尝试使用神经网络识别MNIST手写数字集
日志:
- 导入基本包,从torchvision获取训练与测试集,准备与预处理基本数据材料。这里基于便利,使用了sklearn.preprocessing的StandardScaler进行数据标准化,整合后发送给DataLoader进行打包。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import datetime as dt
data_path = r"C:\Users\Blackool\Desktop\some_datafile\Ai\train_data"
MNIST_train = datasets.MNIST(data_path, train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
MNIST_test = datasets.MNIST(data_path, train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(MNIST_train.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 28 * 28))
MNIST_train.data = torch.tensor(scaler.transform(MNIST_train.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 28 * 28)).reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32)
MNIST_test.data = torch.tensor(scaler.transform(MNIST_test.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 28 * 28)).reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32)
MNIST_train = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(MNIST_train.data, MNIST_train.targets)
MNIST_test = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(MNIST_test.data, MNIST_test.targets)
MNIST_train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(MNIST_train, batch_size=256, shuffle=True)
MNIST_test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(MNIST_test, batch_size=256, shuffle=False)
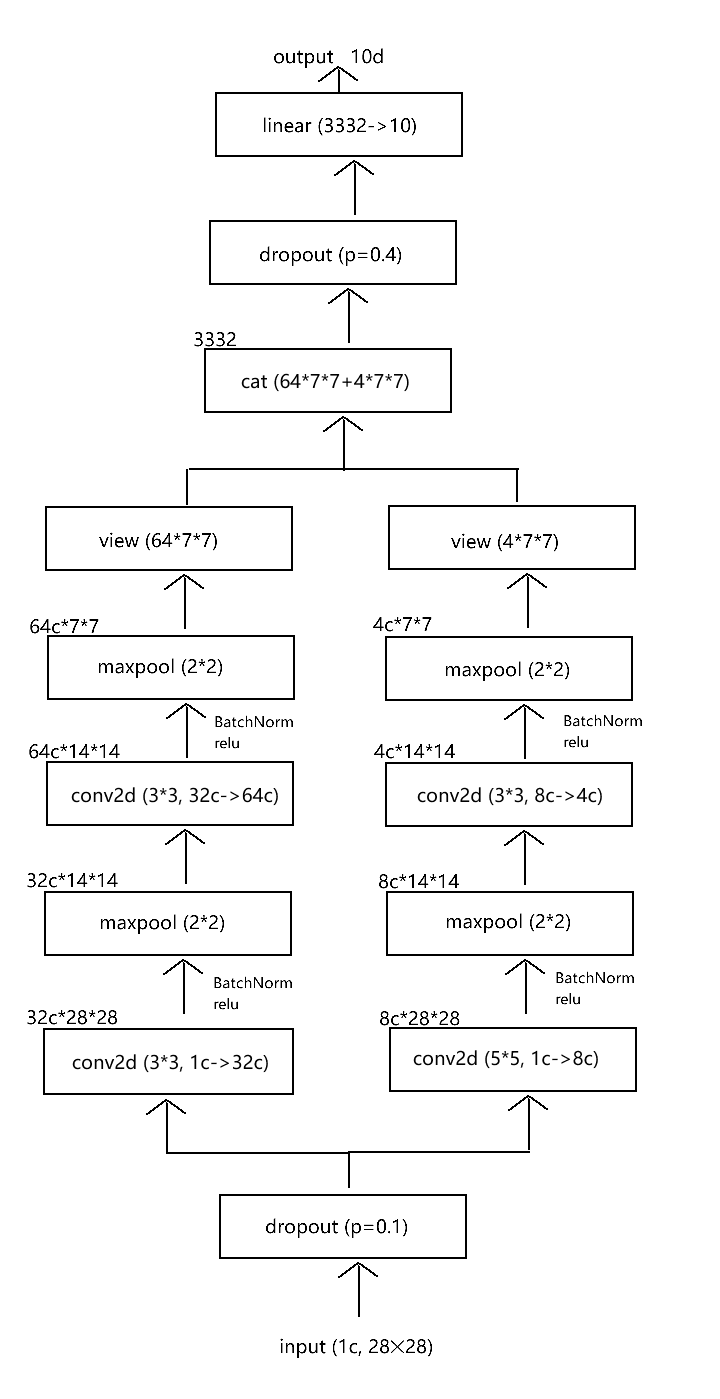
2. 之后搭建模型框架,尝试采
用双分支卷积结构,每个分
支以不同的卷积核进行识别,
最后一层使用线性全连接进
行整合。过程中使用
dropout和BatchNorm增强
训练的稳定性和模型的鲁棒
性,防止过拟合。
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv1_2 = nn.Conv2d(1, 8, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2d(32 , 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2d(8, 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.linear = nn.Linear(64 * 7 * 7 + 4 * 7 * 7, 10)
self.dropout_input = nn.Dropout2d(0.1)
self.dropout_linear = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.conv1_1_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.conv1_2_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(8)
self.conv2_1_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.conv2_2_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(4)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dropout_input(x)
x1 = F.relu(self.conv1_1_bn(self.conv1_1(x)))
x2 = F.relu(self.conv1_2_bn(self.conv1_2(x)))
x1 = F.max_pool2d(x1, kernel_size=2)
x2 = F.max_pool2d(x2, kernel_size=2)
x1 = F.relu(self.conv2_1_bn(self.conv2_1(x1)))
x2 = F.relu(self.conv2_2_bn(self.conv2_2(x2)))
x1 = F.max_pool2d(x1, kernel_size=2)
x2 = F.max_pool2d(x2, kernel_size=2)
x1 = x1.view(-1, 64 * 7 * 7)
x2 = x2.view(-1, 4 * 7 * 7)
x = torch.cat((x1, x2), dim=1)
x = self.dropout_linear(x)
x = self.linear(x)
return x
3. 考虑到模型搭建完成后难以调试,尝试先行运行模型,验证当前是否存在错误
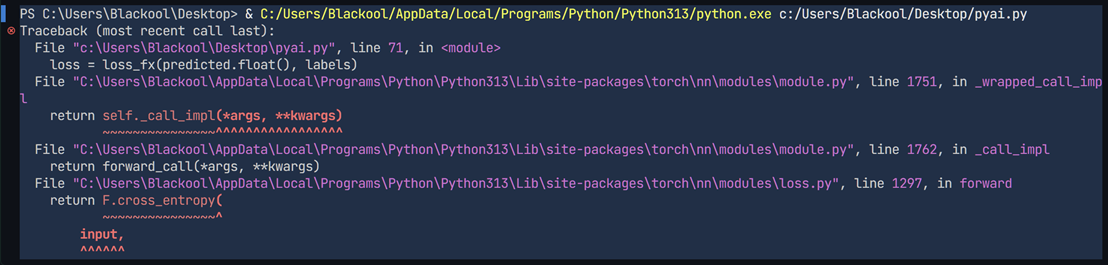
在这里发现程序报错,经查证发现torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss的输入需要线性层的原始输出,但这里直接使用了max给予了他最大值标签。修改后:
model = Net().cuda()
loss_fx = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, weight_decay=0.001)
epochs = 1
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
start_time = dt.datetime.now()
model.train()
for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
loss_total = 0.0
for imgs, labels in MNIST_train_loader:
imgs, labels = imgs.cuda(), labels.cuda()
outputs = model(imgs)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)
loss = loss_fx(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_total += loss.item()
train_losses.append(loss_total / len(MNIST_train_loader))
print(f"Epoch {epoch/epochs*100:.2f}%")
4. 现在准备工作基本完成,开始着手训练模型并收集相关数据。
首先设计训练循环与流程,为了确保不会发生过拟合,所以在优化器使用了L2正则化。
- start_time = dt.datetime.now()
- for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
- loss_total = 0.0
- model.train()
- for imgs, labels in MNIST_train_loader:
- imgs, labels = imgs.cuda(), labels.cuda()
- outputs = model(imgs)
- loss = loss_fx(outputs, labels)
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- loss_total += loss.item()
- train_losses.append(loss_total / len(MNIST_train_loader))
- print(f"Epoch {epoch/epochs*100:.2f}%")
- model.eval()
- with torch.no_grad():
- loss_total = 0.0
- for imgs, labels in MNIST_test_loader:
- imgs, labels = imgs.cuda(), labels.cuda()
- outputs = model(imgs)
- loss = loss_fx(outputs, labels)
- loss_total += loss.item()
- test_losses.append(loss_total / len(MNIST_test_loader))
- train_spot_time = dt.datetime.now()
- print(f"Training time: {(train_spot_time - start_time).seconds} seconds")
- model.eval()
- with torch.no_grad():
- correct = 0
- total = 0
- for imgs, labels in MNIST_test_loader:
- imgs, labels = imgs.cuda(), labels.cuda()
- outputs = model(imgs)
- _, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
- total += labels.size(0)
- correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
- print(f"Accuracy: {correct / total * 100:.2f}%")
- end_time = dt.datetime.now()
- print(f"Total time: {(end_time - start_time).seconds} seconds")
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 4), dpi=110)
- ax.plot(train_losses, label='Train Loss')
- ax.plot(test_losses, label='Test Loss')
- ax.set_xlabel('Epoch')
- ax.set_ylabel('Loss')
- ax.legend()
- plt.show()
5. 现在开始运行程序,查看训练结果:
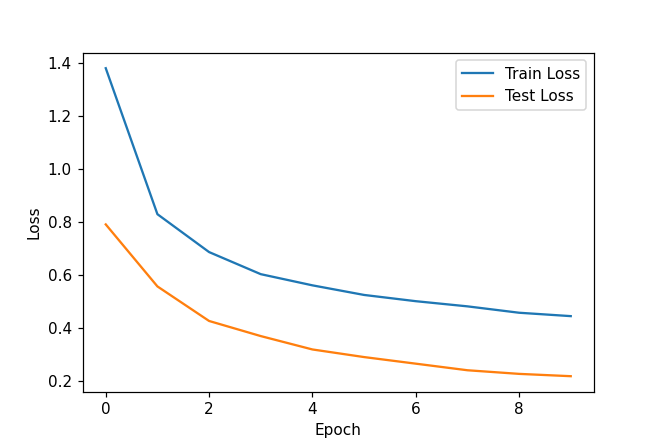
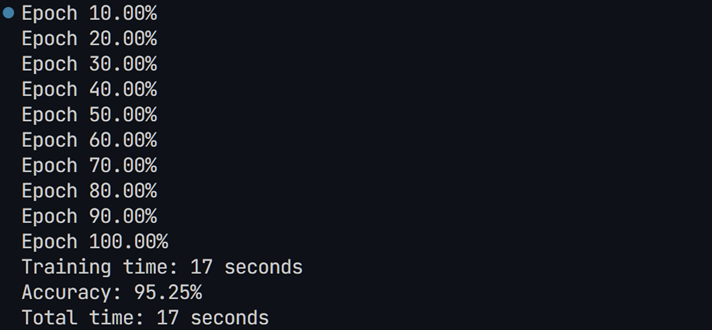
这里发现两个损失曲线都收敛,但还没有收敛完全,测试函数损失意外的比训练函数损失低。所以把训练轮次提升五倍。(epochs: 10 -> 50)再查看结果:
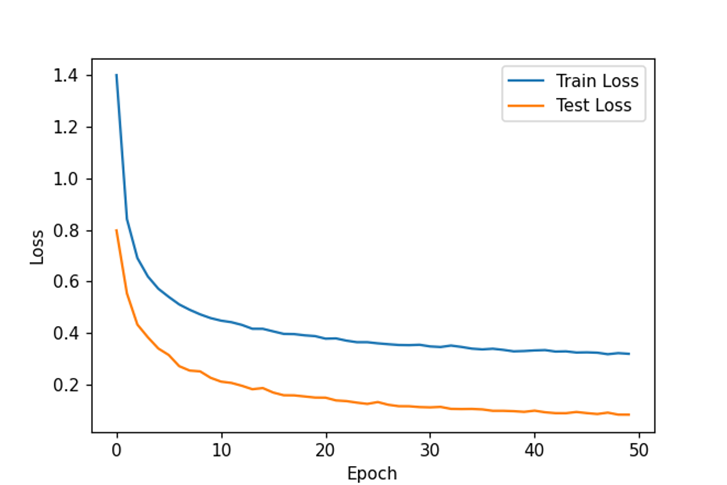
此时发现两个损失曲线并没有发生过拟合现象,推测现在已收敛。对于测试损失比训练损失高,猜测是由dropout函数对于训练集参数的随机丢失引起。
6. 测试集已有95%以上的正确率,但介于任务的难度和模型的大小,现在尝试缩小模型并最大化地保证模型的质量。
先尝试减少卷积的输出特征:
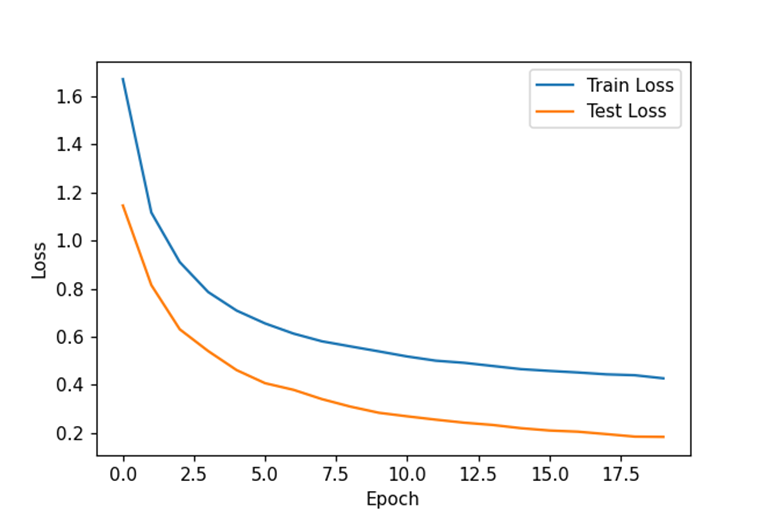
发现大幅减少卷积的特征后,模型的正确率几乎不变。现在尝试去掉一个卷积核,将模型合并为单列卷积网络:
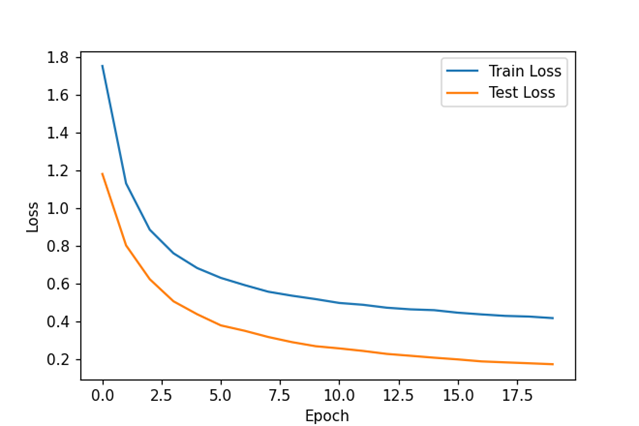
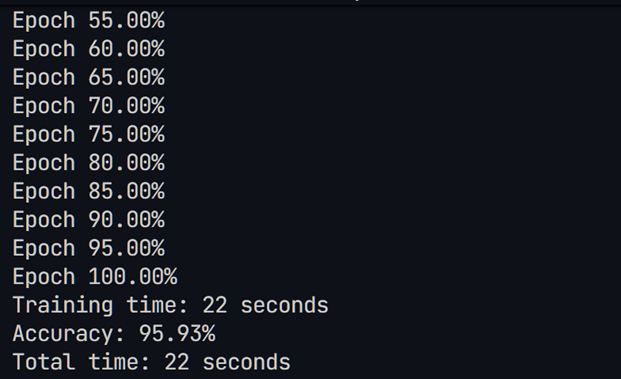
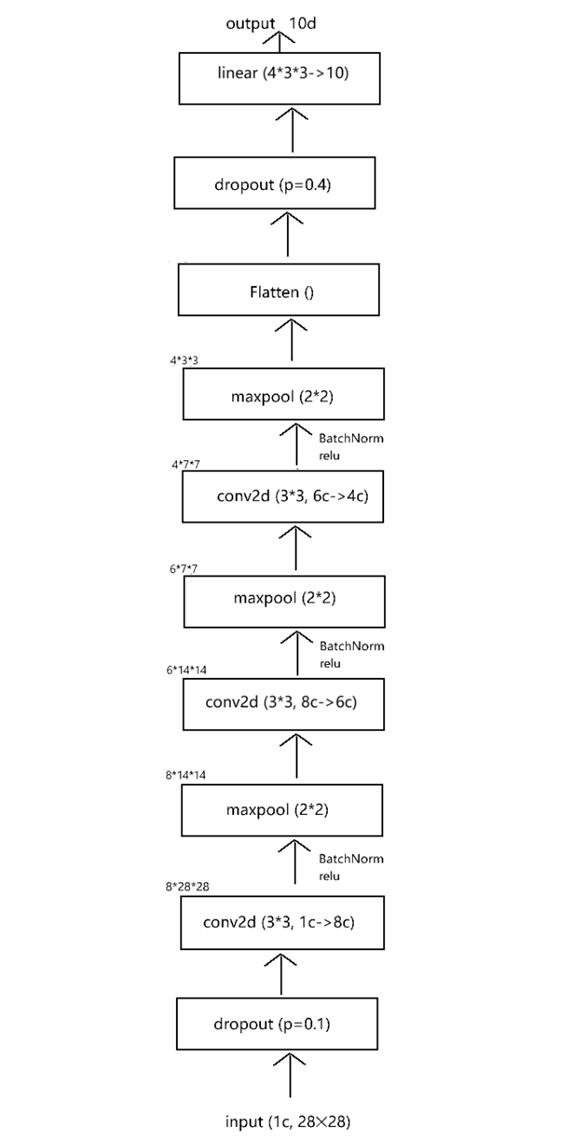
现在我们已经大幅度削减了模型的参数,模型的训练时间从84秒降低到22秒,然而其正确率几乎没有变化。我们现在继续尝试削减模型参数:
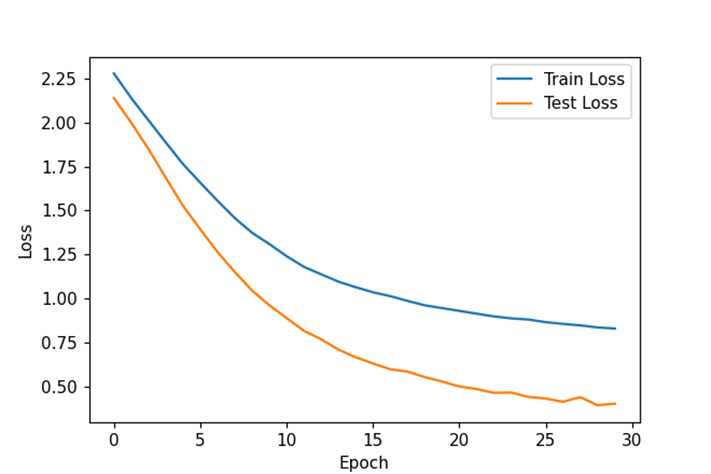
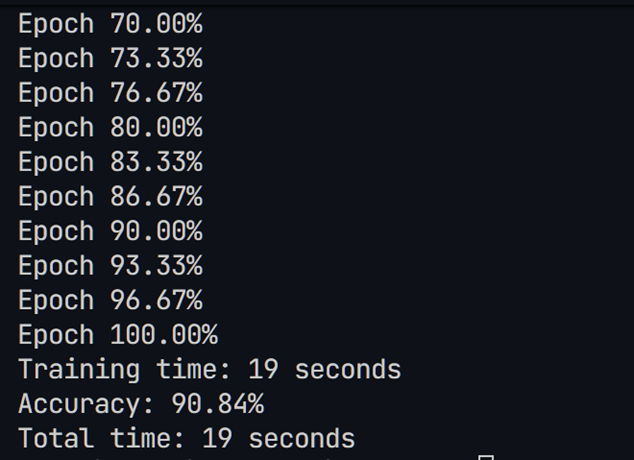
这次增加了一个卷积层,但减少了线性层的宽度,这时发现必须提高训练轮次才能使模型收敛。结果如上,发现我们消耗了更多的时间但正确率有所下滑。现在尝试提高学习率并增加模型宽度:
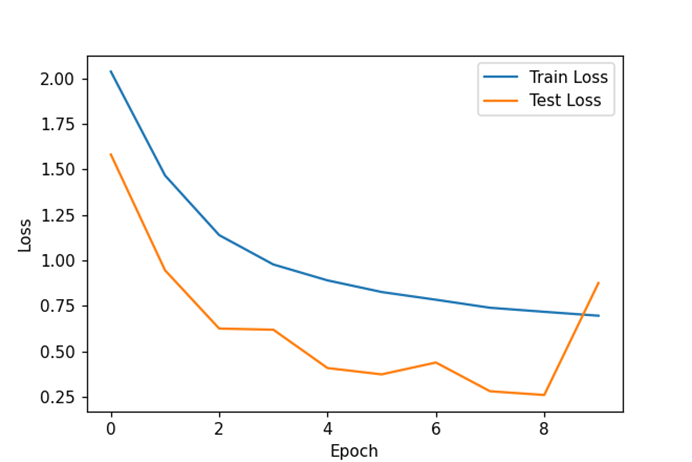
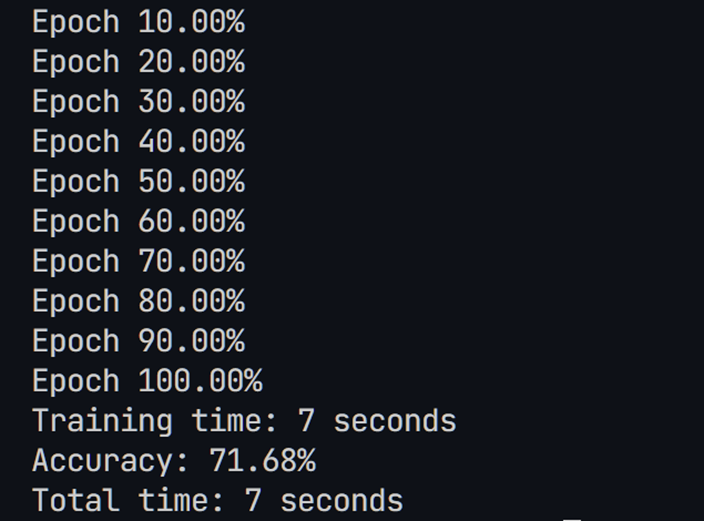
这次我们的训练时间大幅度缩短,但根据损失函数曲线来看,模型出现了过拟合,但根据损失曲线早期的训练轮次损失较低,所以采取早停策略
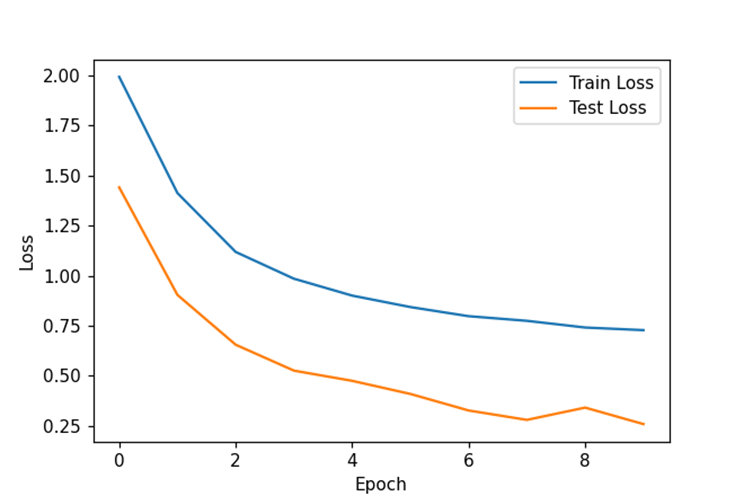
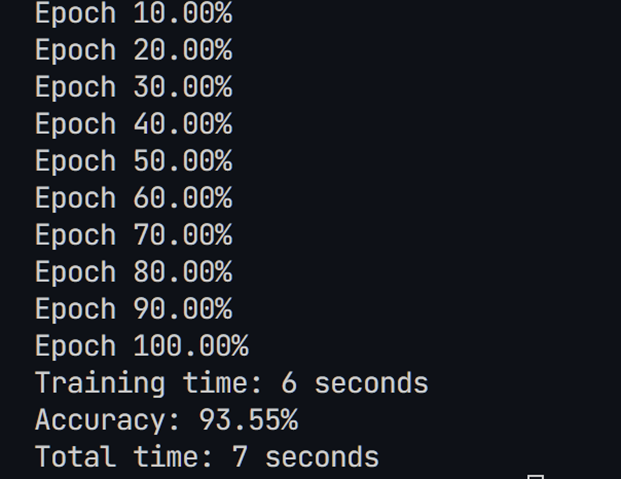
至此,认为模型训练结束。
7. 最后使用torch.save(model, save_path)保存网络模型,以便下次使用。




















 1173
1173

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








