104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
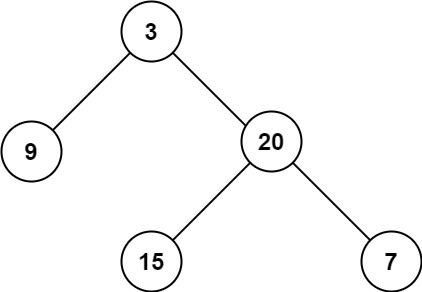
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在 [0, 10^4] 区间内。
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
递归法
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度,所以本题中我们通过后序求得根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
这一点其实是很多同学没有想清楚的,很多题解同样没有讲清楚。
我先用后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度。
确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {}
确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
代码如下:
if root == nil {
return 0
}
确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1(加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
代码如下:
leftDepth := maxDepth(root.Left) // 左
rightDepth := maxDepth(root.Right) // 右
// 根(遍历到根时就是具体的处理逻辑,遍历到左右节点时则是递归)
curNodeDepth = max(leftDepth,rightDepth) + 1
return curNodeDepth
所以整体Go代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftDepth := maxDepth(root.Left) // 左
rightDepth := maxDepth(root.Right) // 右
// 根(遍历到根时就是具体的处理逻辑,遍历到左右节点时则是递归)
curNodeDepth = max(leftDepth,rightDepth) + 1
return curNodeDepth
}
func max(a,b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
代码精简之后Go代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 这里实际是后续遍历(左右根),不过用一行写了
return max(maxDepth(root.Left),maxDepth(root.Right)) + 1
}
func max(a,b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
精简之后的代码根本看不出是哪种遍历方式,也看不出递归三部曲的步骤,所以如果对二叉树的操作还不熟练,尽量不要直接照着精简代码来学。
提示:什么是递归
如果对return max(maxDepth(root.Left),maxDepth(root.Right)) + 1这行代码还是没有绕太明白的话,建议可以先看看一下两篇文章。类别一下青蛙跳台阶问题,以及跟进一下二叉树遍历的实际流程图解。
本题当然也可以使用前序,代码如下:(充分表现出求深度回溯的过程)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 使用前序遍历,不断更新最大深度的变量值
res := 1
dfs(root,1,&res)
return res
}
func dfs(root *TreeNode,depth int,res *int) {
if *res < depth { // 中
*res = depth
}
if root.Left != nil { // 左
depth += 1 // 深度+1
dfs(root.Left,depth,res)
depth -= 1 // 回溯,深度-1
}
if root.Right != nil { // 右
depth += 1 // 深度+1
dfs(root.Right,depth,res)
depth -= 1 // 回溯,深度-1
}
}
可以看出使用前序遍历求的深度,这才是真正求深度的逻辑!
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 使用前序遍历,不断更新最大深度的变量值
res := 1
dfs(root,1,&res)
return res
}
func dfs(root *TreeNode,depth int,res *int) {
if *res < depth { // 中
*res = depth
}
if root.Left != nil { // 左
dfs(root.Left,depth + 1,res)
}
if root.Right != nil { // 右
dfs(root.Right,depth + 1,res)
}
}
迭代法
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
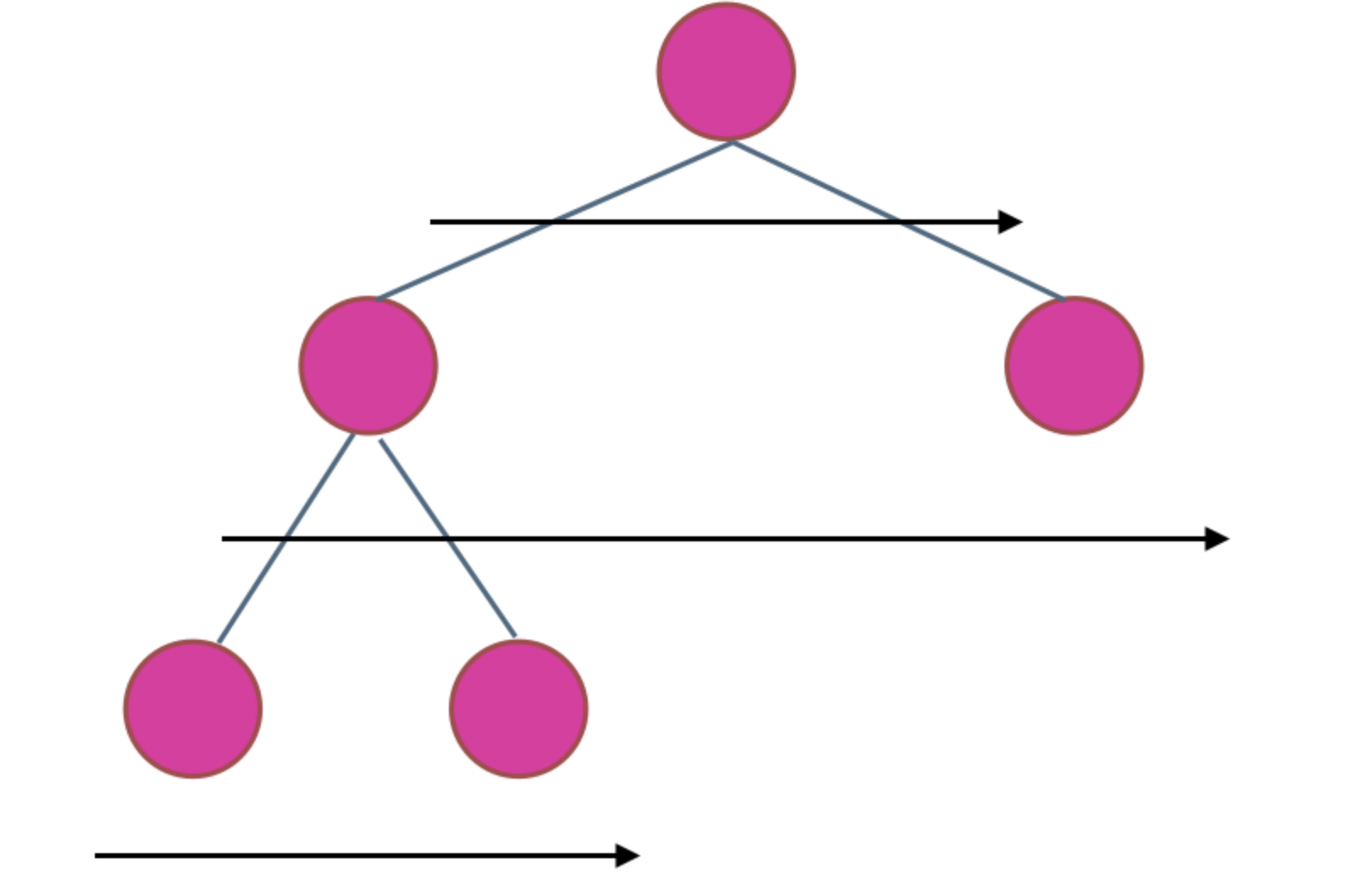
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
Go代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 层序遍历,层数就是最大深度
queue := make([]*TreeNode,0)
queue = append(queue,root)
res := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
queueSize := len(queue)
for i := 0;i < queueSize;i++ {
curNode := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if curNode.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue,curNode.Left)
}
if curNode.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue,curNode.Right)
}
}
// 遍历完一层后,层数+1
res += 1
}
return res
}
那么我们可以顺便解决一下n叉树的最大深度问题
559. N 叉树的最大深度
给定一个N叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:5
提示:
- 树的深度不会超过 1000 。
- 树的节点数目位于 [0, 10^4] 之间。
递归法
Go代码
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
res := 1
dfs(root,1,&res)
return res
}
func dfs(root *Node,depth int,res *int) {
if depth > *res {
*res = depth
}
// 和回溯法几乎没有区别了,一直dfs到底,然后一层一层回溯回来
for i := 0; i < len(root.Children);i++ {
dfs(root.Children[i],depth + 1,res)
}
}
迭代法
Go代码
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 层序遍历,层数就是最大深度
queue := make([]*Node,0)
queue = append(queue,root)
res := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
queueSize := len(queue)
for i := 0;i < queueSize;i++ {
curNode := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for i := 0;i < len(curNode.Children);i++ {
queue = append(queue,curNode.Children[i])
}
}
// 遍历完一层后,层数+1
res += 1
}
return res
}





















 598
598

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








