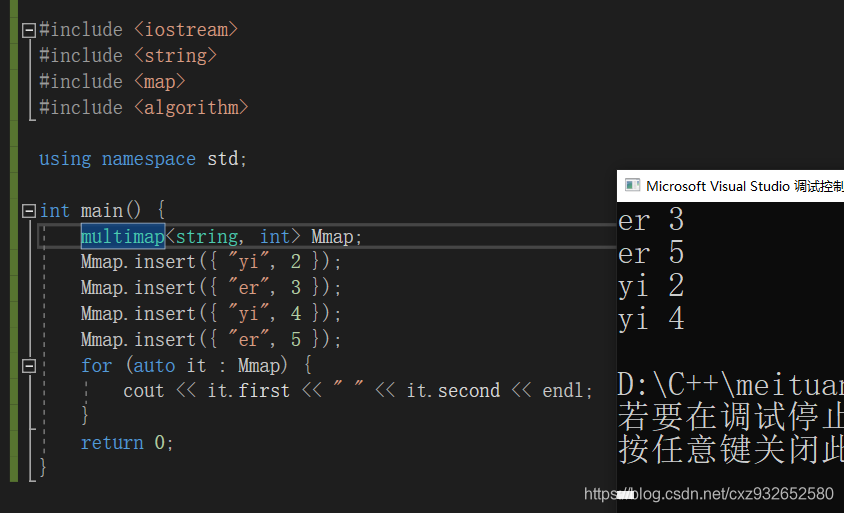
如果想要四条语句都插入成功可以考虑用multimap,multimap是可以存在重复键值的,下面是验证程序
3.1.3 插入相同key,value值改变
map容器最常用的方法——kv对计数,如果插入的元素还没存在就插入,并给value赋值为1,如果插入的元素已经存在就不再插入而是给对应的键的值加1
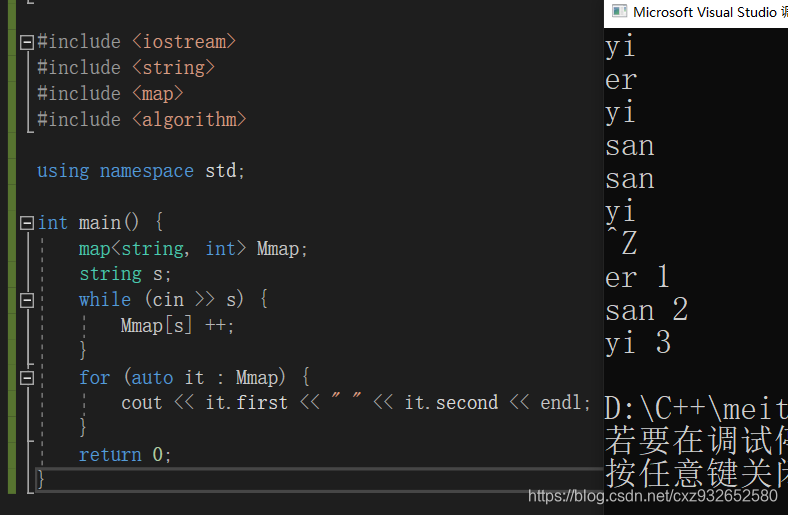
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> Mmap;
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
Mmap[s] ++; //s是键值key,这里是指如果s已经存在于Mmap中,则该key对应的value值加一
}
for (auto it : Mmap) {
cout << it.first << " " << it.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
这里要停止输入需要按:Ctrl+z,才能跳到for循环进行输出
3.2 对map中的value进行排序
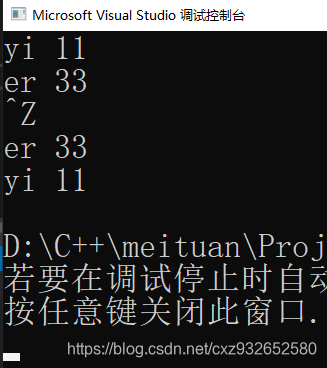
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> Mmap;
vector<pair<string, int>> vec;
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
int x;
cin >> x;
Mmap.insert({ s,x });
}
//将Mmap的key和value以 pair的形式装到vector中,对vector进行排序
for (auto it = Mmap.begin(); it != Mmap.end(); it++) {
vec.push_back(make_pair(it->first, it->second));
}
//a.second > b.second 这里是按照value的值从大到小排序
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](const pair<string, int>&a, const pair<string, int>&b) {return a.second > b.second; });
for (auto it : Mmap) {
cout << it.first << " " << it.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
第二种方式
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int cmp(const pair<string, int>& a, const pair<string, int>& b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
void sortMapByValue(map<string, int>& tMap, vector<pair<string, int>>& tVector) {
for (map<string, int>::iterator curr = tMap.begin(); curr != tMap.end(); curr++) {
tVector.push_back(make_pair(curr->first, curr->second));
}
sort(tVector.begin(), tVector.end(), cmp);
}
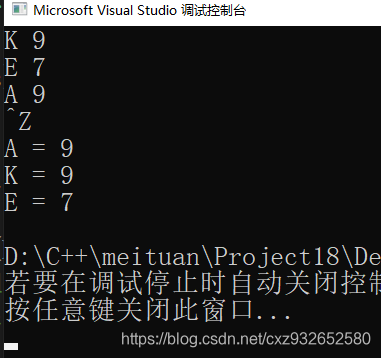
int main() {
map<string, int> Mmap;
vector<pair<string, int>> vec;
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
int x;
cin >> x;
Mmap.insert({ s,x });
}
sortMapByValue(Mmap, vec);
//第一种输出方式
/*for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
cout << vec[i].first << " = " << vec[i].second << endl;
}*/
//第二种输出方式
for (auto it : vec) {
cout << it.first << " = " << it.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
第一种输出方式中如果使用 int i ,会出现警告:
warning C4018: “<”: 有符号/无符号不匹配
原因:Vector容器 ,vec.size() 在容器说明中 被定义为: unsigned int 类型, 而i是int 类型 所以会出现: 有符号/无符号不匹配警告
解决方式:如上述代码,将i定义为unsigned int就可以解决警告了!
3.3 map查找
用find函数来定位数据出现位置,它返回的一个迭代器,当数据出现时,它返回数据所在位置的迭代器,如果map中没有要查找的数据,它返回的迭代器等于end函数返回的迭代器。
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> mapStudent;
mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "student_one"));
mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "student_two"));
mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "student_three"));
map<int, string>::iterator iter;
iter = mapStudent.find(1);
if (iter != mapStudent.end())
{
cout << "Find the value is " << iter->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Do not Find " << endl;
}
}
3.3 map使用例子1
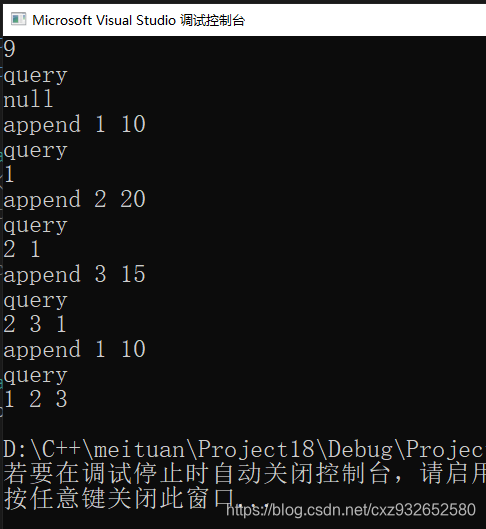
问题描述:
操作1:接收到某条新闻,更新数据库,并调整榜单排行。
操作2:接收到用户的查询操作,返回热度最高的十条新闻。没有十条时,有几条就输出几条。当两条新闻热度相同时,新闻编号小的在前。当数据库中没有新闻时,需要给出null。
输入第一行一个正整数n,表示接下来有n条操作。(1 <=n <= 100000)
接下来n行,每行是两种操作中的一种;
append x, y : 其中x和y是两个正整数,表示接收到新闻x的热度提升了y;x,y的取值范围[1,1000];
query :用户发来的查询
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
map <int, int> map1;
int cmp(const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
void sortN(map<int,int>& tMap, vector<pair<int,int>>& tVector) {
for (map<int, int>::iterator curr = tMap.begin(); curr != tMap.end(); curr++) {
tVector.push_back(make_pair(curr->first, curr->second));
}
sort(tVector.begin(), tVector.end(), cmp);
}
void query() {
vector<pair<int, int>> tVector;
sortN(map1, tVector);
if (map1.empty()) {
cout << "null" <<endl;
}
else {
int I = tVector.size() <= 10 ? tVector.size() : 10;
for (int i = 0; i < I; i++) {
cout << tVector[i].first << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void append(int x, int y) {
if (map1.find(x) != map1.end()) {
auto it = map1.find(x);
map1[it->first] += y;// 找到key,在key对应的value上加y
}
else {
map1.insert({ x,y });
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
vector<int> ans;
vector<string> res;
for(int j = n; j > 0; j--) {
cin >> s;
if (s == "query") {
query();
}
else {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
cin >> x >> y;
append(x, y);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.4 map使用例子2——当map对应的value有两个值的时候怎么办?
map一个key只能对应一个value,所以这个时候应该把那两个值存在一个数组里面,如下面我使用了一个vector储存,想要输出的时候输出map[s][0]输出的就是value里面的第一个值,map[s][1]输出的就是value里面的第二个值。
这里也让我重新思考了find()函数的使用场景,在这个程序中不需要使用fine去查找是否存在s,直接就可以上代码操作,想改就改,想加就加!第一个map使用例子中,需要在map原有的key上再加上value,所以需要使用find()函数找到这个key,而这里等于直接覆盖原有的key!
/*
s 字符串
x,y 是整数
Change s x y:将s的坐标修改为(x,y)
Delete s: 删除s
Add s x y : 添加数据s 的坐标(x,y)
Query s: 查询s的坐标
第一行输入一个正整数n,代表接下来有n条操作
接下来n行,每行从上述三种操作和一种询问中随机一种操作
0 <= n <= 50000, 0 <= x, y< = 100000
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string jz;
unordered_map <string, vector<int> > map;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
if (s == "Add") {
cin >> jz;
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
vector<int> local = { x, y };
map[jz] = local;
}
else if (s == "Delete") {
cin >> jz;
map[jz] = {};
}
else if (s == "Change") {
cin >> jz;
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
vector <int>local = { x, y };
map[jz] = local;
}
else {
cin >> jz;
if (map[jz].empty()) {//查询jz是否在map中,不在就输出no
cout << "no" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "yes" << endl;//查询到有jz,输出yes
//并输出对应的value,这里的value是一个vector,有两个数据
cout << map[jz][0] << " " << map[jz][1] << endl;
}
}
}
}
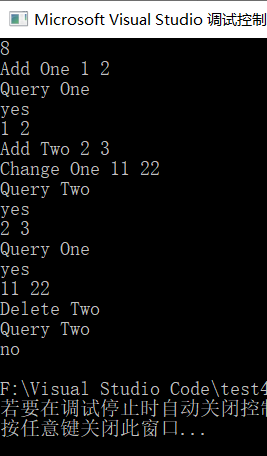
3.5 map使用例子3-count()和size()的用法
使用count,返回的是被查找元素的个数。如果有,返回1;否则,返回0。注意,map中不存在相同元素,所以返回值只能是1或0。
使用find,返回的是被查找元素的位置,没有则返回map.end()。
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unordered_map<string, vector<int> > map1;
string s = "a";
map1.insert(pair<string, vector<int>>("d", {4, 44}));
map1["b"] = {2, 22};
map1.insert({ "c",{3, 33} });
map1.insert({ s,{1, 11, 111} });
if (map1.count("b")) { //计算关键字b的个数,一般都是bool值,1或者0;
cout <<"关键字a对应的数组大小 = " << map1["a"].size() << endl; //输出关键字为a对应的value的vector的size();
}
for (auto it : map1) {
cout << it.first << " "<< it.second[0] << " " << it.second[1] << endl;
//因为这里设置成输出it.second[1],数组里就一定要有两个数字,一个数字是会报错的
}
return 0;
}
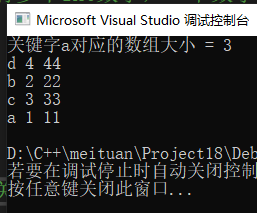
3.6 map相关函数
begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 如果map为空则返回true
end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个map
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
3.7 map反向遍历
class Solution {
public:
int findLucky(vector<int>& arr) {
map<int, int> hash;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){
auto it = hash.find(arr[i]);
if(it != hash.end()){
hash[arr[i]]++;
} else {
hash[arr[i]] = 1;
}
}
for(map<int,int>::reverse_iterator rit=hash.rbegin();rit!=hash.rend();rit++) {
if((*rit).first == (*rit).second){
return (*rit).first;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
347. 前 K 个高频元素
这题也可以用map反序迭代器








 本文详细介绍了C++ STL中的map容器,包括map的简介、功能、添加元素、排序、查找以及多种使用示例,如计数、排序、查找等。map是一个有序的键值对集合,不允许键重复,提供了丰富的操作函数,如insert、find、count等。通过实例展示了map在处理数据时的灵活性。
本文详细介绍了C++ STL中的map容器,包括map的简介、功能、添加元素、排序、查找以及多种使用示例,如计数、排序、查找等。map是一个有序的键值对集合,不允许键重复,提供了丰富的操作函数,如insert、find、count等。通过实例展示了map在处理数据时的灵活性。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








