Collection接口下的结构
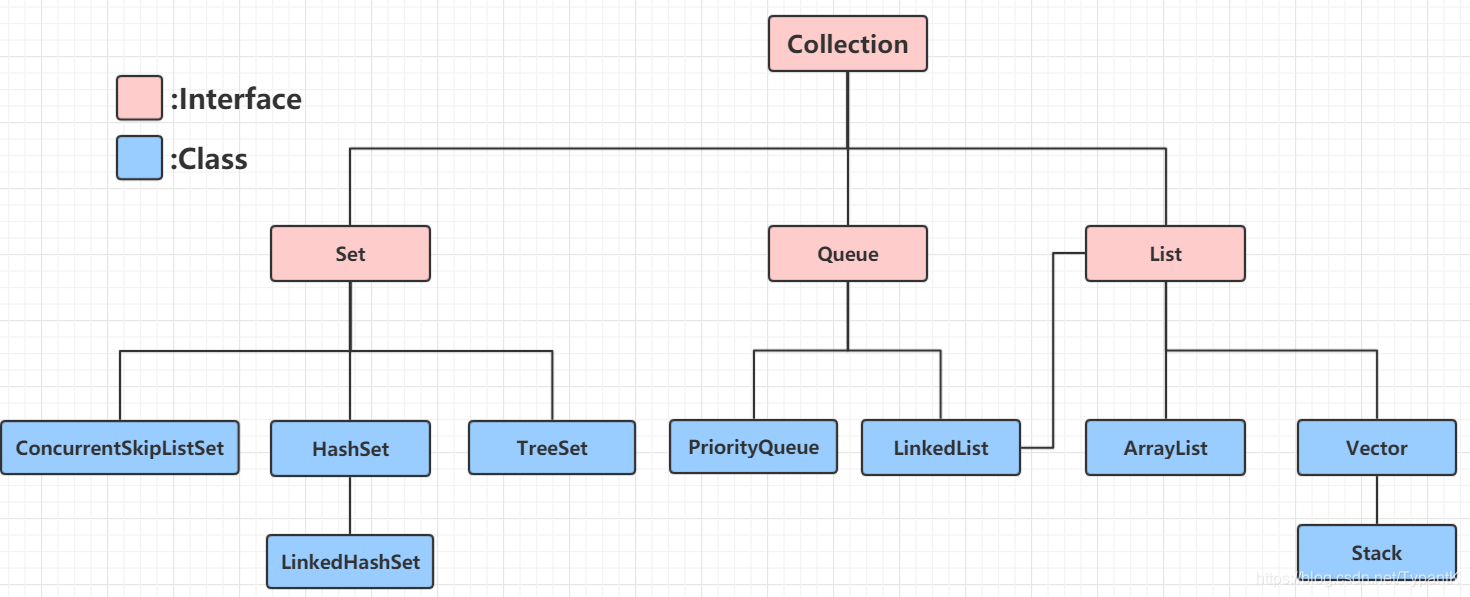
目录
LinkedHashSet(父类HashSet,底层Map为LinkedHashMap)
①public boolean offer(E e) / public boolean add(E e)
addAll(int index, Collection c):
②public boolean remove(Object o)
②public E set(int index, E element)
③public int indexOf(Object o) :可以查找null元素,意味ArrayList可以存放null
⑤public E remove(int index):删除时会移动大量元素
Vector(过时的类,每个方法都有Synchronized)[可以存null]
Set
HashSet
一些属性
*所有的键都有同一个值PRESENT
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
//用作所有键的值,因为HashSet中只存键不存值
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
}方法都是调用HashMap中的方法,不再重复
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
LinkedHashSet(父类HashSet,底层Map为LinkedHashMap)
一些属性
public class LinkedHashSet<E>
extends HashSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
//没有属性,都是调用父类的属性
}构造函数
调用父类的构造函数,使其底层实现变成LinkedHashMap
//两个方法调用同一个父类的构造方法
public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, true);
}
public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity, .75f, true);
}
public LinkedHashSet() {
super(16, .75f, true);
}
public LinkedHashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
super(Math.max(2*c.size(), 11), .75f, true);
addAll(c);
}HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
TreeSet(依赖TreeMap)
一些属性
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The backing map.
*/
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
//同样的套路:所有键的value都是PRESENT
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
}构造函数
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
//还有别的构造方法就不一一列举了
*底层方法实现同TreeMap
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return m.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
ConcurrentSkipListSet
一些属性
构造函数
①
②
List-Queue
PriorityQueue(默认小顶堆)
①public boolean offer(E e) / public boolean add(E e)
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
//数组容量已经不满足下标了,遂扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
//如果原本容量小于64就变2n+2;否则变1.5n
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
//数组最大值 or Integer_MAX_VALUE
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
//有比较器(默认小顶堆) k为x在数组中的下标
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
while (k > 0) {
//父亲结点数组下标
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
//比父亲大,小顶堆,就不用在往上移了
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
break;
//暂时不用赋值x,最后循环出去再赋值
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
//Queue没有比较器,使用插入的对象的比较器
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
List
LinkedList
*可以存null,不支持随机读取,可以不用考虑扩容
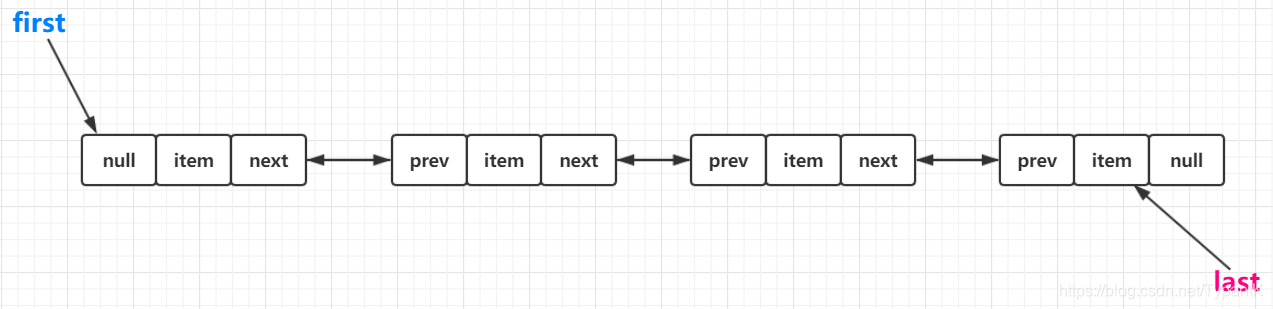
一些属性
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
}private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
//调用无参构造器,然后将集合c中元素添加到LinkedList中
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//默认从尾结点开始插入集合中数据
return addAll(size, c);
}
//返回false表示集合中没有数据,返回true表示添加成功
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//可以检查是否超过size或者小于0(不同于ArrayList只能检查是否超过size)
checkPositionIndex(index);
//熟悉的套路:将集合转换成Object类型数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
//直接从尾结点插入
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
//将集合中数据从第index个结点后开始插入
//获取第index个node(如果小于size/2,从头找;如果大于size/2,从尾找)
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
//依次插入到链表尾
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
//添加操作或者迭代器时使用
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c):
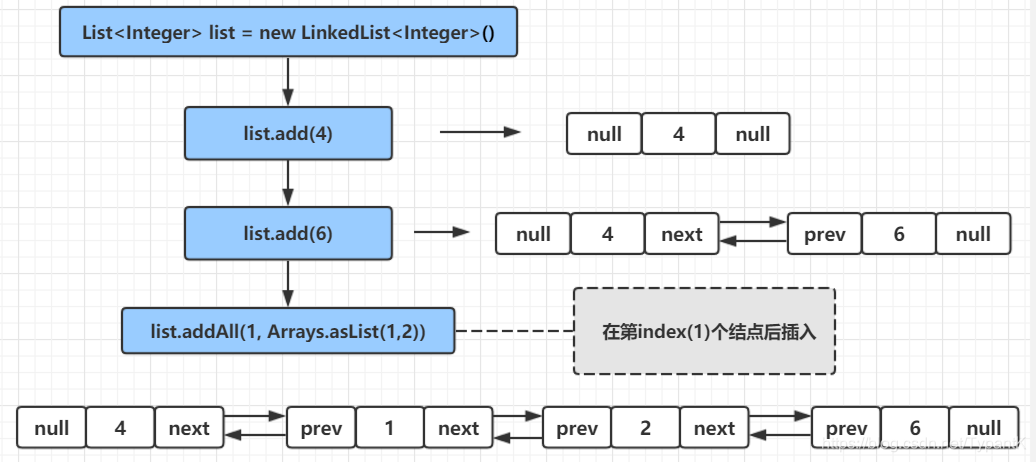
根据index获取到第index个结点方法
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//分为左半和右半,提高查找效率
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}①public boolean add(E e)
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
//如果链表原本为空(last/first都为空,上面为last赋值,下面为first赋值,指向同一节点)
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
②public boolean remove(Object o)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
//1.前驱结点空-->删除的是头结点
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
//2.后继结点为空-->删除的是尾结点
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
//3.结点值设置为空
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
ArrayList:动态扩容
*可以插入null元素,还可以任意随机读取,不好的地方就是删除时需要移动大量元素
一些属性
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* 实际元素数量
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
* 默认初始化容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
//用来赋值给elementData元素数组
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
//当使用无参构造器,用来赋值给elementData元素数组
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* 元素数组
*/
//存的是Object,get的时候会偷偷转型
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
}
构造函数
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) { //初始容量>0
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) { //初始容量为0,返回空对象数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else { //初始容量<0,抛出非法初始容量异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
//未赋值参数,会给elementData设置为空数组
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//将传递进来的集合转换成数组
elementData = c.toArray();
//如果数组不为空
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//转换的数组可能没转换成Object类型数组
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//采用复制的方式,将元素复制进elementData
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
//如果集合为空,就传递空数组给元素数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}①public boolean add(E e)
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* 将指定元素添加到此列表的末尾
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
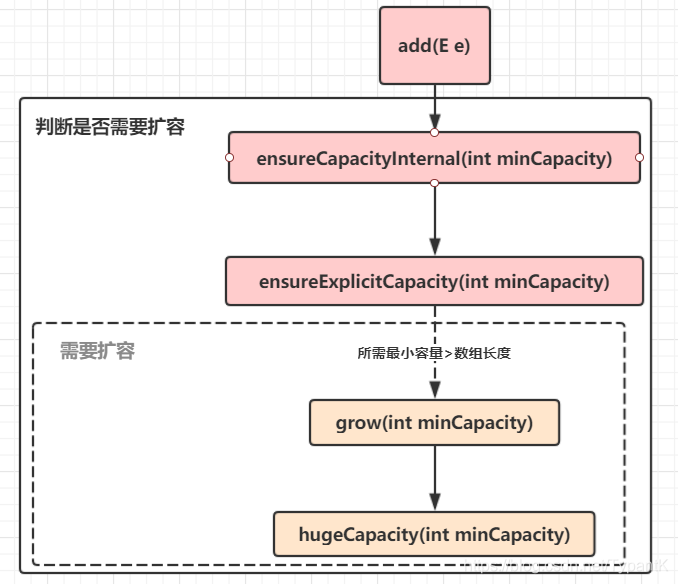
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
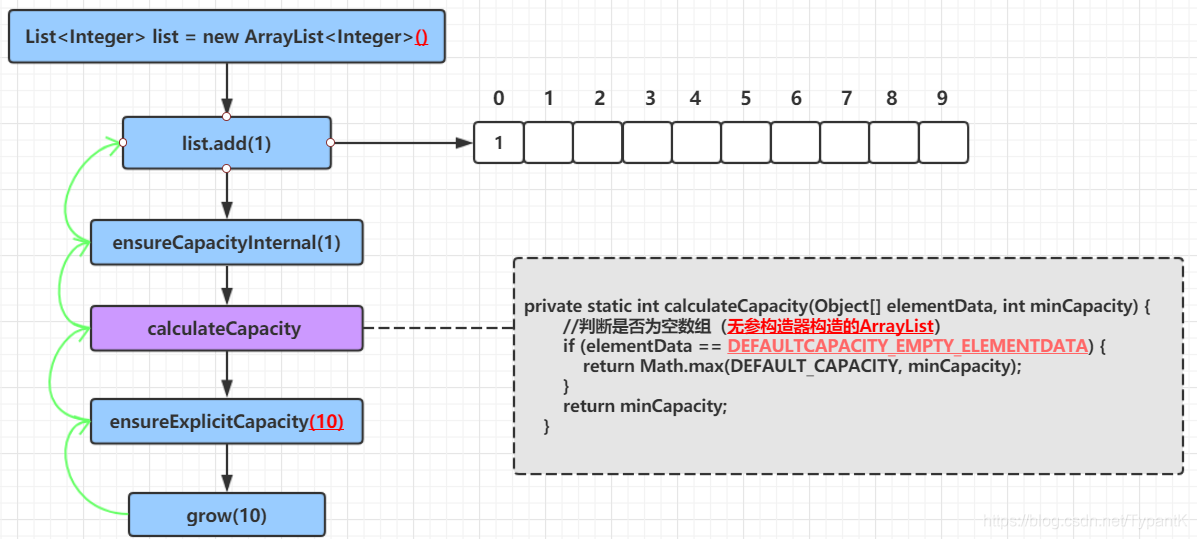
//minCapacity 指的是所需的最小容量
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
//判断是否为空数组(无参构造器构造的ArrayList)
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//熟悉的操作次数+1
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
//溢出
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新容量为旧容量的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//新容量小于参数指定容量
//也就是空数组插入时,直接将容量从0扩充成10,否则会变成1,这样新数组一开始插入的时候很容易触发扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//新容量超过了数组能接受的最大容量
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//拷贝+扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
*为了防止ArrayList在初期插入数据时频繁扩容,所以对于没有设置长度限制的,第一次插入数据就给予了默认长度(10)
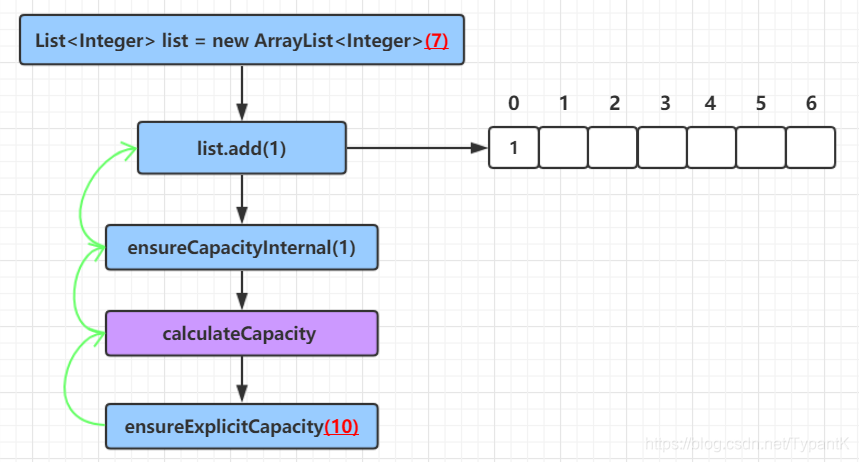
②public E set(int index, E element)
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
//将列表中指定元素替换
public E set(int index, E element) {
//检查index合法性
rangeCheck(index);
//三部曲:得到旧值,替换旧值,返回旧值
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
*/
//不检查负数,似乎交给数组类来进行检查了?如果是负数抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,和下面这个异常不一样
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}③public int indexOf(Object o) :可以查找null元素,意味ArrayList可以存放null
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
//返回第一个o的数组下标,如果不存在就返回-1
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
//null就用不了equals方法了
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}④public E get(int index)
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
//返回指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
//index范围检查
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}隐藏了向下转型的细节(将Object转成了E)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}⑤public E remove(int index):删除时会移动大量元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++; //和添加一样,操作次数+1
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//需要移动的元素个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//真正意义上的删除,将要删除的元素设置为null,这样才gc,而不是仅仅改一个size
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}通过本地数组复制函数来进行移动元素
/* 需要被复制的数组
* @param src the source array.
* 从哪个元素开始复制
* @param srcPos starting position in the source array.
* 需要被复制到哪个数组
* @param dest the destination array.
* 从新数组的哪个位置赋值
* @param destPos starting position in the destination data.
* 需要复制的数
* @param length the number of array elements to be copied.
*/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
Vector(过时的类,每个方法都有Synchronized)[可以存null]
首先说一下Vector是否线程安全的结论:
Vector 和 ArrayList 实现了同一接口 List, 但所有的 Vector 的方法都具有 synchronized 关键修饰,也就单一操作还是线程安全的。但对于复合操作,Vector 仍然需要进行同步处理
复合操作:
if (!vector.contains(element))
vector.add(element);
...
}在执行contains()和add()方法时,可以保证没有方法在使用Vector对象,都是原子性操作(Synchronized作用)。
但是执行完contains(),无法保证下一个执行的就是add()
要想实现复合操作的线程安全,还得用Synchronized再加一个锁,锁住Vector对象
Synchronized(vector){
boolean b = vector.contains(element);
if(!b)vector.add(element);
}这也就是Vector被弃用原因,明明一个锁就够,还得两个锁才能解决线程安全问题
Vector属性
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
//Vector底层实现数组
protected Object[] elementData;
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
//实际元素个数
protected int elementCount;
/**
* The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically
* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If
* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity
* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.
*
* @serial
*/
//如果扩容未指定此参数,Vector就增长为原来两倍
//如果扩容指定此参数(capacitryIncrement>0),就增加capacityIncrement这么多容量
protected int capacityIncrement;
}
构造函数
//下面两个构造器的最终构造器
//设置初始参数和增长容量大小,以及新建数组空间
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
//指定数组空间大小,没有指定增加容量大小
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
//数组空间为10,没有设定增加容量大小
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
/**
* Constructs a vector containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this
* vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
//还是熟悉的套路:c.toArray可能不是Object对象数组;不是的话就手动转(Arrays.copyOf)
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}Vector的方法实现还是比较简单的,就不一一列出了。
Stack
Stack类的代码就只有这么多,还是比较简单的。
通过继承Vector(数组)来实现,主要是pop()
public
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}
//直接添加到数组
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
//很好理解,拿数组大小最后一个元素
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
//检查len-1合法性,将最后一个元素置为空(gc),数量-1
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.
* If the object <tt>o</tt> occurs as an item in this stack, this
* method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the
* occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the
* stack is considered to be at distance <tt>1</tt>. The <tt>equals</tt>
* method is used to compare <tt>o</tt> to the
* items in this stack.
*
* @param o the desired object.
* @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where
* the object is located; the return value <code>-1</code>
* indicates that the object is not on the stack.
*/
//返回距离栈顶的距离
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
}







 本文深入剖析Java Collection接口及其主要实现类,包括HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet、ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector。讨论了它们的内部结构、特点以及关键方法的实现,如HashSet的HashMap底层实现、TreeSet的TreeMap依赖、ArrayList的动态扩容等。同时,文章也提及了过时的Vector类和其线程安全性问题。
本文深入剖析Java Collection接口及其主要实现类,包括HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet、ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector。讨论了它们的内部结构、特点以及关键方法的实现,如HashSet的HashMap底层实现、TreeSet的TreeMap依赖、ArrayList的动态扩容等。同时,文章也提及了过时的Vector类和其线程安全性问题。
















 1384
1384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








