怎么删除C盘中的Window.old文件?
最近又自动更新了一次win10系统,开机后发现系统盘一下满了,郁闷之余打开C盘一看,好家伙,有个25个GB的
Windows.old文件夹!兄弟别怪我不客气,回收站里见哈,我一个猛击删除,结果被告知权限不够无法删除,这是我的电脑还是你微软的电脑?心中一阵沸腾。。。

说干就干。首先在空白处右击打开属性,点击磁盘清理,但是在要删除的文件中,依然是找不到能清理windows更新文件这个选项的,我被欺骗了?别急,这时候再点击清理系统文件,然后,这个窗口就自动关闭了。。。没了?

莫慌,刚才只是虚晃一招,我们再次点击磁盘清理,这一次弹出的窗口中,终于出现了以前的Windows安装文件这个选项,勾选然后选择确定删除。
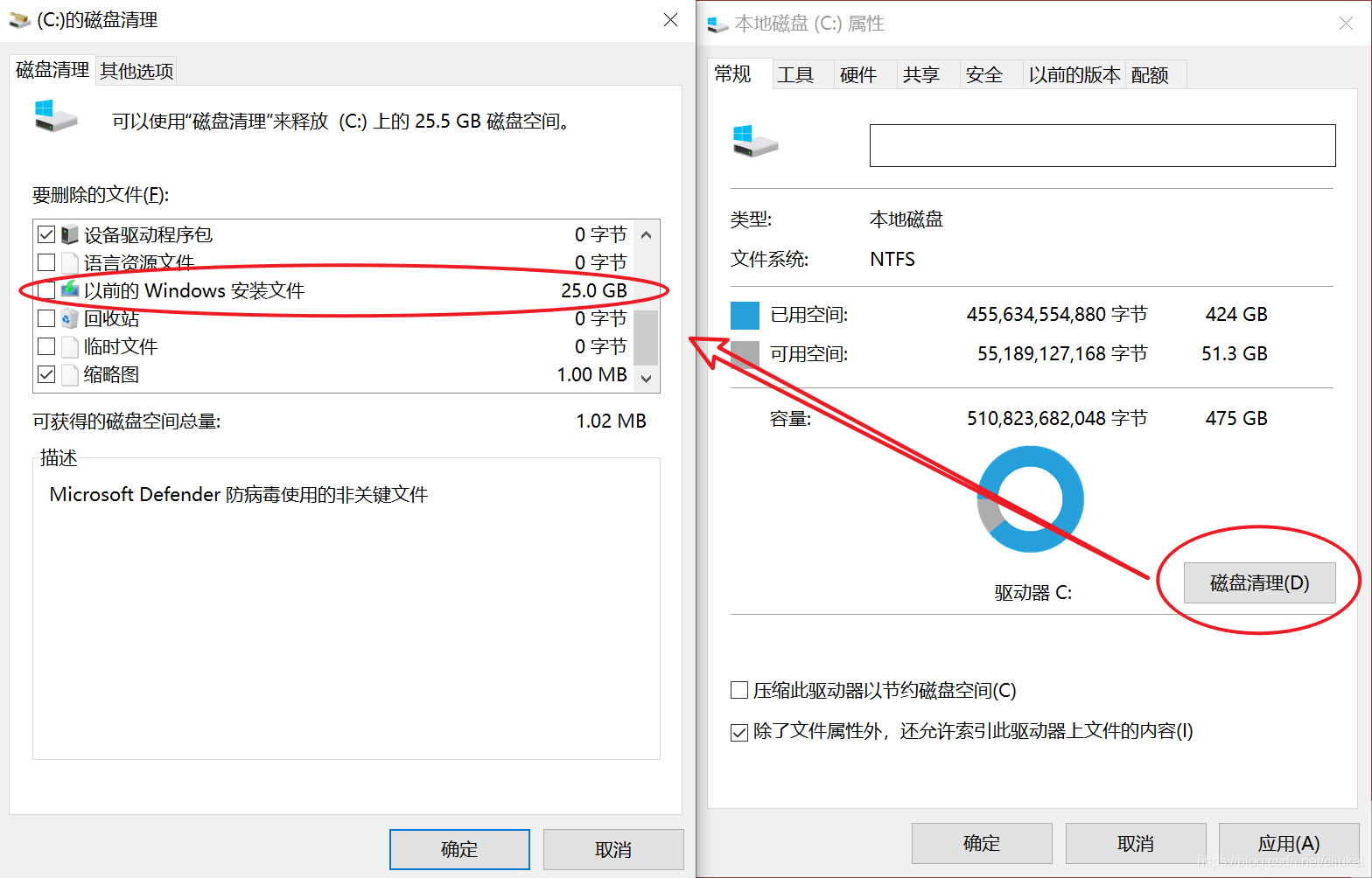
最后会跳出这个提示,意思是清理之后就无法版本回退了,如果对现在的系统还算满意,就直接点是吧。

再次回到C盘看一下,Windows.old文件夹已经没有了,大功告成,YES!






 本文介绍了一种有效的方法来清除Windows 10系统更新后产生的Windows.old文件夹,通过磁盘清理工具进行操作,避免因权限问题导致的删除失败。
本文介绍了一种有效的方法来清除Windows 10系统更新后产生的Windows.old文件夹,通过磁盘清理工具进行操作,避免因权限问题导致的删除失败。
















 2295
2295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








