2022“杭电杯”中国大学生算法设计超级联赛(1)
[题目链接](Search Result (hdu.edu.cn))
K Random
题目大意
在[0,1]中随机取N个数字,进行M次操作。对于每次操作,有一半的概率删除最大值,一半的概率删除最小值。问剩余数字的和的期望值(mod109+7)。
题解
易得,剩余的数字分布一定关于0.5对称,所以就是剩余的数字的个数(n-m)除以2,即乘以2的逆元(109+7)。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n, m, mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll qpow(ll a, ll n, ll mod)
{
ll res = 1;
while (n)
{
if (n & 1)
res = (res * a) % mod;
a = (a * a) % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
ll inv(ll a, ll p)
{
return qpow(a, p - 2, p);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ll t;
cin >> t;
ll ni = inv(2, mod);
while (t--)
{
cin >> n >> m;
cout << ((n - m) * ni) % mod << endl;
}
return 0;
}
L Alice and Bob
题目大意
Alice和Bob玩游戏,有m个数字,数字都在0-n之间,游戏规则如下:
Alice可以把数字任意分成两堆,Bob可以把这两堆数字删除一堆,并且另一堆数字都减一。
如果有0出现,Alice赢,否则Bob赢。
题解
Alice的操作,对于一个数字i,有ai个,每次将i平分到两堆数字中,Bob删掉其中一堆,另一堆的每个i都会减一。若到i变为0后,ai仍然不为零,即Alice赢;否则Bob赢。
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
int n, t;
int a[maxn];
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--)
a[i - 1] += a[i] / 2;
if (a[0])
cout << "Alice" << endl;
else
cout << "Bob" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C Backpack
题目大意
Alice有一个容量为m的背包。
现在有n件物品,每一个物品有体积vi和价值wi。
问这n件物品是否可以把背包装满,如果可以,输出装入背包的物品的价值的最大异或和,否则输出-1。
题解
因为wi小于210(1024),所以wi的异或和不可能超过1024;且m小于210,所以只需要存储容量不超过m的情况下的结果即可。因此可以定义两个bitset<1050>数组f和g来实现,其中f表示当前的情况,g暂时存储对f数组值的操作。
f[i]数组存储价值异或和为i的容积情况,即假如f[2]等于10010,表示价值异或和为2时,容积可以为1和4;f[0]等于00001,表示价值异或和为0时,容积为0。
初始化f[0] [0] = 1,表示一个物品都未添加时,价值的异或和为0,容积为0。
当添加商品i时,g[i]存储的是价值异或和为i^wi,容积添加vi以后的容积。此时f[i]等于以前的异或和为i的情况|(或)上现在的异或和为i的情况。
g[i]的i此时实际是i异或w,f[i]所要找的为,w异或x=i的g[x],x=i异或w(a异或b等于c,则a异或c等于b)。
最后判断所有的f[i],若其第m位为1,说明有该种结果,否则没有。
表达可能比较混乱。
小tip(提交语言使用G++)
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
const int Size = 1024;
int n, m, t, v, w, res;
bitset<1050> f[1050], g[1050];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
f[i].reset();
}
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &v, &w);
for (int j = 0; j < Size; j++)
{
g[j] = f[j];
g[j] <<= v;
}
for (int j = 0; j < Size; j++)
{
f[j] |= g[j ^ w];
}
}
res = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
if (f[i][m])
res = i;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
B Dragon slayer
题目大意
英雄需要到龙所在的地方拯救公主。已知地图的左下角是(0,0),右上角是(n,m),英雄坐标(xs+0.5,ys+0.5),龙坐标(xt+0.5,yt+0.5),英雄可以向任意方向走。在地图中有一些水平或垂直的墙,英雄不能穿过这些墙(包括边界),但是英雄可以击破这些墙。问英雄到达龙的位置需要击破的最少的墙。
题解
参考了大佬的题解。
因为墙的数量最大为15,可以使用状态压缩,枚举所有情况。
英雄和龙的坐标(+0.5,+0.5)意思是他们在方格正中间。因为墙只有水平和垂直的,所以可以只看英雄是否可以到他的邻近的上下左右四个格子即可。如下图。
该图为判断左边的黑点是否可以到达右边的黑点,只需要判断两点之间是否有墙(即图中黑色的线)。可以将两个点都向左下移动(图中绿色的点),然后将左边的点按紫色的线移动到新的位置,此时只需判断是否有墙的坐标满足以下条件,wall[i].y <= y1(靠下的绿点) && wall[i].yy >= y2(靠上的绿点)。
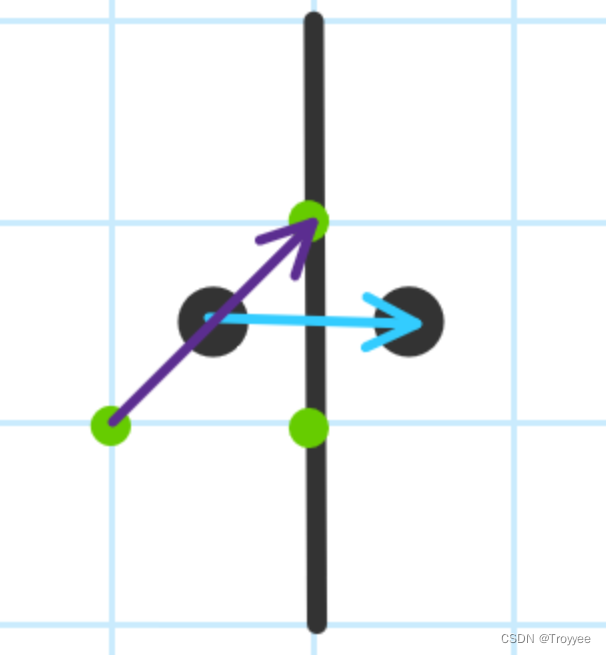
其余方向可以类似变化。
向上移动
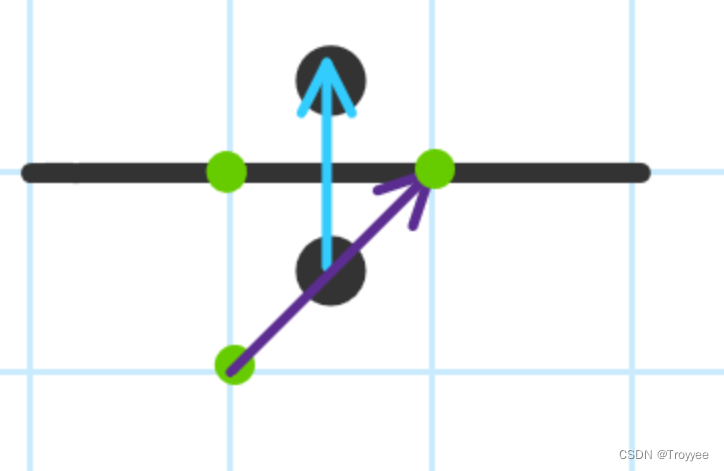
向左移动
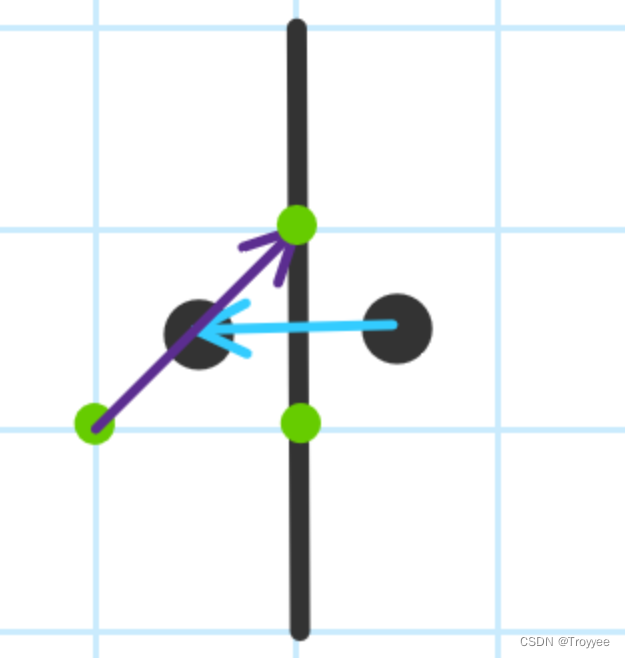
向下移动
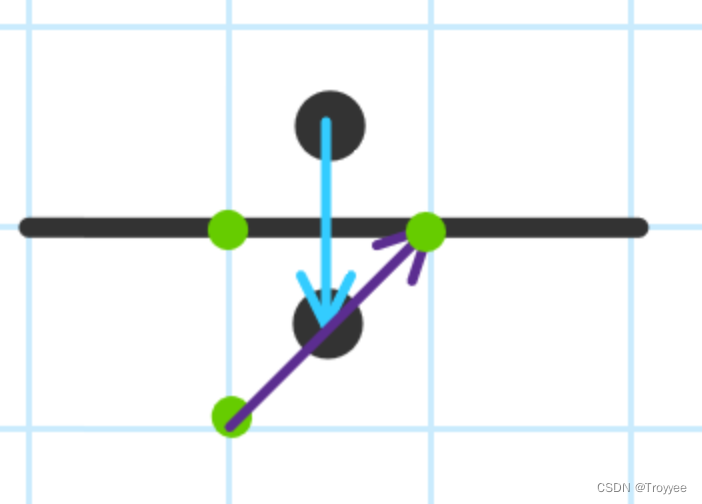
总之就是,要把两绿点中不在“墙”上的一点移动到“墙”上,以判断是否有墙满足条件,若有,则说明英雄在该点无法向此方向移动。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
int n, m, k, sx, sy, tx, ty, t, res;
bool vis1[20], vis2[20][20];
int dx[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
struct Wall
{
int x, y, xx, yy;
} wall[20];
int getnum(int state)
{
memset(vis1, 0, sizeof vis1);
int ans = 0, in = 1;
while (state)
{
if (state & 1)
{
ans++;
vis1[in] = 1;
}
in++;
state >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
bool checkWall(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
if (vis1[i])
continue;
if (x1 == x2 && wall[i].x == wall[i].xx && x1 == wall[i].x && wall[i].y <= y1 && wall[i].yy >= y2)
return 0;
if (y1 == y2 && wall[i].y == wall[i].yy && y1 == wall[i].y && wall[i].x <= x1 && wall[i].xx >= x2)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
bool bfs()
{
memset(vis2, 0, sizeof vis2);
queue<P> q;
q.push(make_pair(sx, sy));
vis2[sx][sy] = 1;
while (q.size())
{
P now = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = now.first + dx[i], ny = now.second + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx == n || ny < 0 || ny == m || vis2[nx][ny])
continue;
if ((i == 0 || i == 2) && checkWall(nx, ny, now.first + 1, now.second + 1))
{
if (nx == tx && ny == ty)
return 1;
vis2[nx][ny] = 1;
q.push(make_pair(nx, ny));
}
if ((i == 1 || i == 3) && checkWall(now.first, now.second, nx + 1, ny + 1))
{
if (nx == tx && ny == ty)
return 1;
vis2[nx][ny] = 1;
q.push(make_pair(nx, ny));
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k, &sx, &sy, &tx, &ty);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &wall[i].x, &wall[i].y, &wall[i].xx, &wall[i].yy);
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << k); i++)
{
int cnt = getnum(i);
if (cnt >= res)
continue;
if (bfs())
res = cnt;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
I Laser
题目大意
一个二维平面,一共有n个敌人,第i个敌人的位置是(xi,yi)。现在有一个激光武器,你可以把它放在任意(x,y)(x, y 是实数)上,对于任何实数 k,坐标为 (x+k, y),(x,y+k),(x+k,y+k),(x+k,y−k)的敌人将被消灭,即“米”字。问是否有可能消灭所有敌人。
题解
先选取两个不在同一条线(指横竖斜)的点,对每一个点作四条直线,交出十二个点,只需判断这十二个点是否至少有一个满足条件,因为答案肯定出现在这十二个点中(因为肯定需要满足扫到这两个“不共线”的点)。
这十二个点需要一个个去判断是否能消灭其他点。
具体步骤:以第一个点为一个基点遍历其他点,若没找到“不共线”的点,则说明在第一个点放置武器即可,否则,以找到的第一个“不共线”的点为第二个基点,进行上述过程。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 5e5 + 5;
int t, n;
int x[maxn], y[maxn];
int tx, ty;
bool flag;
bool check(int x, int y)
{
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x == y || x + y == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &x[i], &y[i]);
flag = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!check(x[1] - x[i], y[1] - y[i]))
{
flag = 0;
tx = x[i], ty = y[i];
break;
}
}
if (flag)
printf("YES\n");
else
{
vector<pair<int, int>> v;
v.emplace_back(x[1], ty + tx - x[1]);
v.emplace_back(x[1], ty);
v.emplace_back(x[1], x[1] - tx + ty);
v.emplace_back(tx - ty + y[1], y[1]);
v.emplace_back(tx, y[1]);
v.emplace_back(tx + ty - y[1], y[1]);
v.emplace_back(tx, tx - x[1] + y[1]);
v.emplace_back(x[1] + ty - y[1], ty);
v.emplace_back(x[1] - ty + y[1], ty);
v.emplace_back(tx, y[1] - tx + x[1]);
v.emplace_back((tx + x[1] + ty - y[1]) / 2, (tx - x[1] + y[1] + ty) / 2);
v.emplace_back((x[1] - ty + y[1] + tx) / 2, (ty + y[1] - tx + x[1]) / 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
flag = 1;
int dx = v[i].first, dy = v[i].second;
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++)
{
if (!check(dx - x[j], dy - y[j]))
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
if (flag)
break;
}
if (flag)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
D Ball
题目大意
在一个M*M的棋盘上有N个点,如果某三个点之间的距离的中位数是质数则算满足条件,问有几对满足条件。
题解
首先需要判断出一个数是不是质数,可以使用埃氏筛预处理。
然后考虑枚举一下三个点,可以分别计算距离并进行判断,但这样子时间复杂度太高,所以考虑枚举两个点,即算出所有的边。
最后是确定第三个点,要求其中一条边小于等于这条边,另一条边大于等于这条边,即这条边就是中间的边。
具体实现:将所有的边从小到大排序,然后从前往后遍历,如果该边的长度为质数,则根据bitset数组s计算结果,然后标记一些数据;否则,只标记数据。
bitset数组s存储信息:因为从小到大遍历边,所以s[i] [j]为1表示从i点到j点有一条边,该边小于等于当前循环的边(之前的循环标记的),s[i] [j]为0表示从i点到j点有一条边,该边大于等于当前循环的边(之前的循环未标记)。
s[edge[i].a] ^ s[edge[i].b],对于每一位有四种情况。00,说明a到c和b到c的边都大于该边(如果等于,会在后面计算,不会遗漏,后面同),不满足,为0;01和10,说明a到c和b到c的边一个大于该边,一个小于该边,满足,为1;11,说明a到c和b到c的边都小于该边,不满足,为0。所以计算s[edge[i].a] ^ s[edge[i].b]中1的个数即可。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e3 + 5;
const int maxm = 2e5 + 5;
int n, m, t, cnt;
long long res;
bool isnp[maxm];
bitset<maxn> s[maxn];
struct Point
{
int x, y;
} point[maxn];
struct Edge
{
int dis, a, b;
Edge(int dis = 0, int a = 0, int b = 0) : dis(dis), a(a), b(b) {}
bool operator<(const Edge &a) const
{
return dis < a.dis;
}
} edge[maxn * maxn];
void init(int n)
{
isnp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++)
{
if (!isnp[i])
{
for (int j = i * i; j <= n; j += i)
isnp[j] = 1;
}
}
}
int main()
{
init(200000);
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
cnt = res = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
s[i].reset();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &point[i].x, &point[i].y);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
edge[++cnt] = Edge(abs(point[i].x - point[j].x) + abs(point[i].y - point[j].y), i, j);
}
}
sort(edge + 1, edge + cnt + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++)
{
if (!isnp[edge[i].dis])
{
res += (s[edge[i].a] ^ s[edge[i].b]).count();
}
s[edge[i].a][edge[i].b] = 1;
s[edge[i].b][edge[i].a] = 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
若有理解不对的地方,多多包含。




 本文介绍了几个算法设计问题,包括基于概率的删除操作求期望、数字分堆游戏、背包问题、最短路径优化和激光武器路径规划。通过深入分析题意和巧妙的数学建模,给出了高效的解决方案,涉及到了概率计算、动态规划和图论等算法思想。
本文介绍了几个算法设计问题,包括基于概率的删除操作求期望、数字分堆游戏、背包问题、最短路径优化和激光武器路径规划。通过深入分析题意和巧妙的数学建模,给出了高效的解决方案,涉及到了概率计算、动态规划和图论等算法思想。
















 243
243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








