基础的4种数据结构

| 类型 | 标准用法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | a = 'playera’ b = ‘‘playerb’‘ c = ‘’‘playerabcdefg’’’ | 可以用单引号,双引号,和三引号 三引号一般是说明 |
| c = ‘playera’ + b | 字符串可以直接连接 | |
| words = ‘word’ * 3 | 多个重复字符串连接 | |
| words[2:10] | 字符串切片索引,左闭右开 | |
| 列表 | album = [] | 创建一个新的列表list |
| album.append(‘new song’) | 在列表list末尾追加 | |
| ‘new song’ in album | 成员运算符,测试是列表中的一员 | |
| a_list = [1,2,3] sum(a_list) | sum求和 |
1 列表List

列表的增删改查



2 字典Dictionary

字典的增删改查

3 元组Tuple和集合Set
元组Tuple

集合Set

4 数据结构的一些技巧
4.1 用sorted(list)函数排序技巧
# 使用sorted函数进行排序
num_list = [6,2,7,4,1,3,5]
print(sorted(num_list))
sorted(num_list,reverse=True) # reverse表示逆序排列
4.2 for a,b in zip(string_a,string_b)整理两个列表

for a,b in zip(num,str):
4.3 [item for item in iterable]推导式(列表解析式)


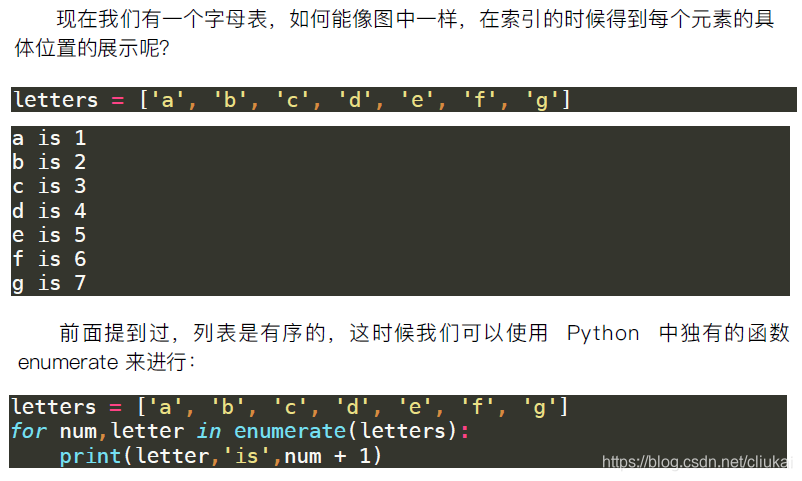
4.4 for ii,ch in enumerate(list)循环列表获取元素下标
python3种运算:数值,比较和布尔运算
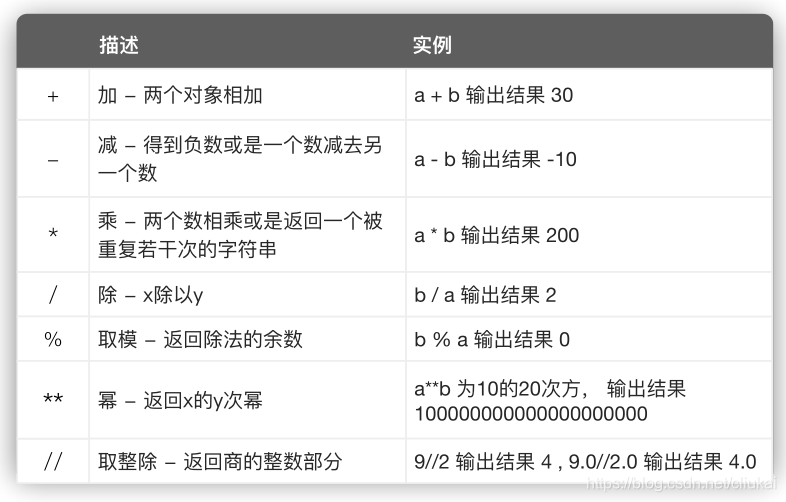
1 数值基础运算
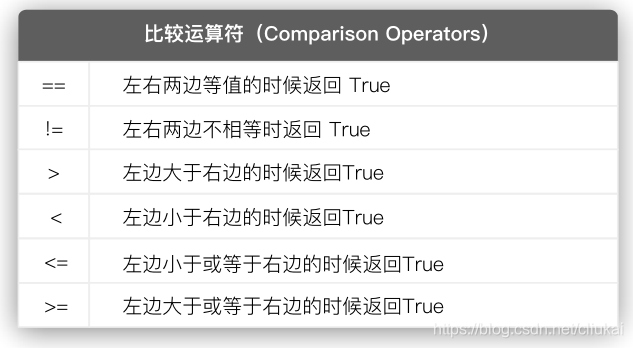
2 比较运算
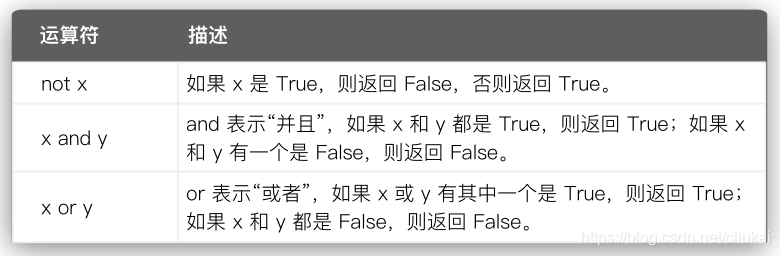
3 布尔运算
基础的常用函数(类型转换,随机数函数random等)
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| print(a+b) | 打印输出a和b,加号可以直接连接两个字符串 |
| print(a,b) | 打印输出a和b,区别是a和b之间有空格 |
| type(word) | 返回word这个变量的类型 |
| file = open(’/path/file.txt’,‘w’) | 文件打开 |
| file.write(‘hello world!’) | 文件写入 |
| file.close() | 文件关闭 |
| len(‘a looong word’) | 对字符串求长度 |
| number.replace(string_a,string_b) | 字符串替换,用b去替换a |
| print(’{} love {}’.format(‘I’,‘You’)) | 字符串格式化符,注意format()后面是单括号 |
| city = input(“please input …”) | 格式化输入,默认是字符串格式 |
| for num in range(1,11) | range()范围从1到11,左闭右开 |
强制类型转换函数
| 强制类型转换函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| aa = int(‘a’) | 转换成int型 |
| str() | 转换成string类型 |
随机数函数
random.randrange(a,b)在两个数之间随机选择
import random
point = random.randrange(1,7)
random.choice(lists)在几个变量(列表中的量)之间选择
gender = random.choice(['male','female','unknown'])
name = random.choice(name_lists)
其他的内置函数
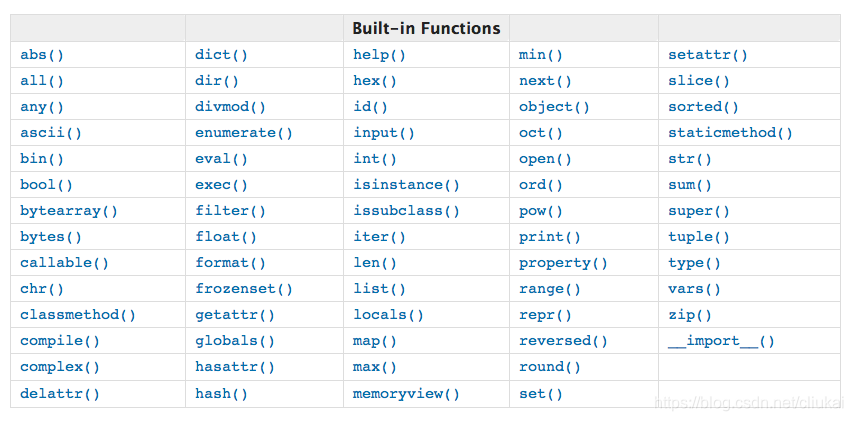
参考官方文档学习:
-
内置函数 — Python 3.7.4 文档内置函数介绍
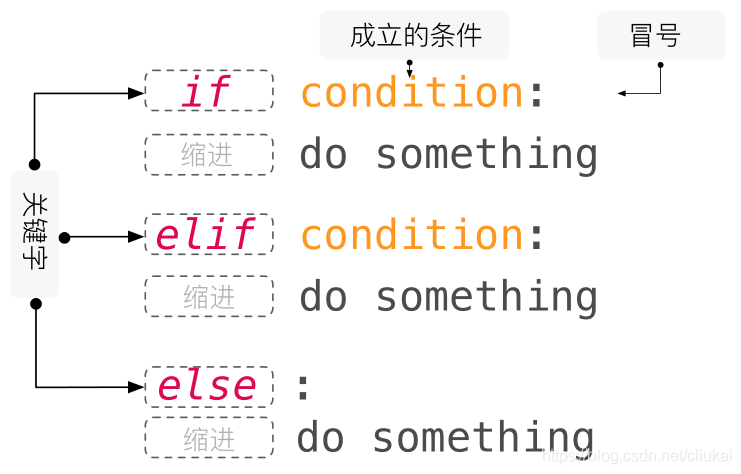
循环和判断
if:elif:else:条件判断
password_list = ['*#*#','12345']
def account_login():
password = input('Please input your password:')
password_correct = password == password_list[-1]
password_reset = password == password_list[0]
if password_correct:
print('Login success!')
elif password_reset:
print('Reset password, please input your new password:')
new_password = input()
password_list.append(new_password)
print('Reset password successfully')
account_login()
else:
print('Wrong password, try again !')
account_login()
account_login()
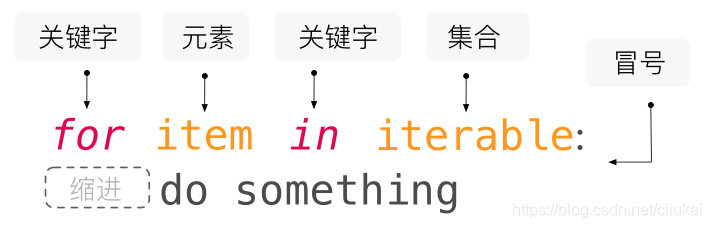
for循环
# 打印乘法口诀表
for i in range(1,10):
for j in range(1,10):
print('{} * {} = {}'.format(i,j,i*j))
while循环

while不会像for那样,在一定时候停止下来,所以必须自己手动创造停止条件!
count = 0
while True:
print('Repeat this line !')
count = count + 1
if count == 5:
break # 在这里跳出循环
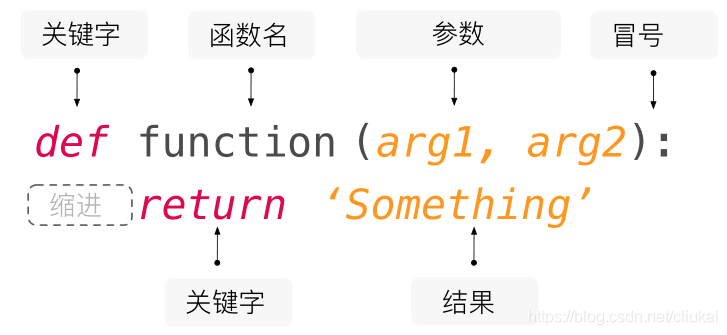
自定义函数def func(arg1,arg2):return
基础格式如下





 这篇博客总结了Python的基础知识,包括四种数据结构——列表、字典、元组和集合,以及它们的增删改查操作。此外,还介绍了数据结构的排序技巧、循环和判断语句,如for、while,以及自定义函数的定义方法。内容涵盖了数值、比较和布尔运算,以及内置函数如random的使用。
这篇博客总结了Python的基础知识,包括四种数据结构——列表、字典、元组和集合,以及它们的增删改查操作。此外,还介绍了数据结构的排序技巧、循环和判断语句,如for、while,以及自定义函数的定义方法。内容涵盖了数值、比较和布尔运算,以及内置函数如random的使用。
















 1972
1972

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








