Mod Tree
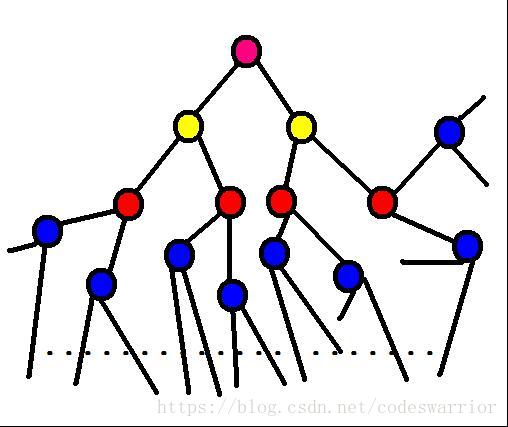
The picture indicates a tree, every node has 2 children.
The depth of the nodes whose color is blue is 3; the depth of the node whose color is pink is 0.
Now out problem is so easy, give you a tree that every nodes have K children, you are expected to calculate the minimize depth D so that the number of nodes whose depth is D equals to N after mod P.
Input
The input consists of several test cases.
Every cases have only three integers indicating K, P, N. (1<=K, P, N<=10^9)
Output
The minimize D.
If you can’t find such D, just output “Orz,I can’t find D!”
Sample Input
3 78992 453
4 1314520 65536
5 1234 67
Sample Output
Orz,I can’t find D!
8
20
题意:
给定每个节点的孩子数K求最小层数使得该层的节点数模P等于N
分析:
即求
Kx≡N (mod P)
K
x
≡
N
(
m
o
d
P
)
因为P不一定是素数故需要用扩展BSGS
很奇怪的是做了好几道BSGS的题目了,抄模板一直wa,在抄一遍又过了,都不知道哪里错的
ACcode:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll q_pow(ll a, ll b, ll mod){
ll ans = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) ans = ans * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){
return b ? gcd(b,a%b) : a;
}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){
if(!b){
x = 1;
y = 0;
return;
}
ex_gcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y -= a / b * x;
return;
}
ll BSGS(ll a,ll b,ll p){
a %= p;
b %= p;
ll ret = 1;
for(ll i = 0; i <= 50; i++){
if(ret == b) return i;
ret = ret * a % p;
}
ll x,y,d,v = 1,cnt = 0;
while((d = gcd(a,p)) != 1){
if(b % d) return -1;
b /= d;
p /= d;
v = v * (a / d) % p;
cnt++;
}
map<ll,ll>h;
ll m = ceil(sqrt(p)),t = 1;
for(ll i = 0; i < m; i++){
if(h.count(t)) h[t] = min(h[t],i);
else h[t] = i;
t = t * a % p;
}
for(ll i = 0; i < m; i++){
ex_gcd(v,p,x,y);
x = (x * b % p + p) % p;
if(h.count(x)) return i * m + h[x] + cnt;
v = v * t % p;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
ll k,p,n;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&k,&p,&n)){
if(n >= p){
puts("Orz,I can’t find D!");
continue;
}
ll ans = BSGS(k,n,p);
if(ans == -1) puts("Orz,I can’t find D!");
else printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}




 本文探讨了一种算法问题——给定一棵每个节点有K个孩子的树,寻找最小的层数D,使得该层的节点数量模P等于N。文章通过扩展BSGS算法解决了这一问题,并提供了完整的AC代码。
本文探讨了一种算法问题——给定一棵每个节点有K个孩子的树,寻找最小的层数D,使得该层的节点数量模P等于N。文章通过扩展BSGS算法解决了这一问题,并提供了完整的AC代码。
















 659
659

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








