文章目录
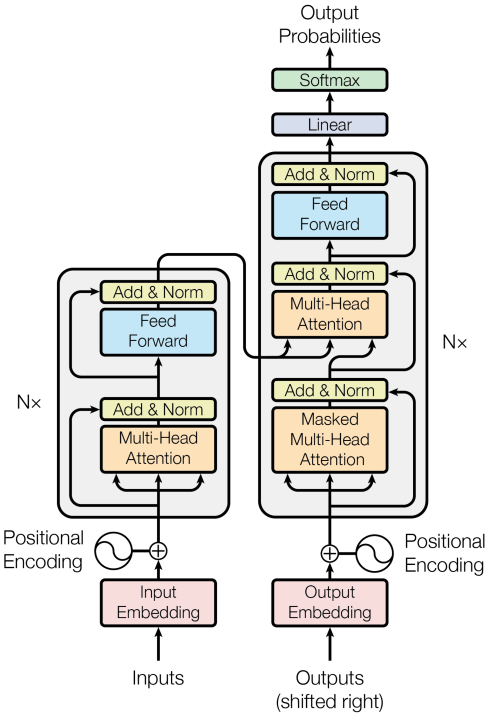
一、Transformer Model
-
Transformer由Attention和self-Attention层组成
-
Transformer 模型完全基于Attention
-
Attention原本是用在RNN上的,这节课把RNN去掉,只保留Attention
-
Original paper: Vaswani et al. Attention Is All You Need. In NIPS, 2017.
-
Transformer is a Seq2Seq model.(Transformer是一种Seq2Seq模型,它有一个encoder和一个decoder,很适合做机器翻译)
-
Transformer is not RNN.(Transformer不是循环神经网络,Transformer没有循环的结构)
-
Purely based attention and dense layers.(Transformer只有Attention和全连接层)
-
Higher accuracy than RNNs on large datasets. (Transformer有更高的准确度)
二、Attention for RNN
2.1 Attention for Seq2Seq Model
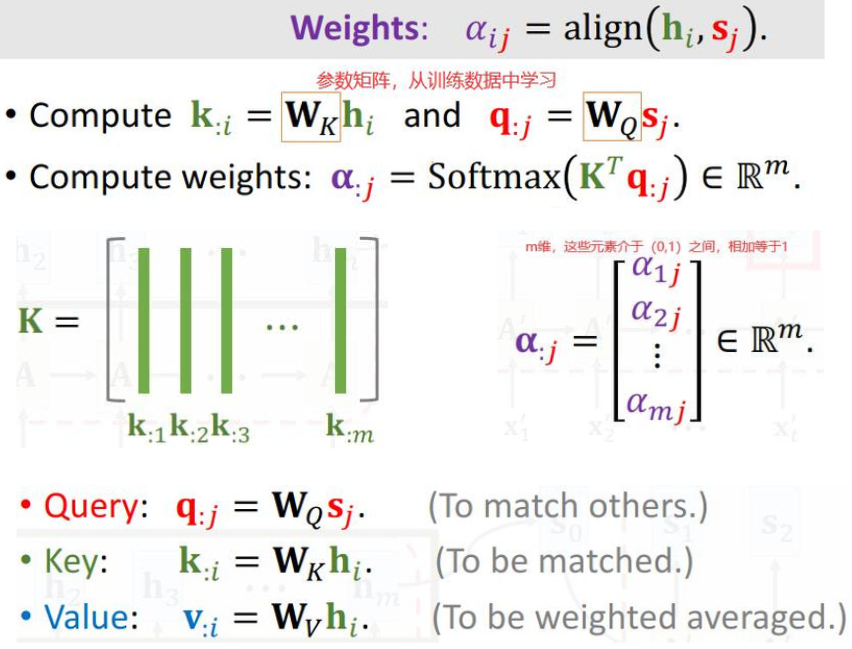
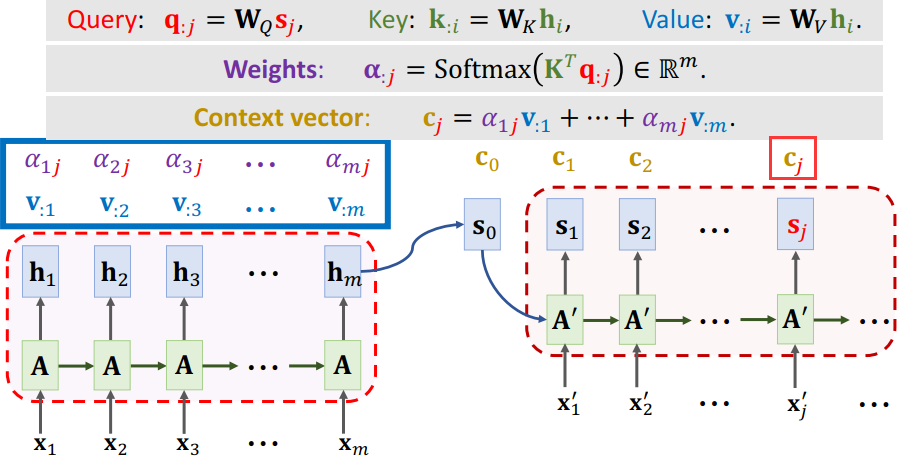
- Seq2Seq模型:有一个encoder和一个decoder,encoder的输入是m个向量(X1 ,X2 ,···,Xm ),encoder把这些输入的信息压缩到状态向量h中,最后一个状态hm ,是对所有输入的概括。
- decoder是一个文本生成器,依次生成状态S,然后根据状态S生成单词,把新生成的单词作为下一个输入。
- 如果用attention还需要计算向量C,每计算一个状态S,就计算一个向量C。
三、Attention without RNN(去掉RNN,只保留Attention)
Question: How to remove RNN while keeping attention?(Attention原本是用在RNN上,怎么样才能剥离RNN,只保留Attention)
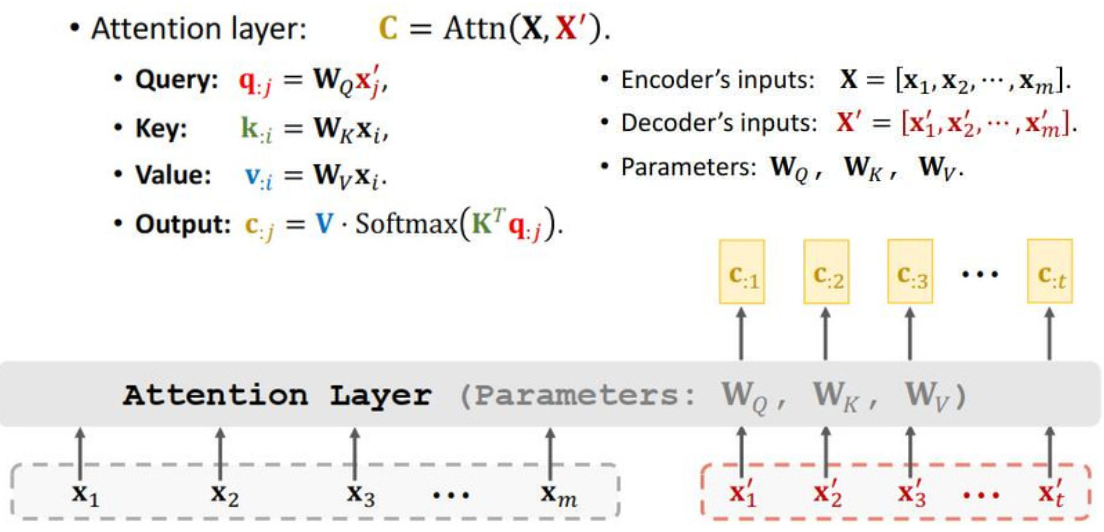
3.1 Attention Layer
设计Attention层用于Seq2Seq模型,我们移除了RNN,现在搭建Attention。
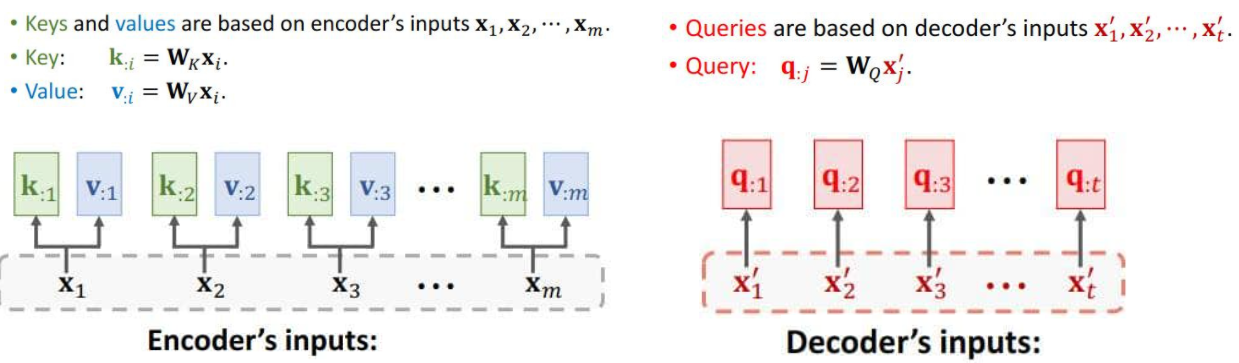
- We study Seq2Seq model (encoder + decoder).
- Encoder’s inputs are vectorsX1 ,X2 ,···,Xm 。(encoder的输入)
- Decoder’s inputs are vectors X‘1 ,X’2 ,···,X‘t 。(decoder的输入)
3.1.1 Compute weights和Compute context vector
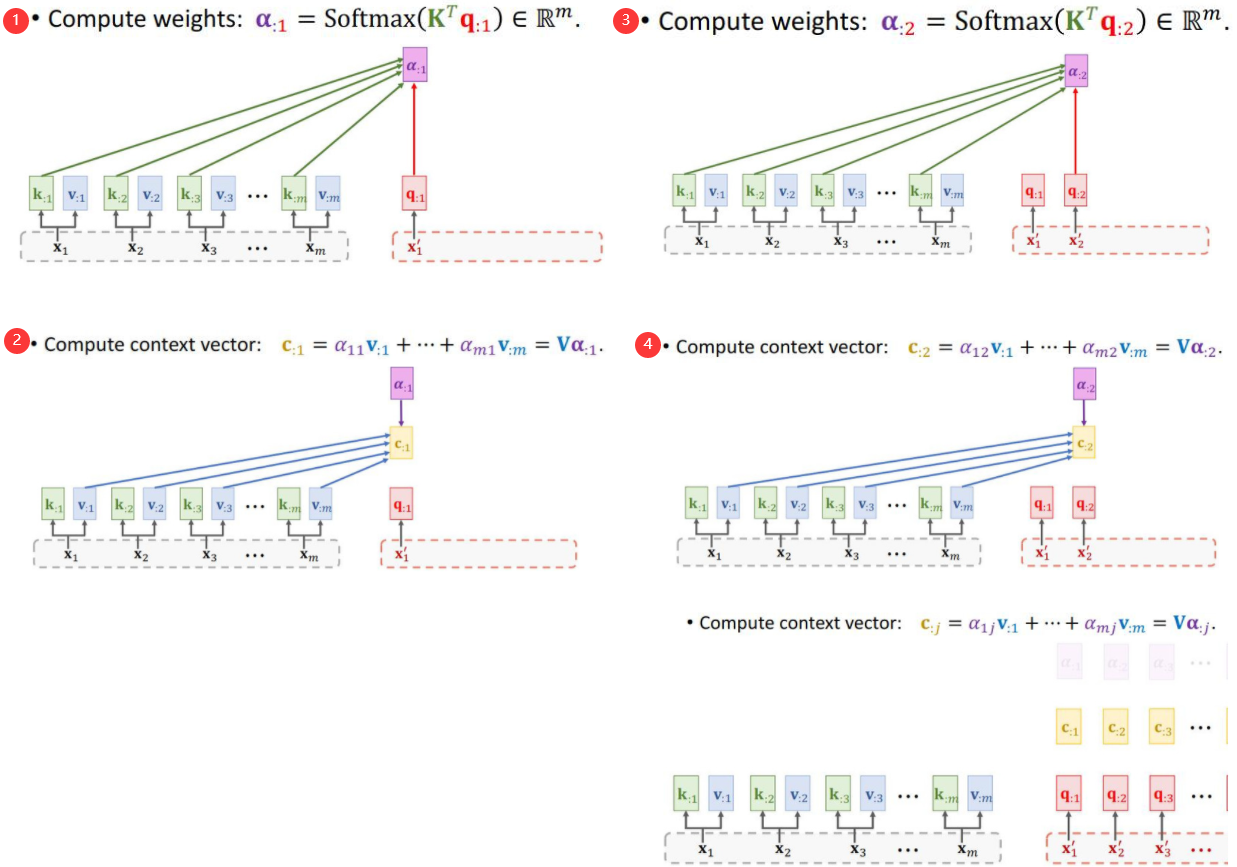
3.1.2 Output of attention layer:
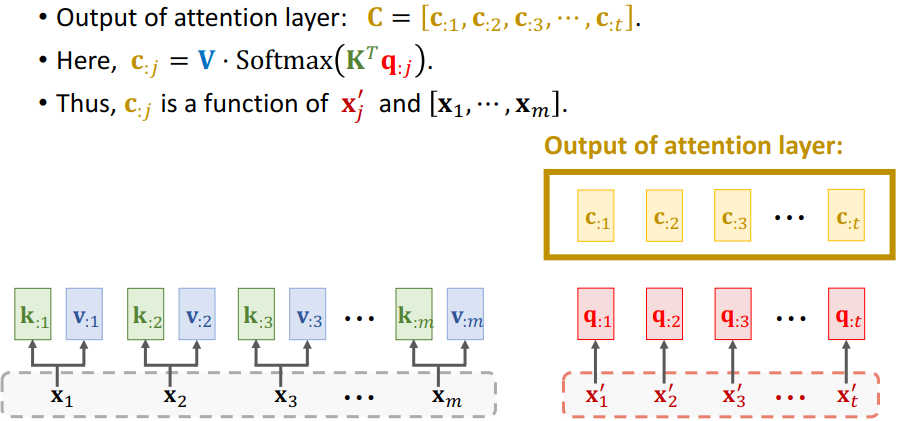
3.2 Attention Layer for Machine Translation
- Translate English to German.
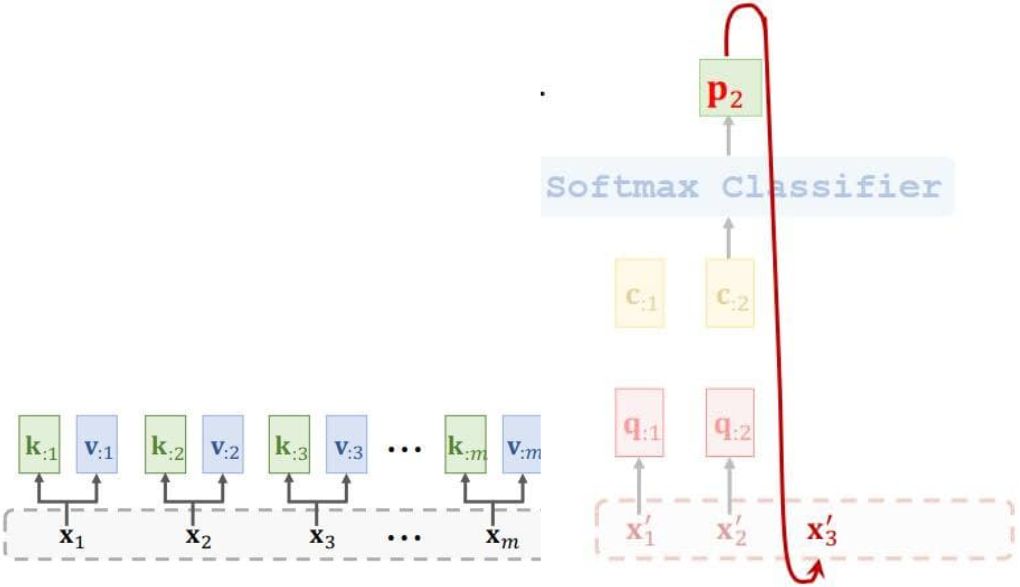
- Use C:2 to generate the 3rd German word.(产生第三个德语单词)
- 用RNN会把状态h作为特征向量,用Attention会把C作为特征向量。
- 不论用Attention或者RNN来搭建一个Seq2Seq 模型,输入与输出的大小一样,因此可以用Attention Layer代替RNN。
- Attention Layer的好处是不会遗忘。
四、Self-Attention without RNN
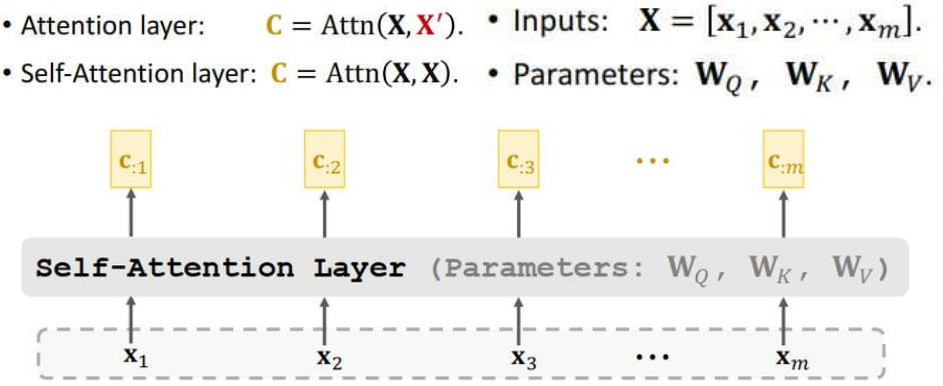
4.1 Self-Attention Layer
- Self-Attention层不是Seq2Seq,它只有一个输入序列 ,这就像普通的RNN一样。、
- Ci 依赖于所有的m个Xi 向量。
- 改变任何一个X,Ci都会发生变化。
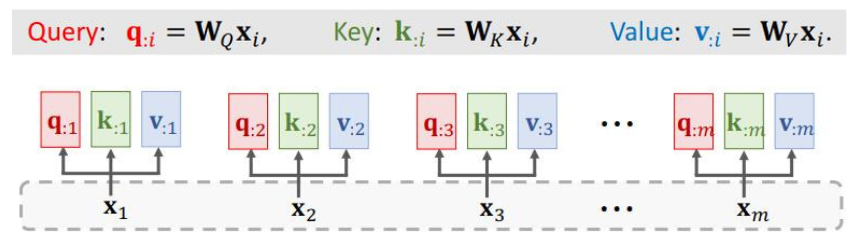
4.1.1 Compute weights和Compute context vector
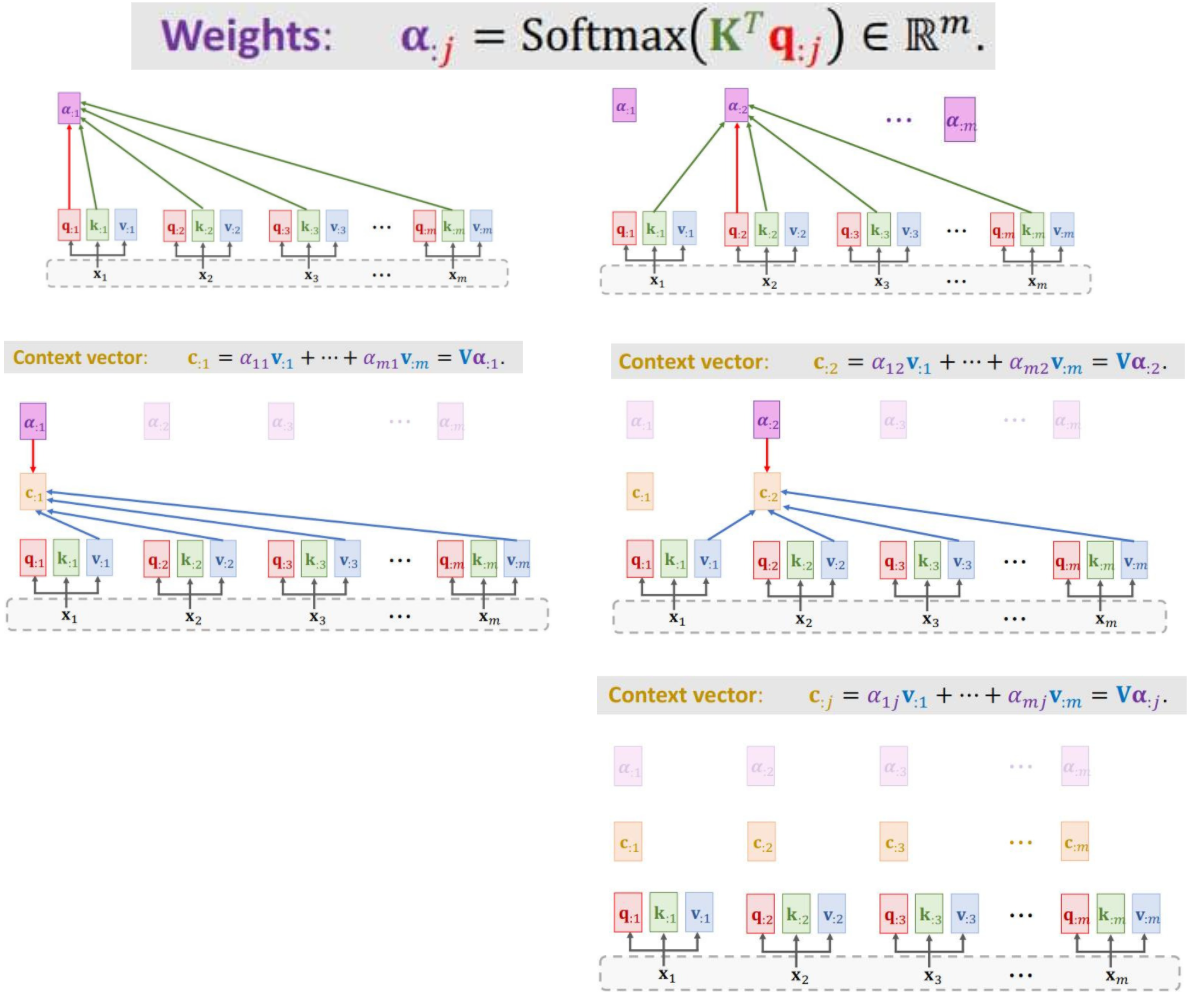
4.1.2 Output of self-attention layer
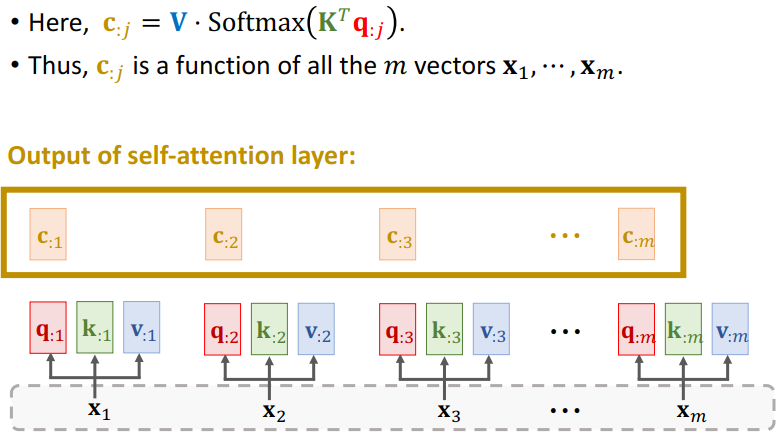
五、Summary(总结)
- Attention was originally developed for Seq2Seq RNN models [1].
- Self-attention: attention for all the RNN models (not necessarily Seq2Seq models [2].
- Attention can be used without RNN [3].
- We learned how to build attention layer and self-attention layer.
Reference:
- Bahdanau, Cho, & Bengio. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In ICLR, 2015.
- Cheng, Dong, & Lapata. Long Short-Term Memory-Networks for Machine Reading. In EMNLP, 2016.
- Vaswani et al. Attention Is All You Need. In NIPS, 2017.
5.1 Attention Layer
5.2 Self-Attention Layer





 本文深入探讨了Transformer模型,一种基于纯Attention机制而非RNN的Seq2Seq模型,它在大规模数据集上表现优于RNN。Transformer包括Attention层和Self-Attention层,其中Attention层用于Seq2Seq模型,解决了RNN的遗忘问题,而Self-Attention层则允许模型同时考虑所有输入序列,增强了模型的表示能力。通过剥离RNN,Transformer展示了Attention在机器翻译等任务中的潜力。
本文深入探讨了Transformer模型,一种基于纯Attention机制而非RNN的Seq2Seq模型,它在大规模数据集上表现优于RNN。Transformer包括Attention层和Self-Attention层,其中Attention层用于Seq2Seq模型,解决了RNN的遗忘问题,而Self-Attention层则允许模型同时考虑所有输入序列,增强了模型的表示能力。通过剥离RNN,Transformer展示了Attention在机器翻译等任务中的潜力。

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










