1/Max()函数不能出现在where子句中
2/select…from…where…group by having…order by…
3/left join…允许为空的放在left join前面
4/字符串用单引号’’
5/MySQL四舍五入Floor
6/保留3位小数位数round(,3)
7/select子句中不能出现group by子句中未出现的列名
8/limit 从0开始
9/MySQL 比较两个Date,DATEDIFF(大,小)=1
1.表table1(usr_id int,usr_dt string),其中id字段数值相同,找出表中连续活跃的天数,如果不连续,则当前行连续活跃字段设为1,返回查询结果table2(窗口函数)
select uid,active_dt,c1
,count() over(partition by uid,c1 order by active_dt rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as rs1
from(
select a.uid,a.active_dt
,a.rank
,date_sub(a.active_dt,a.rank) as c1
from(
select uid
,from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(active_dt,'yyyyMMdd'),'yyyy-MM-dd') as active_dt
,row_number() over(partition by uid order by active_dt) as rank
from log_test
)a
)x;
需求:对用户的订单进行分析,将不同订单类型分别多少单展示出来,每个用户一行
原数据:
| user | order_type | order_number |
|---|---|---|
| user1 | delivered | 10 |
| user2 | returned | 1 |
| user1 | returned | 3 |
| user2 | delivered | 20 |
目标:
| user | order |
|---|---|
| user1 | delivered(10),returned(3) |
| user2 | delivered(20),returned(1) |
1.使用concat()函数将order_type和order_number连接起来
concat(order_type,'(',order_number,')')
| user | order |
|---|---|
| user1 | delivered(10) |
| user2 | returned(1) |
| user1 | returned(3) |
| user2 | delivered(20) |
2.使用concat_ws()和collect_set()进行合并行
将上面列表中一个user可能会占用多行转换为每个user占一行的目标表格式,实际是“列转行”
select user,concat_ws(',',collect_set(concat
(order_type,'(',order_number,')'))) order from table group by user
collect_set的作用:
(1)去重,对group by后面的user进行去重
(2)对group by以后属于同一user的形成一个集合,结合concat_ws对集合中元素使用,进行分隔形成字符串
假设有一个网站, 每次登陆的时候都会记录改用户的登陆信息,字段设计如下:
client_id user_name, login_ts
题目: 请帮忙统计最近10天登陆最频繁的10个用户,排序并打印出这10个用户各登陆多少次
select * , row_number() over(
partition by client_id order by freq)as rank where rank<=10 from (
select client_id,user_name,count(*) as freq from tab group by client_id where login_ts<=10);
学生选课,找出至少选了语文,数学,英语这三门课的学生。如果上面的SQL选课系统上亿时,怎么做(把十个科目变成十个字段,0和1这种代表选课没选课,类似于Kylin思想)
大学考试成绩如下表A:id,subject,score
找出每一科都是这一科前30%的学生的id
select table.id from(
select id,row_number() over(partition by subject order by score desc) as rank where rank<=10)
table group by table.id having count(*)=学科数目
同比环比
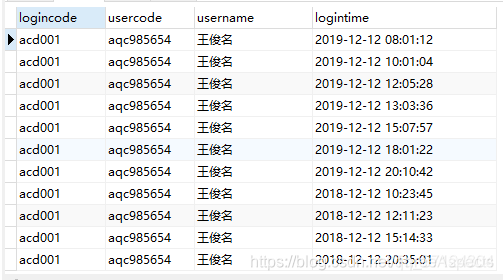
-- 同比操作
SELECT
t.username,
t.logincountnow,
t2.logincountlastyear,
( t.logincountnow / t2.logincountlastyear ) - 1 AS rat -- 这个列就是你要的同比增长值
FROM
-- 主数据
( SELECT t.username, count( 0 ) logincountnow FROM logintime t WHERE date(logintime)= '2019-12-12' GROUP BY t.username ) t
LEFT JOIN
-- 对比数据
( SELECT t.username, count( 0 ) logincountlastyear FROM logintime t WHERE date(logintime)= '2018-12-12' GROUP BY t.username ) t2
ON t.username = t2.username;
-- 环比操作
SELECT
t.username,
t.logincountnow,
t2.logincountlastyear,
( t.logincountnow / t2.logincountlastyear ) - 1 AS rat -- 这个列就是你要的环比增长值
FROM
-- 主数据
( SELECT t.username, count( 0 ) logincountnow FROM logintime t WHERE year(logintime)= '2019' GROUP BY t.username ) t
LEFT JOIN
-- 对比数据
( SELECT t.username, count( 0 ) logincountlastyear FROM logintime t WHERE year(logintime)= '2018' GROUP BY t.username ) t2
ON t.username = t2.username;
select date,gmv,(gmv-gmv_1)/gmv_1,(gmv-gmv_7)/gmv_7
from
(select date,gmv,
lead(gmv,1) over(order by date desc) as gmv_1,
lead(gmv,7) over(order by date desc) as gmv_7 from tablename) a
SQL> select id,name,lead(name,1,0) over ( order by id ) from kkk;
ID NAME LEAD(NAME,1,0)OVER(ORDERBYID)
---------- -------------------- -----------------------------
1 1name 2name
2 2name 3name
3 3name 4name
4 4name 5name
5 5name 0
lag ,lead 分别是向前,向后;
lag 和lead 有三个参数,第一个参数是列名,第二个参数是偏移的offset,第三个参数是 超出记录窗口时的默认值)
用户签到表【t_user_attendence】,包含三个字段:日期【fdate】,用户id【fuser_id】,用户当天是否签到【fis_sign_in:0否1是】;问题:请计算截至当前每个用户已经连续签到的天数(输出表仅包含当天签到的所有用户,计算连续签到天数)
输出表【t_user_consecutive_days】:用户id【fuser_id】,用户联系签到天数【fconsecutive_days】
答:直接求出用户最新的未签到日期,用今天的日期减掉即可
select fdate+1-absent as days from (
select fuser_id,max(fdate) as absent from f_user_attendence where fis_sign_in=0 group by fuser_id
) group by fuser_id
选出买了a也买了b但没有买c的用户
SELECT CustomerID
FROM #Purchase
WHERE ProductCode IN ('A','B')
GROUP BY CustomerID
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT ProductCode) = 2
EXCEPT
SELECT CustomerID
FROM #Purchase
WHERE ProductCode IN ('C')
;
数据库中有如下三个表:
学生表(学号id,姓名name,性别sex,系部depart,年龄age)8个学生记录
选课表(学号id,课程号cid,成绩grade) 12门课程
课程表(课程号cid,课程名cname,学分Ccredit) 6门课程
查找同时选修了C01及C02两门课程的学生姓名及学号
https://www.imooc.com/wenda/detail/410795
select C.姓名,C.学号 from 学生表 as C where C.学号 in (
select A.学号 from 选课表 as A join 课程表 as B on A.课程号=B.课程号where B.课程名 in ('C01','C02')
group by A.学号 having count(A.学号>=2)
给定一个表,有学期,学号,课程号,成绩,求连续两个学期都选了数学的学生
给一个简单日志表,包含userid ,activateddate,每个用户每天最多只有一条数据,输出连续7天登陆快手的userid
select userid
from
(
select userid, groupday, count(*)as days
from
(
select
userid, activateddate- row_number() over (partition by userid order by activateddate)as groupday
from mytable
)
groupby userid, groupday
)
groupby userid
--having max(days)>=7
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/73283606
查询7天连续登陆用户
具体思路:
1、因为每天用户登录次数可能不止一次,所以需要先将用户每天的登录日期去重
2、再用row_number() over(partition by _ order by _)函数将用户id分组,按照登陆时间进行排序
3、计算登录日期减去第二步骤得到的结果值,用户连续登陆情况下,每次相减的结果都相同
4、按照id和日期分组并求和,筛选大于等于7的即为连续7天登陆的用户
select id,count(*) from (
select *,date(日期)-cum as 结果 from (
select *,row_number() over(PARTITION by id order by 日期) as cum from (
select DISTINCT date(date) as 日期,id from orde //第一步:用户登录日期去重
)a//第二步:用row_number() over()函数计数
)b//第三步:日期减去计数值得到结果
)c GROUP BY id,结果 having count(*)>=7;//第四步:根据id和结果分组并计算总和,大于等于7的即为连续登陆7天的用户
https://www.cnblogs.com/ikww/p/12012831.html
求用户当天登陆是登陆的第几次。求用户当天登陆是连续登陆的第几次。
员工表,求截止当天连续打卡天数
第一天登录的,第二天也登陆的
某天在线的用户在第7天后那天也在线的用户,意思是:
user date
AA 2020-9-11
BB 2020-9-11
DD 2020-9-11 查询出 AA
BB 2020-9-15
AA 2020-9-18
SELECT id FROM table
WHERE date IN (2020-1-2,2020-1-3) GROUP BY id
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT date) = 2;
行转列/列转行
行转列
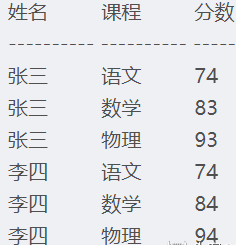
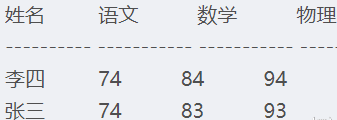
方法一
select 姓名,
max(case 课程 when '语文' then 分数 else 0 end)语文,
max(case 课程 when '数学'then 分数 else 0 end)数学,
max(case 课程 when '物理'then 分数 else 0 end)物理
from tb
group by 姓名
方法二PIVOT用于将列值旋转为列名(即行转列)PIVOT的一般语法是:PIVOT(聚合函数(列) FOR 列 in (…) )AS P
select * from tb pivot(max(分数) for 课程 in (语文,数学,物理))
列转行
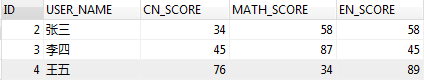
select user_name, '语文' COURSE , CN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union select user_name, '数学' COURSE, MATH_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union select user_name, '英语' COURSE, EN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
order by user_name,COURSE;
select AVG(DISTINCT income)
from (
select T1.income from graduates T1,graduates T2
group by T1.income
having sum(case when T2.income >= T1.income then 1 else 0 end) >= count(*)/2
and sum(case when T2.income <= T1.income then 1 else 0 end) >= count(*)/2
) tmp;
员工部门表(注:可以增加表,解决如下问题)
CREATE TABLE emp_dept
(
dept_no STRING COMMENT ‘部门编号’,
dept_name STRING COMMENT ‘部门名称’,
super_work_no STRING COMMENT ‘部门主管’,
super_dept_no STRING COMMENT ‘上级部门编号’,
super_dept_name STRING COMMENT ‘上级部门名称’,
dept_type STRING COMMENT ‘部门类型:root/dept ,root 表示根节点’
)
1.计算负责部门总数最多的10个主管及负责部门数。
2.根据一个部门编号,查询出所有下级部门。
3.计算主管负责顶点部门数(比如:张三负责部门A,B,C;其中A的上级部门B,那么张三管理的顶点是:B、C)。
Sql 取A、B两个表的交集,A表减交集,B表减交集
假设id是主键:
AB两表的交集
select * from A a where exists (select * from B b where b.id=a.id)
A表减交集
select * from A a where not exists (select * from B b where b.id=a.id)
B表减交集
select * from B b where not exists (select * from A a where b.id=a.id)
【1】film表
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| film_id | 电影id |
| title | 电影名称 |
| description | 电影描述信息 |
category表
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| category_id | 电影分类id |
| name | 电影分类名称 |
| last_update | 电影分类最后更新时间 |
film_category表
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| film_id | 电影id |
| category_id | 电影分类id |
| last_update | 电影id和分类id对应关系的最后更新时间 |
查找描述信息中包括robot的电影对应的分类名称以及电影数目,而且还需要该分类对应电影数量>=5部
说明:cc是一个虚表,因为虚表cc是按category_id进行了分组,这意味着每个category_id分类下只返回一条数据,所以无法替代film_category表来做为连接表
select c.name,count(c.name) from
(select category_id,count(film_id) as s from film_category group by category_id having s>=5) as cc,
category c,film f,film_category fc where
f.film_id=fc.film_id and c.category_id=fc.category_id and c.category_id=cc.category_id and
f.description like '%robot%';
【2】对于employees表中,给出奇数行的first_name
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
birth_date date NOT NULL,
first_name varchar(14) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(16) NOT NULL,
gender char(1) NOT NULL,
hire_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
SELECT e1.first_name FROM
(SELECT e2.first_name,
(SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees AS e3
WHERE e3.first_name <= e2.first_name)
AS rowid FROM employees AS e2) AS e1
WHERE e1.rowid % 2 = 1
【3】获取有奖金的员工相关信息。
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
birth_date date NOT NULL,
first_name varchar(14) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(16) NOT NULL,
gender char(1) NOT NULL,
hire_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLE dept_emp (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
dept_no char(4) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
create table emp_bonus(
emp_no int not null,
recevied datetime not null,
btype smallint not null);
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
给出emp_no、first_name、last_name、奖金类型btype、对应的当前薪水情况salary以及奖金金额bonus。 bonus类型btype为1其奖金为薪水salary的10%,btype为2其奖金为薪水的20%,其他类型均为薪水的30%。 当前薪水表示to_date=‘9999-01-01’
select e.emp_no,e.first_name,e.last_name,eb.btype,s.salary,
(case eb.btype
when 1 then s.salary*0.1
when 2 then s.salary*0.2
else s.salary*0.3 end)as bonus
from salaries s,emp_bonus eb,employees e
where s.to_date='9999-01-01' and s.emp_no=e.emp_no and s.emp_no=eb.emp_no;
【4】给出每个员工每年薪水涨幅超过5000的员工编号emp_no、薪水变更开始日期from_date以及薪水涨幅值salary_growth,并按照salary_growth逆序排列。
提示:在sqlite中获取datetime时间对应的年份函数为strftime(’%Y’, to_date)
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
select s1.emp_no,s1.from_date,(s1.salary-s2.salary) as salary_growth
from salaries s1,salaries s2 where s1.emp_no=s2.emp_no
and (strftime('%Y',s1.to_date)-strftime('%Y',s2.to_date)=1)
and (s1.salary-s2.salary)>5000
order by salary_growth desc;
【5】查找当前薪水(to_date=‘9999-01-01’)排名第二多的员工编号emp_no、薪水salary、last_name以及first_name,不准使用order by
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
birth_date date NOT NULL,
first_name varchar(14) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(16) NOT NULL,
gender char(1) NOT NULL,
hire_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
select e.emp_no,max(s.salary)as salary,e.last_name,e.first_name from employees e,salaries s
where e.emp_no=s.emp_no and s.to_date='9999-01-01' and
s.salary<(select max(salary) from salaries where to_date='9999-01-01');
【6】对所有员工的当前(to_date=‘9999-01-01’)薪水按照salary进行按照1-N的排名,相同salary并列且按照emp_no升序排列
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
select s1.emp_no,s1.salary,
(select count(distinct salary) from salaries where salary>=s1.salary and to_date='9999-01-01')as rank
from salaries s1 where s1.to_date='9999-01-01'
order by rank,s1.emp_no;
【7】获取当前(to_date=‘9999-01-01’)薪水第二多的员工的emp_no以及其对应的薪水salary
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
提示:
limit i,n
i:为查询结果的索引值(默认从0开始),当i=0时可省略i
n:为查询结果返回的数量
select emp_no,salary from salaries
where salary=
(select distinct salary from salaries order by salary desc limit 1,1);
【8】查找薪水涨幅超过15次的员工号emp_no以及其对应的涨幅次数t
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
select a.emp_no,count(*) t from salaries a inner join salaries b
on a.emp_no=b.emp_no and a.to_date = b.from_date
where a.salary < b.salary
group by a.emp_no
having t>15;
【9】查找入职员工时间排名倒数第三的员工所有信息
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
birth_date date NOT NULL,
first_name varchar(14) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(16) NOT NULL,
gender char(1) NOT NULL,
hire_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
提示:
LIMIT m,n : 表示从第m+1条开始,取n条数据;
LIMIT n : 表示从第0条开始,取n条数据,是limit(0,n)的缩写。
(1)首先需要加distinct去重。
假设 5-23(入职最晚日期)入职的有a,b,c 3人;5-22(入职第二晚日期)入职的有d,e 2人;5-21(入职倒数第三晚)入职的有f,g,h 3人;5-21前入职的若干…若不加distinct去重,那么按照日期倒序,limit 2,1(从倒数第2行开始,取一条数据)的查询结果为 5-23;加了distinct去重,会按入职日期进行分组,多个相同入职日期会分为一组,这样limit 2,1的结果即为 5-21。
(2)外层的where条件中根据子查询查出的倒数第三晚入职的日期,就能查询出符合条件的员工信息。
select * from employees
where hire_date = (
select distinct hire_date from employees order by hire_date desc limit 2,1
);
【10】按照salary的累计和running_total,其中running_total为前两个员工的salary累计和,其他以此类推。 具体结果如下Demo展示。。
CREATE TABLE salaries ( emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
salary int(11) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
select s1.emp_no,s1.salary,sum(s2.salary)as running_total from salaries s2,salaries s1
where s2.emp_no<=s1.emp_no and s2.to_date='9999-01-01' and s1.to_date='9999-01-01'
group by s1.emp_no;
SELECT s1.emp_no, s1.salary,
(SELECT SUM(s2.salary) FROM salaries AS s2
WHERE s2.emp_no <= s1.emp_no AND s2.to_date = '9999-01-01') AS running_total
FROM salaries AS s1 WHERE s1.to_date = '9999-01-01' ORDER BY s1.emp_no;
【11】编写一个 SQL 查询来重新格式化表,使得新的表中有一个部门 id 列和一些对应 每个月 的收入(revenue)列。查询结果格式如下面的示例所示:
Department 表:
| id | revenue | month |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8000 | Jan |
| 2 | 9000 | Jan |
| 3 | 10000 | Feb |
| 1 | 7000 | Feb |
| 1 | 6000 | Mar |
查询得到的结果表:
| id | Jan_Revenue | Feb_Revenue | Mar_Revenue | … | Dec_Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8000 | 7000 | 6000 | … | null |
| 2 | 9000 | null | null | … | null |
| 3 | null | 10000 | null | … | null |
思路:行转列问题
通过使用GROUP BY ,sql引擎为GROUP BY子句中的每个元素创建一组结果行,并且仅允许针对多个值(例如SUM,AVG,MIN,MAX,COUNT)进行聚合操作。由于我们的集合包含一个元素,因此我们无法直接从GROUP BY中提取该元素,因此我们使用了一种技巧-单个元素的聚合函数。一个元素的聚合函数=此元素。
select
id
, sum(case `month` when 'Jan' then revenue else null end) as Jan_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Feb' then revenue else null end) as Feb_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Mar' then revenue else null end) as Mar_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Apr' then revenue else null end) as Apr_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'May' then revenue else null end) as May_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Jun' then revenue else null end) as Jun_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Jul' then revenue else null end) as Jul_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Aug' then revenue else null end) as Aug_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Sep' then revenue else null end) as Sep_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Oct' then revenue else null end) as Oct_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Nov' then revenue else null end) as Nov_Revenue
, sum(case `month` when 'Dec' then revenue else null end) as Dec_Revenue
from Department group by id
【12】给定一个 Weather 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,来查找与之前(昨天的)日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 Id。
提示:MySQL 使用 DATEDIFF 来比较两个日期类型的值。
select w2.Id from Weather w1,Weather w2 where w2.Temperature>w1.Temperature and DATEDIFF(w2.RecordDate, w1.RecordDate)=1;
【13】编写一个 SQL 查询,来删除 Person 表中所有重复的电子邮箱,重复的邮箱里只保留 Id 最小 的那个。Id 是这个表的主键。
| Id | |
|---|---|
| 1 | john@example.com |
| 2 | bob@example.com |
| 3 | john@example.com |
delete p1 from Person p1,Person p2 where p1.Email=p2.Email and p1.Id>p2.Id;
DELETE FROM Person
WHERE Id NOT IN ( -- 删除不在查询结果中的值
SELECT id FROM
(
SELECT MIN(Id) AS Id -- 排除Email相同时中Id较大的行
FROM Person
GROUP BY Email
) AS temp -- 此处需使用临时表,否则会发生报错
)
【14】编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第二高的薪水(Salary) 。
| Id | Salary |
|---|---|
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
例如上述 Employee 表,SQL查询应该返回 200 作为第二高的薪水。如果不存在第二高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
提示:select distinct salary from Employee order by salary desc limit 1,1 就可以,但是输不出null,所以外面再加一层 select (select distinct salary from Employee order by salary desc limit 1,1) as SecondHighestSalary ;
select (select distinct Salary from Employee order by Salary desc limit 1,1)as SecondHighestSalary;
【15】小美是一所中学的信息科技老师,她有一张 seat 座位表,平时用来储存学生名字和与他们相对应的座位 id。其中纵列的 id 是连续递增的,小美想改变相邻俩学生的座位。你能不能帮她写一个 SQL query 来输出小美想要的结果呢?
示例:
| id | student |
|---|---|
| 1 | Abbot |
| 2 | Doris |
| 3 | Emerson |
| 4 | Green |
| 5 | Jeames |
假如数据输入的是上表,则输出结果如下:
| id | student |
|---|---|
| 1 | Doris |
| 2 | Abbot |
| 3 | Green |
| 4 | Emerson |
| 5 | Jeames |
注意:如果学生人数是奇数,则不需要改变最后一个同学的座位。
SELECT (CASE
WHEN MOD(id,2) = 1 AND id = (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM seat) THEN id
WHEN MOD(id,2) = 1 THEN id+1
ElSE id-1
END) AS id, student
FROM seat
ORDER BY id;
【16】Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的 Id, salary 和 department Id。
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
| Id | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门工资最高的员工。例如,根据上述给定的表格,Max 在 IT 部门有最高工资,Henry 在 Sales 部门有最高工资。
select d.Name as Department,e.Name as Employee,e.Salary as Salary
from Employee e,Department d where e.DepartmentId=d.Id
and (e.Salary,e.DepartmentId) in (select max(Salary),DepartmentId from Employee group by DepartmentId);
【17】编写一个 SQL 查询,查找所有至少连续出现三次的数字。
| Id | Num |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 |
思路1:需要添加关键字 DISTINCT ,因为如果一个数字连续出现超过 3 次,会返回重复元素。
思路2:用2个变量统计。pre变量统计上一次Num,cnt统计连续次数。
SELECT DISTINCT
l1.Num AS ConsecutiveNums
FROM
Logs l1,
Logs l2,
Logs l3
WHERE
l1.Id = l2.Id - 1
AND l2.Id = l3.Id - 1
AND l1.Num = l2.Num
AND l2.Num = l3.Num
_______________________________________________
SELECT DISTINCT a.Num ConsecutiveNums FROM (
SELECT t.Num ,
@cnt:=IF(@pre=t.Num, @cnt+1, 1) cnt,
@pre:=t.Num pre
FROM Logs t, (SELECT @pre:=null, @cnt:=0) b) a
WHERE a.cnt >= 3
【18】编写一个 SQL 查询来实现分数排名。如果两个分数相同,则两个分数排名(Rank)相同。请注意,平分后的下一个名次应该是下一个连续的整数值。换句话说,名次之间不应该有“间隔”。
| Id | Score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.50 |
| 2 | 3.65 |
| 3 | 4.00 |
| 4 | 3.85 |
| 5 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 3.65 |
例如,根据上述给定的 Scores 表,你的查询应该返回(按分数从高到低排列):
| Score | Rank |
|---|---|
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 3.85 | 2 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.50 | 4 |
select s1.Score,count(distinct s2.Score) as Rank
from Scores s1,Scores s2
where s2.Score>=s1.Score
group by s1.Id
order by Rank;
___________________________________
//由于有子查询的存在,执行效率很糟糕
select s1.Score,
(select count(distinct Score) from Scores where Score>=s1.Score)as Rank
from Scores s1 order by Rank;
除了以上的思路外,还可以用窗口函数来解决
select *,
rank() over (order by 成绩 desc) as ranking,
dense_rank() over (order by 成绩 desc) as dese_rank,
row_number() over (order by 成绩 desc) as row_num
from 班级
- rank函数:如果有并列名次的行,会占用下一名次的位置。比如正常排名是1,2,3,4,但是现在前3名是并列的名次,结果是:1,1,1,4
- dense_rank函数:如果有并列名次的行,不占用下一名次的位置。比如正常排名是1,2,3,4,但是现在前3名是并列的名次,结果是:1,1,1,2
- row_number函数:不考虑并列名次的情况。比如前3名是并列的名次,排名是正常的1,2,3,4
【19】编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第 n 高的薪水(Salary)。
| Id | Salary |
|---|---|
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
例如上述 Employee 表,n = 2 时,应返回第二高的薪水 200。如果不存在第 n 高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(N INT) RETURNS INT
BEGIN
SET N = N - 1;
RETURN (
SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT N, 1
);
END
【20】X 市建了一个新的体育馆,每日人流量信息被记录在这三列信息中:序号 (id)、日期 (visit_date)、 人流量 (people)。请编写一个查询语句,找出人流量的高峰期。高峰期时,至少连续三行记录中的人流量不少于100。提示:每天只有一行记录,日期随着 id 的增加而增加。
例如,表 stadium:
| id | visit_date | people |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2017-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2017-01-02 | 109 |
| 3 | 2017-01-03 | 150 |
| 4 | 2017-01-04 | 99 |
| 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
| 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
| 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
| 8 | 2017-01-08 | 188 |
对于上面的示例数据,输出为:
| id | visit_date | people |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
| 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
| 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
| 8 | 2017-01-08 | 188 |
//最直观的方法
select distinct a.* from stadium a,stadium b,stadium c
where a.people>=100 and b.people>=100 and c.people>=100
and (
(a.id = b.id-1 and b.id = c.id -1) or
(a.id = b.id-1 and a.id = c.id +1) or
(a.id = b.id+1 and b.id = c.id +1)
) order by a.id
//自定义3个变量
select p.id,
p.visit_date,
p.people
from(
select id,
visit_date,
people,
@i1 := @i2 as p1,
@i2 := id as p2,
case when @i1 = @i2 -1 then @count := @count + 1
else @count := 1 end as cnt
from stadium,(select @i1 := null,@i2 := null,@count := null) c
where people >=100
) t
join stadium p
on (t.cnt >=3 and t.id = p.id) or (t.cnt = 3 and p.id in(t.id - 1,t.id - 2))
//Oracle的窗口函数
SELECT a.id, to_char(a.visit_date, 'yyyy-MM-dd') AS visit_date, a.people
FROM (
SELECT id, visit_date, people, COUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY a.id - a.rk ) AS allCount
FROM (
SELECT id, visit_date, people, rownum AS rk
FROM stadium
WHERE people >= 100
) a
) a
WHERE a.allCount >= 3
ORDER BY a.id
【21】Trips 表中存所有出租车的行程信息。每段行程有唯一键 Id,Client_Id 和 Driver_Id 是 Users 表中 Users_Id 的外键。Status 是枚举类型,枚举成员为 (‘completed’, ‘cancelled_by_driver’, ‘cancelled_by_client’)。
| Id | Client_Id | Driver_Id | City_Id | Status | Request_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed | 2013-10-01 |
| 2 | 2 | 11 | 1 | cancelled_by_driver | 2013-10-01 |
| 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-01 |
| 4 | 4 | 13 | 6 | cancelled_by_client | 2013-10-01 |
| 5 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 6 | 2 | 11 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 7 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 8 | 2 | 12 | 12 | completed | 2013-10-03 |
| 9 | 3 | 10 | 12 | completed | 2013-10-03 |
| 10 | 4 | 13 | 12 | cancelled_by_driver | 2013-10-03 |
Users 表存所有用户。每个用户有唯一键 Users_Id。Banned 表示这个用户是否被禁止,Role 则是一个表示(‘client’, ‘driver’, ‘partner’)的枚举类型。
| Users_Id | Banned | Role |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | client |
| 2 | Yes | client |
| 3 | No | client |
| 4 | No | client |
| 10 | No | driver |
| 11 | No | driver |
| 12 | No | driver |
| 13 | No | driver |
写一段 SQL 语句查出 2013年10月1日 至 2013年10月3日 期间非禁止用户的取消率。基于上表,你的 SQL 语句应返回如下结果,取消率(Cancellation Rate)保留两位小数。取消率的计算方式如下:(被司机或乘客取消的非禁止用户生成的订单数量) / (非禁止用户生成的订单总数)
| Day | Cancellation Rate |
|---|---|
| 2013-10-01 | 0.33 |
| 2013-10-02 | 0.00 |
| 2013-10-03 | 0.50 |
SELECT t1.Request_at AS Day,
ROUND(SUM(case t1.Status WHEN 'completed' THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)/COUNT(t1.Id),2) AS 'Cancellation Rate'
FROM Trips t1 inner join Users u1 on u1.Users_Id=t1.Client_Id
inner join Users u2 ON u2.Users_Id =t1.Driver_Id
WHERE u1.Banned='No' AND u2.Banned='No' AND t1.Request_at BETWEEN '2013-10-01' AND '2013-10-03'
GROUP BY t1.Request_at
【22】Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的工号 Id,姓名 Name,工资 Salary 和部门编号 DepartmentId 。
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Joe | 85000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
| 5 | Janet | 69000 | 1 |
| 6 | Randy | 85000 | 1 |
| 7 | Will | 70000 | 1 |
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
| Id | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门获得前三高工资的所有员工。例如,根据上述给定的表,查询结果应返回:
| Department | Employee | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| IT | Randy | 85000 |
| IT | Joe | 85000 |
| IT | Will | 70000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
| Sales | Sam | 60000 |
SELECT
d.NAME AS Department,
e1.NAME AS Employee,
e1.Salary AS Salary
FROM
Employee AS e1,Department d
WHERE
e1.DepartmentId = d.Id
AND 3 > (SELECT count( DISTINCT e2.Salary )
FROM Employee AS e2
WHERE e1.Salary < e2.Salary AND e1.DepartmentId = e2.DepartmentId )
ORDER BY d.NAME,Salary DESC;





 本文探讨了多种SQL查询场景,包括用户连续活跃天数计算、数据聚合与转换、连续登录用户统计、行转列与列转行操作、SQL取交集与差集等。通过实例展示了如何使用窗口函数、聚合函数、子查询等技术解决复杂的数据分析问题。
本文探讨了多种SQL查询场景,包括用户连续活跃天数计算、数据聚合与转换、连续登录用户统计、行转列与列转行操作、SQL取交集与差集等。通过实例展示了如何使用窗口函数、聚合函数、子查询等技术解决复杂的数据分析问题。
















 1426
1426

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








