GCD Array
Time Limit: 11000/5500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1445 Accepted Submission(s): 430
Problem Description
Teacher Mai finds that many problems about arithmetic function can be reduced to the following problem:
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to a x for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query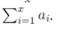
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to a x for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query
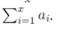
Input
There are multiple test cases, terminated by a line "0 0".
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
Output
For each case, output "Case #k:" first, where k is the case number counting from 1.
Then output the answer to each query.
Then output the answer to each query.
Sample Input
6 4 1 4 1 2 2 5 1 3 3 3 2 3 0 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 6 7
Author
xudyh
Source
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 200000 + 10;
int N, Q;
int mu[maxn];
LL Tree[maxn];
vector<int> p[maxn];//约数
bool valid[maxn];
int prime[maxn];
void Mobius()
{
int tot = 0;
mu[1] = 1;
memset(valid, true, sizeof(valid));
p[1].clear();
for(int i = 2; i < maxn; i++)
{
p[i].clear();
if(valid[i])
{
mu[i] = -1;
prime[++tot] = i;
}
for(int j = 1; j <= tot && i * prime[j] < maxn; j++)
{
valid[i * prime[j]] = false;
if(i % prime[j] == 0)
{
mu[i * prime[j]] = 0;
break;
}
mu[i * prime[j]] = -mu[i];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < maxn; i++)
{
for(int j = i; j < maxn; j += i)
{
p[j].push_back(i);
}
}
}
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void add(int loc, LL value)
{
for(int i = loc; i <= N; i += lowbit(i))
{
Tree[i] += value;
}
}
LL get(int loc)
{
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = loc; i >= 1; i -= lowbit(i))
{
ans += Tree[i];
}
return ans;
}
void init()
{
memset(Tree, 0, sizeof(Tree));
}
int main()
{
Mobius();
int Case = 1;
while(~scanf("%d%d", &N, &Q) && N && Q)
{
init();
int type ,x, n, d;
LL v;
printf("Case #%d:\n", Case++);
for(int i = 1; i <= Q; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &type);
if(type == 1)
{
scanf("%d%d%lld", &n, &d, &v);
if(n % d) continue;
n /= d;
for(int j = 0; j < p[n].size(); j++)
{
int pp = p[n][j];
add(pp * d, (LL)mu[pp] * v);
}
}
else
{
scanf("%d", &x);
LL sum = 0;
int nxt;
for(int j = 1; j <= x; j = nxt + 1)
{
nxt = min(x / (x / j), x);
sum += (get(nxt) - get(j - 1)) * (LL)(x / j);
}
printf("%lld\n", sum);
}
}
}
return 0;
}










 本文详细解析了一道关于数组操作的问题GCDArray,利用莫比乌斯函数的特性,通过巧妙的数据结构和算法实现了高效的查询与更新操作。
本文详细解析了一道关于数组操作的问题GCDArray,利用莫比乌斯函数的特性,通过巧妙的数据结构和算法实现了高效的查询与更新操作。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








