点击查看系列文章 =》 Interrupt Pipeline系列文章大纲-优快云博客
原创不易,需要大家多多鼓励!您的关注、点赞、收藏就是我的创作动力!
4.5 只在head domain注册的设备中断
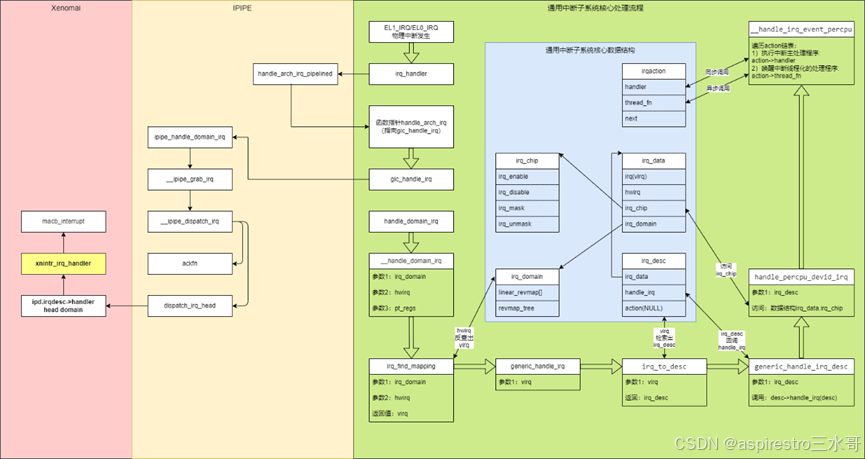
哪些设备会只在head domain Xenomai中注册中断呢?这就需要说一下Xenomai中的实时驱动模型(RTDM)。
在J. Kiszka的论文《The Real-Time Driver Model and First Applications》中指出:自从所谓的双内核硬实时Linux扩展(如RTLinux[1]和RTAI[2])被引入以来,已经开发了大量的驱动程序。仅举几例,就有像Comedi[3]、rtcan[4]或rtcom[5]这样的独立厂商项目,以及厂商提供的驱动包[7, 6]。尽管这些驱动程序针对类似的硬件,但到目前为止,在统一的应用程序编程接口上投入的努力很少。大多数驱动程序都定义了自己的库式API,这阻碍了硬件的轻松替换,因为应用程序软件需要适应新硬件的驱动程序。实时驱动模型(RTDM)旨在统一在实时Linux下开发设备驱动程序及其相关应用程序的接口。
在Xenomai 3中,已经包含了一些RTDM设备驱动,例如can、net、spi、serial、gpio等设备驱动。这些设备注册中的接口是rtdm_irq_request。
以drivers/xenomai/net/drivers/macb.c为例,驱动加载后,匹配到对应的platform_device(.name = “macb”),调用macb_probe执行设备初始化。
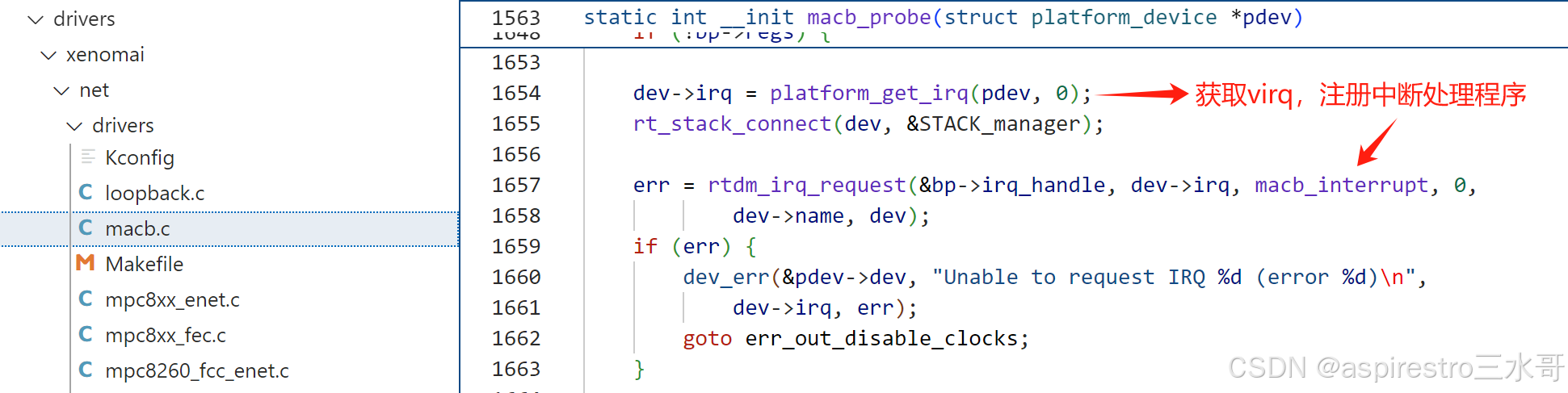
第1654行,通过platform_get_irq->of_irq_get获取Linux virq。
第1657行,调用rtdm_irq_request为virq注册中断处理程序macb_interrupt。先埋个伏笔,macb_interrupt的返回值为RTDM_IRQ_HANDLED。注意rtdm_irq_request的第一个参数,它是一个rtdm_irq_t类型(即struct xnintr)的数据结构实例。
typedef struct xnintr rtdm_irq_t;
struct xnintr {
#ifdef CONFIG_XENO_OPT_SHIRQ
/** Next object in the IRQ-sharing chain. */
struct xnintr *next;
#endif
/** Number of consequent unhandled interrupts */
unsigned int unhandled;
/** Interrupt service routine. */
xnisr_t isr;
/** User-defined cookie value. */
void *cookie;
/** runtime status */
unsigned long status;
/** Creation flags. */
int flags;
/** IRQ number. */
unsigned int irq;
/** Interrupt acknowledge routine. */
xniack_t iack;
/** Symbolic name. */
const char *name;
/** Descriptor maintenance lock. */
raw_spinlock_t lock;
#ifdef CONFIG_XENO_OPT_STATS_IRQS
/** Statistics. */
struct xnirqstat *stats;
#endif
};
接着分析rtdm_irq_request,它经过层层调用走到ipipe_request_irq,向head domain Xenomai注册中断处理程序。但是它注册的中断程序是xnintr_irq_handler,为啥?
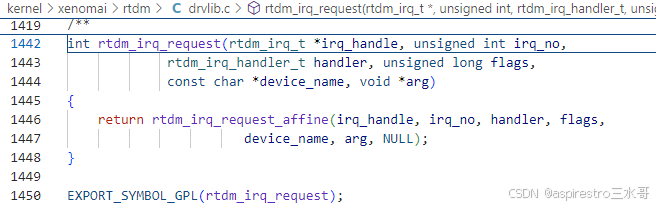
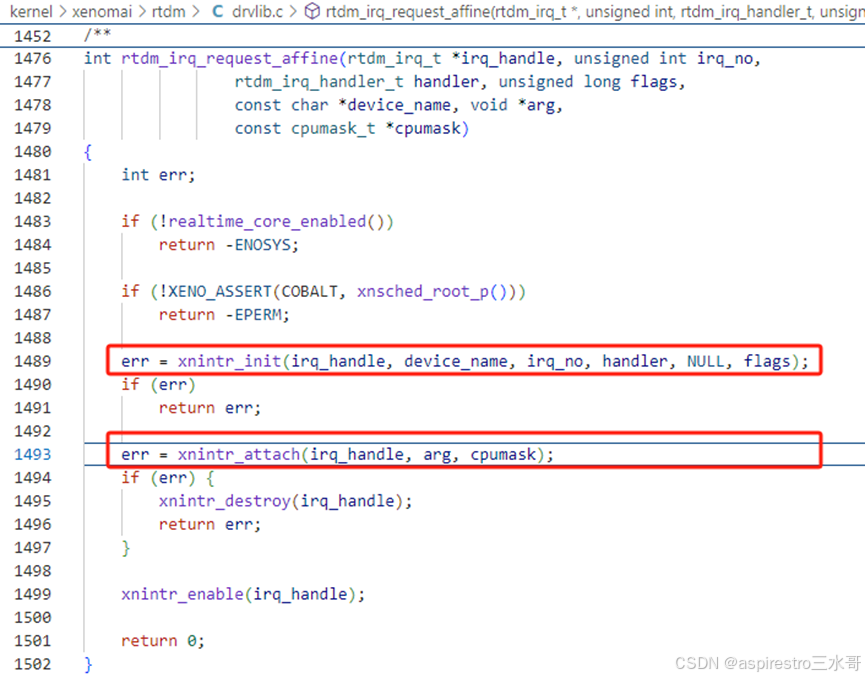
第1489行,在xnintr_init中,对irq_handle进行初始化,其中irq成员初始化为virq,isr成员指向中断处理程序macb_interrupt。
int xnintr_init(struct xnintr *intr, const char *name,
unsigned int irq, xnisr_t isr, xniack_t iack,
int flags)
{
secondary_mode_only();
if (irq >= IPIPE_NR_IRQS)
return -EINVAL;
intr->irq = irq;
intr->isr = isr;
intr->iack = iack;
intr->cookie = NULL;
intr->name = name ? : "<unknown>";
intr->flags = flags;
intr->status = _XN_IRQSTAT_DISABLED;
intr->unhandled = 0;
raw_spin_lock_init(&intr->lock);
#ifdef CONFIG_XENO_OPT_SHIRQ
intr->next = NULL;
#endif
alloc_irqstats(intr);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(xnintr_init);
第1493行,继续调用xnintr_attach。
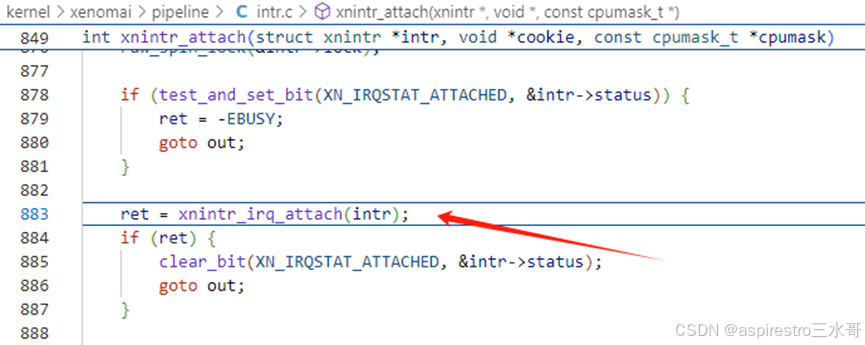
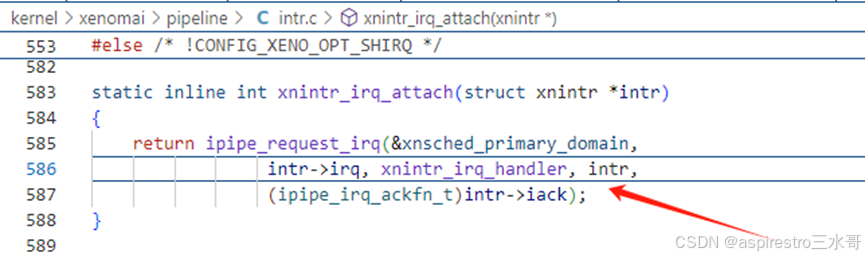
第586行,此处向head domain Xenomai注册中断处理程序是xnintr_irq_handler,把指针intr(指向irq_handle)作为xnintr_irq_handler执行的参数。
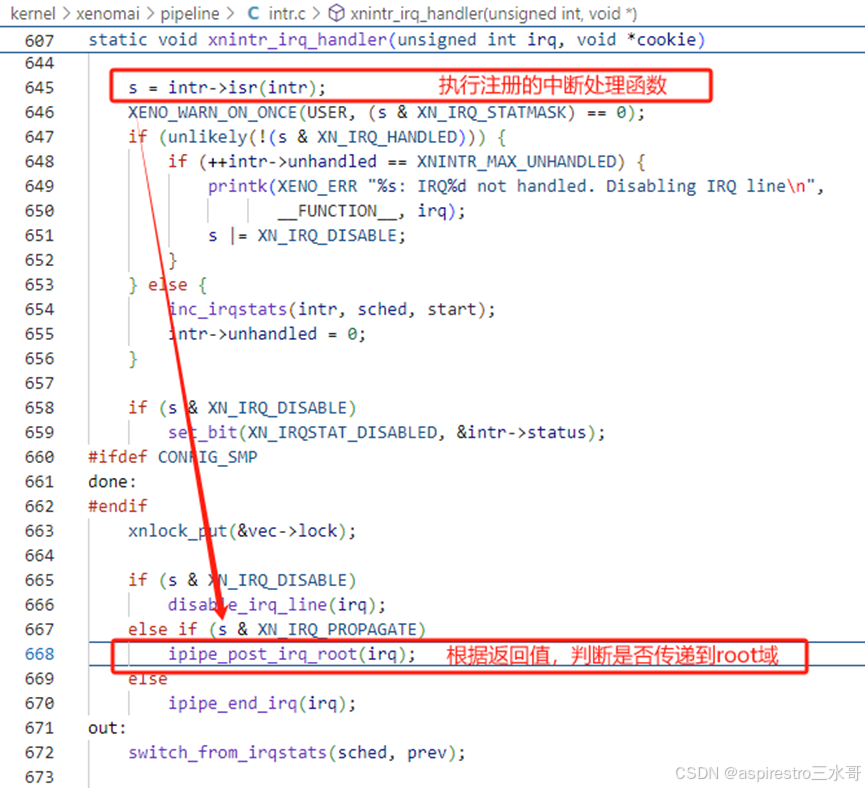
在xnintr_irq_handler执行的过程中,先是执行intr->isr即macb_interrupt,然后根据macb_interrupt的返回值,判断是否要传递中断到root domain。只有当返回值为XN_IRQ_PROPAGATE时,才会传递中断到root domain。
上面已经提到了,macb_interrupt的返回值是XN_IRQ_HANDLED,所有第668行不会执行,会走到第670行,结束中断。
在xnintr_init的注释中,明确写道:强烈不建议使用XN_IRQ_PROPAGATE。
/**
* @fn int xnintr_init(struct xnintr *intr,const char *name,unsigned int irq,xnisr_t isr,xniack_t iack,int flags)
* @brief Initialize an interrupt descriptor.
*
* When an interrupt occurs on the given @a irq line, the interrupt
* service routine @a isr is fired in order to deal with the hardware
* event. The interrupt handler may call any non-blocking service from
* the Cobalt core.
*
* Upon receipt of an IRQ, the interrupt handler @a isr is immediately
* called on behalf of the interrupted stack context, the rescheduling
* procedure is locked, and the interrupt line is masked in the system
* interrupt controller chip. Upon return, the status of the
* interrupt handler is checked for the following bits:
*
* - XN_IRQ_HANDLED indicates that the interrupt request was
* successfully handled.
*
* - XN_IRQ_NONE indicates the opposite to XN_IRQ_HANDLED, meaning
* that no interrupt source could be identified for the ongoing
* request by the handler.
*
* In addition, one of the following bits may be present in the
* status:
*
* - XN_IRQ_DISABLE tells the Cobalt core to disable the interrupt
* line before returning from the interrupt context.
*
* - XN_IRQ_PROPAGATE propagates the IRQ event down the interrupt
* pipeline to Linux. Using this flag is strongly discouraged, unless
* you fully understand the implications of such propagation.
*
* @warning The handler should not use these bits if it shares the
* interrupt line with other handlers in the real-time domain. When
* any of these bits is detected, the interrupt line is left masked.
*
* A count of interrupt receipts is tracked into the interrupt
* descriptor, and reset to zero each time such descriptor is
* attached. Since this count could wrap around, it should be used as
* an indication of interrupt activity only.
*
* @param intr The address of a descriptor the Cobalt core will use to
* store the interrupt-specific data.
*
* @param name An ASCII string standing for the symbolic name of the
* interrupt or NULL.
*
* @param irq The IRQ line number associated with the interrupt
* descriptor. This value is architecture-dependent. An interrupt
* descriptor must be attached to the system by a call to
* xnintr_attach() before @a irq events can be received.
*
* @param isr The address of an interrupt handler, which is passed the
* address of the interrupt descriptor receiving the IRQ.
*
* @param iack The address of an optional interrupt acknowledge
* routine, aimed at replacing the default one. Only very specific
* situations actually require to override the default setting for
* this parameter, like having to acknowledge non-standard PIC
* hardware. @a iack should return a non-zero value to indicate that
* the interrupt has been properly acknowledged. If @a iack is NULL,
* the default routine will be used instead.
*
* @param flags A set of creation flags affecting the operation. The
* valid flags are:
*
* - XN_IRQTYPE_SHARED enables IRQ-sharing with other interrupt
* objects.
*
* - XN_IRQTYPE_EDGE is an additional flag need to be set together
* with XN_IRQTYPE_SHARED to enable IRQ-sharing of edge-triggered
* interrupts.
*
* @return 0 is returned on success. Otherwise, -EINVAL is returned if
* @a irq is not a valid interrupt number.
*
* @coretags{secondary-only}
*/
点击查看系列文章 =》 Interrupt Pipeline系列文章大纲-优快云博客
原创不易,需要大家多多鼓励!您的关注、点赞、收藏就是我的创作动力!






















 232
232

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








