Pytorch顺序:
-
Prepare dataset
-
Design model using Class
inherit from nn.Module -
Construct loss and optimizer
using PyTorch API -
Training cycle
forward, backward, update
import numpy as np
import torch
# Prepare dataset
#数据必须转化成Tensors
#x_data=torch.Tensor([[1.0],[2.0],[3.0]])
#y_data=torch.Tensor([[2.0],[4.0],[6.0]])
x=np.array([1,2,3],float)
y=np.array([2,4,6])
x_data=torch.Tensor(x.reshape(3,1))
y_data=torch.Tensor(y.reshape(3,1))
print(x_data,y_data)
#Design model using Class
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
#Member methods __init__() andforward() have to be implemented.
super(LinearModel,self).__init__()#初始化父类
self.linear=torch.nn.Linear(1,1)#初始化对象,Linear参数为输入输出的维度数
#Class nn.Linear contain two member Tensors: weight and bias.
def forward(self,x):
y_predict=self.linear(x)
return y_predict
#Construct loss and optimizer
model=LinearModel()#创建LinearModel()的实例
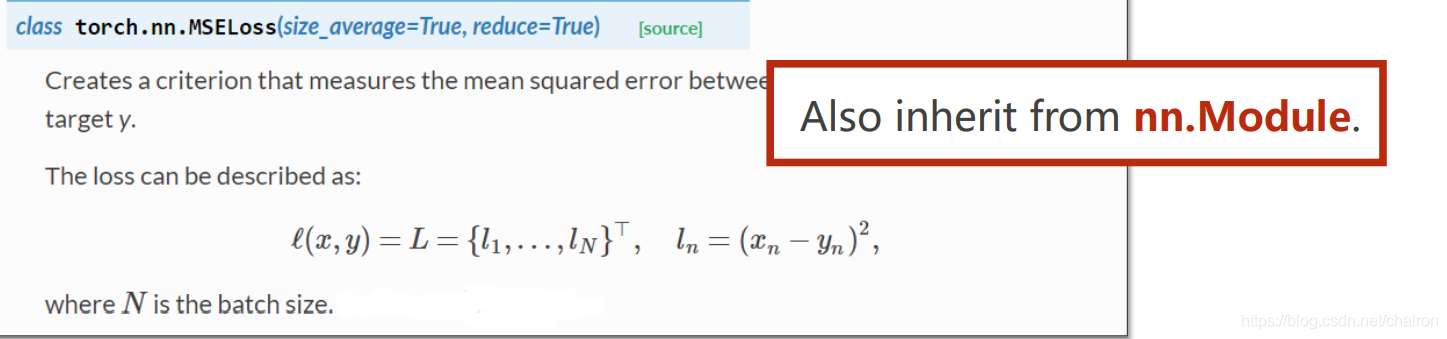
criterion=torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=False)
optimizer=torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01)
#Training cycle:forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(1000):
y_predict=model(x_data)#计算y_predict,Forward: Predict
loss=criterion(y_predict,y_data)#计算loss,Forward: Loss
print(epoch,loss.item())
# before backward, remember set the grad to ZERO
optimizer.zero_grad()#梯度先清零
loss.backward()#backward
optimizer.step()#更新
#输出
print('w=',model.linear.weight.item())
print('b=',model.linear.bias.item())
x_test=torch.Tensor([[4.0]])
y_test=model(x_test)
print('y_predict',y_test.data)
- torch.optim.Adagrad
- torch.optim.Adam
- torch.Adamax
- torch.optim.ASGD
- torch.optim.RMSprop
- torch.optim.Rprop
- torch.optim.SGD






 该博客演示了如何使用PyTorch构建并训练一个简单的线性模型。首先,准备了数据集并将数据转化为张量。接着,定义了一个继承自`nn.Module`的线性模型类,并创建了损失函数`MSELoss`和优化器`SGD`。然后,通过训练循环进行了前向传播、计算损失、反向传播和参数更新。最终,展示了训练后的权重和偏置,以及对新输入的预测结果。
该博客演示了如何使用PyTorch构建并训练一个简单的线性模型。首先,准备了数据集并将数据转化为张量。接着,定义了一个继承自`nn.Module`的线性模型类,并创建了损失函数`MSELoss`和优化器`SGD`。然后,通过训练循环进行了前向传播、计算损失、反向传播和参数更新。最终,展示了训练后的权重和偏置,以及对新输入的预测结果。
















 1161
1161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








