题目描述

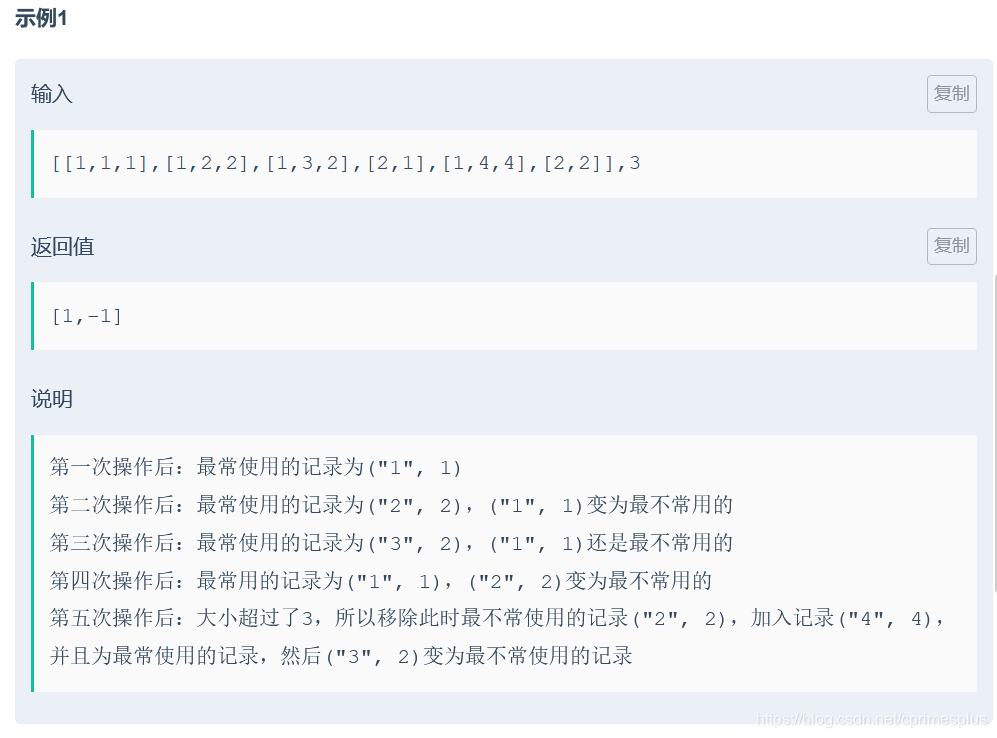
分析(hash+双链表)
若维护一个记录缓存中所有元素生存时长的数组,每过一轮将数组中所有元素生存时间+1,那么需要O(N)的复杂度,显然不可行。
若将lru中元素,以链表形式进行时序串联,新加入的元素放到链表尾部,而链表头部则代表最近最久未使用的元素,那么每次更新或者取元素,便只需对该链表进行操作即可了。
存在如下情况:
(1)lru缓存未满时,将元素直接插入到链表尾部。
(2)lru缓存已满,此时
① 新加入的元素key未在缓存中出现,则将最近最久未使用的元素(链表头部)摘掉,将新元素key插入到链表尾部。
② 新加入的元素key存在于缓存中,则从原本key出现的位置取下元素,并将该元素插入到链表尾,代表更新。
为了不遍历整个链表便能得知key原本所在位置,另外使用哈希法map<int, list< int>::iterator>保存key值到位置的映射。
代码
class Solution {
public:
/**
* lru design
* @param operators int整型vector<vector<>> the ops
* @param k int整型 the k
* @return int整型vector
*/
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
unordered_map<int, list<int>::iterator > index;
list<int> ls;
void set(int key, int value, int k) {
if(mp.empty() || mp.size() < k) {
ls.push_back(key);
mp[key] = value;
// index[key] = ls.end();
index[key] = prev(ls.end());
return ;
}
// mp.size()==k
// 若key未出现过,将链表头取下,尾插key,并更新mp[key]的值
if(mp.find(key) == mp.end()) {
auto temp = ls.front();
ls.pop_front();
ls.push_back(key);
mp.erase(temp);
mp[key] = value;
index.erase(temp);
index[key] = prev(ls.end());
}
// 若key出现过,在双链表中找到key摘下,并尾插key,更新mp[key]
else {
ls.erase(index[key]);
ls.push_back(key);
mp[key] = value;
index[key] = prev(ls.end());
}
}
int get(int key) {
int ret = (!mp.empty())&&mp.find(key)!=mp.end() ? mp[key] : -1;
// 若key出现过,则在双链表中找到key摘下,并尾插key
if(ret != -1) {
ls.erase(index[key]);
ls.push_back(key);
index[key] = prev(ls.end());
}
return ret;
}
vector<int> LRU(vector<vector<int> >& operators, int k) {
// write code here
if(operators.empty()) return {};
int vec_size = operators.size();
// 构造大小为k的map
vector<int> res_vec;
for(int i = 0; i < vec_size; i++) {
int opt = operators[i][0];
// 不管插入还是返回,都相当于更新值
if(opt == 1) {
set(operators[i][1], operators[i][2], k);
}
else {
res_vec.push_back(get(operators[i][1]));
}
}
return res_vec;
}
};





 本文介绍了一种高效实现LRU(最近最少使用)缓存的方法。通过结合哈希表和双向链表的数据结构,实现了O(1)的时间复杂度进行缓存的更新和获取操作。适用于需要频繁进行缓存操作的场景。
本文介绍了一种高效实现LRU(最近最少使用)缓存的方法。通过结合哈希表和双向链表的数据结构,实现了O(1)的时间复杂度进行缓存的更新和获取操作。适用于需要频繁进行缓存操作的场景。
















 9122
9122

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








