摘要
思维链(CoT)推理使大语言模型(LLMs)能够通过中间token进行额外计算,以解决复杂任务。然而,我们认为典型的推理过程包含许多冗余token,导致了额外的推理成本。通过研究当前大语言模型的输出分布,我们发现它们相较于默认行为,具备更简洁推理的潜在能力。为激发这种能力,我们提出了简单的微调方法,在特定任务设置中,利用通过N选1采样(best-of-N sampling)和少样本条件设定(few-shot conditioning)生成的自生成简洁推理路径。我们的组合方法在GSM8K和MATH数据集上,对五个模型系列进行实验,结果显示平均输出token减少了30%,同时保持了平均准确率。通过利用大语言模型的基本随机性和上下文学习能力,我们的自训练方法在广泛的模型上都能有效地激发简洁推理,包括那些经过大量后期训练的模型。
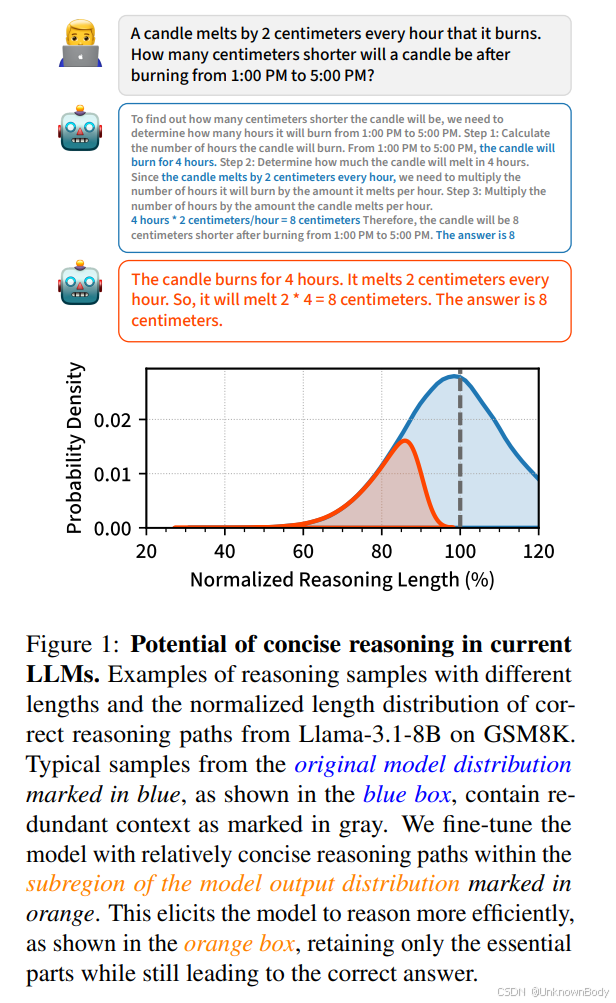
引言
思维链(CoT)推理显著提升了大语言模型(LLMs)执行复杂任务的能力(Wei等人,2022b)。CoT推理的有效性归因于推理过程中分配的额外计算量,因为每个中间推理标记都能让模型通过其参数进行一次额外的前向传递(Nye等人,2021;Wei等人,2022b)。另一方面,这必然会带来额外的推理成本和延迟,大致与输出标记的数量成正比(Agrawal等人,2024;Ho等人,2024)。
我们认为,当前的模型在完成任务时,往往会生成比必要数量更多的标记,从而产生额外的推理成本。从原始模型分布中采样得到的典型推理链











 订阅专栏 解锁全文
订阅专栏 解锁全文


















 994
994

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










