调用方式
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# 创建样本
X, y = [[9], [8]], [1, 0]
# 建模
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 训练
model.fit(X, y)
# 概率预测
print(model.predict_proba(X))
参数
| 参数 | 注释 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| criterion | 基尼系数或信息增益(gini or entropy) | “gini” |
| splitter | 全部或随机选择特征(best or random) | “best” |
| max_depth | 树最大深度 | None |
| min_samples_split | 节点样本数小于该值则不再切分 | 2 |
| min_samples_leaf | 叶子节点的最小样本数 | 1 |
| min_weight_fraction_leaf | The minimum weighted fraction of the sum total of weights (of all the input samples) required to be at a leaf node. 样本权重默认相等 | 0. |
| max_features | 最大特征数 | None |
| random_state | 设置随机状态,默认用numpy.random | None |
| max_leaf_nodes | 叶子节点的最大个数 | None |
| min_impurity_decrease | A node will be split if this split induces a decrease of the impurity greater than or equal to this value. | 0. |
| min_impurity_split | Threshold for early stopping in tree growth. A node will split if its impurity is above the threshold, otherwise it is a leaf. | None |
| class_weight | 指定样本中各类别的权重 | None |
| presort | 是否预分类 以加快 在拟合过程中寻找最优切分 的速度(默认否) | False |
概率预测
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# 创建样本
df = pd.DataFrame({
'高': [1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
'富': [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
'帅': [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
'约': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]}
)
X = df[['高', '富', '帅']].values
y = df[['约']].values
# 建模训练
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(X, y)
# 约会预测
men = {'高': [1, 0, 0],
'富': [0, 1, 0],
'帅': [0, 0, 1]}
for man in men:
probability = model.predict_proba([men[man]])[0][1]
print('【{}man】约到女神的概率是:{:.1f}%'.format(man, probability * 100))
【高man】约到女神的概率是:66.7%
【富man】约到女神的概率是:100.0%
【帅man】约到女神的概率是:33.3%
可视化
随机森林
import numpy as np, matplotlib.pyplot as mp
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# 创建随机数据集、数据标准化、训练集测试集切分
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=200, noise=.2)
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
# 建模、训练、评分
clf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=4, min_samples_split=9)
clf.fit(X, y)
# 等高线图
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, .01),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, .01))
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
mp.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=.3)
# 散点图
mp.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=50, c=y)
mp.show()

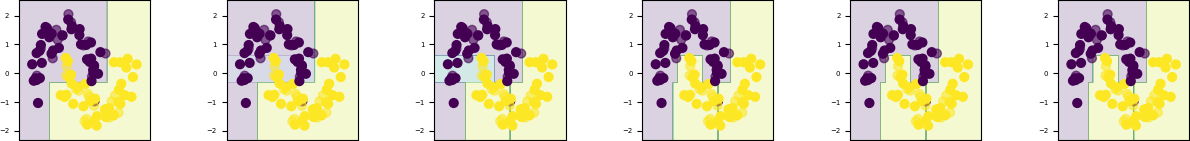
不同树深度的比较
import numpy as np, matplotlib.pyplot as mp
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
X, y = make_moons(noise=.2)
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
s, e = 3, 7
for i in range(s, e + 1):
# 建模、训练、得分
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
print(score)
# 可视化
mp.subplot(1, e - s + 1, i - s + 1)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, .01),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, .01))
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
mp.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=.2) # 等高线图
mp.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], s=40, c=y_train)
mp.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], s=40, c=y_test, alpha=0.6)
mp.tight_layout() # 防止重叠
mp.show()
附录
sklearn版本:0.19.1
注释
| en | cn |
|---|---|
| criterion | 准则 |
| fraction | 分数;部分 |
| probability | 概率 |
| impurity | 杂质 |
| presort | 预分类 |
| feature | n. 特征;vt. 特写 |
| threshold | 门槛;阈值 |
| contour | n. 轮廓、等高线;vt. 画轮廓 |
| mesh | 网眼 |
| grid | n. 网格;栅格; |
| meshgrid | 用于三维曲面的分格线座标;产生“格点”矩阵 |
| tight | 密封的 |
| layout | 布局;陈列 |






















 4366
4366

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










