目录
问题描述
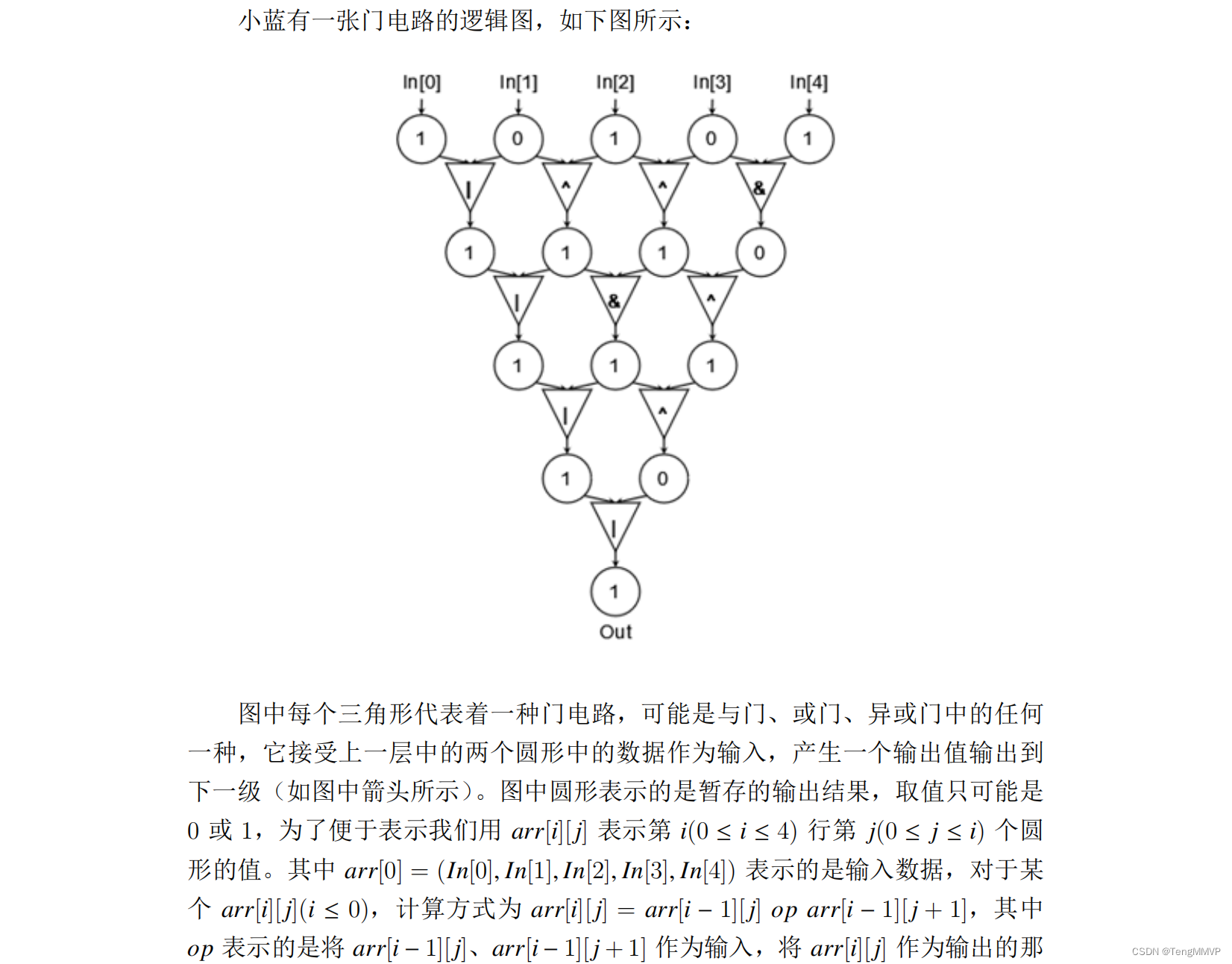

参考代码
示例一
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;
public class Main {
// AND、OR和XOR操作的二元操作符
private static final BinaryOperator<Integer> AND = (x, y) -> x & y;
private static final BinaryOperator<Integer> OR = (x, y) -> x | y;
private static final BinaryOperator<Integer> XOR = (x, y) -> x ^ y;
private static final BinaryOperator<Integer>[] operations = new BinaryOperator[]{AND, OR, XOR};
// 计算有效组合数的方法
public static int countValidCombinations(int level, int[] values) {
// 基本情况:如果我们已经到达最后一级
if (level == 1) {
return values[0] == 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
int validCombinations = 0;
// 生成当前级别的所有可能组合
for (int opIndex = 0; opIndex < Math.pow(3, level - 1); opIndex++) {
int[] newValues = new int[level - 1];
int tempIndex = opIndex;
// 计算当前组合的输出
for (int i = 0; i < level - 1; i++) {
int op = tempIndex % 3;
tempIndex /= 3;
newValues[i] = operations[op].apply(values[i], values[i + 1]);
}
// 递归计算下一级别的组合数
validCombinations += countValidCombinations(level - 1, newValues);
}
return validCombinations;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始输入值
int[] inputValues = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1};
// 从顶级开始计数
int result = countValidCombinations(inputValues.length, inputValues);
// 输出结果
System.out.println("总的有效组合数:" + result);
}
}示例二
public class Main {
private int[][] circuit = new int[6][6];
private int answer = 0;
private final int target = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main().run();
}
private void run() {
// 初始化电路的基本情况。
circuit[5] = new int[]{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1};
// 从电路的顶部开始深度优先搜索。
depthFirstSearch(1, 5);
// 打印计算出的答案。
System.out.println(answer);
}
private void depthFirstSearch(int index, int level) {
if (level <= 1) {
// 基本情况:如果当前单元格与目标匹配,增加答案。
if (circuit[level][index] == target) {
answer++;
}
} else {
if (index < level) {
// 执行与运算并继续搜索。
circuit[level - 1][index] = circuit[level][index] & circuit[level][index + 1];
depthFirstSearch(index + 1, level);
// 执行或运算并继续搜索。
circuit[level - 1][index] = circuit[level][index] | circuit[level][index + 1];
depthFirstSearch(index + 1, level);
// 执行异或运算并继续搜索。
circuit[level - 1][index] = circuit[level][index] ^ circuit[level][index + 1];
depthFirstSearch(index + 1, level);
} else {
// 移动到电路的下一个深度级别。
depthFirstSearch(1, level - 1);
}
}
}
}





 本文展示了两个Java代码示例,一个是使用`BinaryOperator`实现AND、OR和XOR操作的组合计数,另一个是深度优先搜索算法在电路分析中的应用。通过递归计算有效组合数和电路中满足特定条件的路径数。
本文展示了两个Java代码示例,一个是使用`BinaryOperator`实现AND、OR和XOR操作的组合计数,另一个是深度优先搜索算法在电路分析中的应用。通过递归计算有效组合数和电路中满足特定条件的路径数。

















 4002
4002

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








