/Military / Avionics /What are the three algorithms of UAV flight control, and what are their characteristics and applications
- August 17, 2021
- admin
- Military / Avionics
There are three UAV flight control algorithms: strapdown inertial navigation system, Kalman filter algorithm and flight control PID algorithm.
1、 Strapdown inertial navigation system
When it comes to navigation, I have to say GPS. It calculates its position by receiving the signal sent by the satellite, but when the top of the GPS device is blocked, the GPS device cannot locate. For example, in indoor, tunnel, underground and other places, GPS signals are basically not received.
Quotation: any product with shortcomings must achieve another product that can overcome its shortcomings.
Another navigation method is independent of external information. This navigation is called inertial navigation.
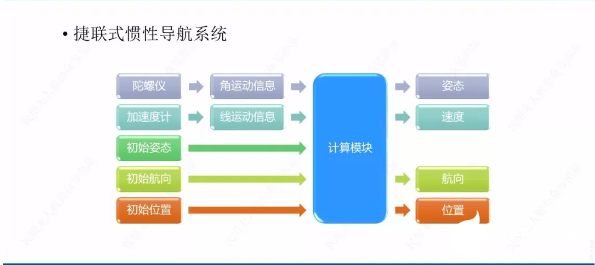
What is inertial navigation? It is an autonomous navigation method that uses the two inertial foresight of accelerometers and gyroscopes on the carrier to measure the angular motion information and linear motion information of the aircraft respectively, and hand them over to the calculation module together with the initial attitude, initial heading and initial position. The calculation module calculates the attitude, speed, heading, position and other navigation parameters of the aircraft.
(keep improving: how does the gyroscope calculate the attitude through the angular motion information and then through the calculation module? Similarly, how does the accelerometer calculate the velocity through the linear motion information and then through the calculation module?)
In addition, inertial navigation system is divided into platform inertial navigation and strapdown inertial navigation.
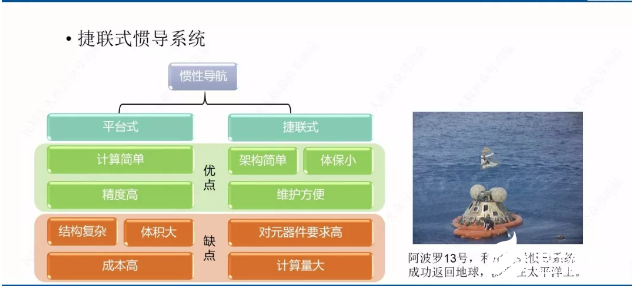
Inertial navigation system is divided into platform inertial navigation and strapdown inertial navigation.
The early inertial navigation systems were platform type. The platform type inertial navigation had a physical platform. The gyroscope and accelerometer were placed on the platform stabilized by the gyroscope. The platform tracked the navigation coordinate system to realize the speed and position calculation. The attitude data was directly taken from the ring of the platform.
Advantages: the navigation coordinate system is directly simulated, and the calculation is relatively simple; It can isolate the angular motion of the carrier and has high system accuracy.
Disadvantages: complex structure, large volume and high manufacturing cost.
There is another strapdown inertial navigation. The original English meaning of Strapdown is “binding”. Therefore, strapdown inertial navigation means that inertial measurement elements, including gyroscopes and accelerometers, are directly installed on the main body that needs navigation information such as attitude, speed and heading, and the measurement signals of the computer are transformed into navigation parameters.
The advantages are no platform, simple architecture, small volume and convenient maintenance.
Disadvantages: the inertial element is directly installed on the carrier, the environment is bad, and the requirements for the element are high; There is a large amount of calculation in coordinate transformation.
Overall, strapdown inertial navigation has obvious advantages over platform inertial navigation.
In 1969, as the emergency backup device of apollo-13 lunar landing spacecraft, strapdown inertial navigation system played a decisive role in successfully guiding the spacecraft to the earth return orbit when its service module exploded, and became a milestone in the development of strapdown inertial navigation system
2、 Kalman filter algorithm
The Kalman filter algorithm uses the state space model of signal and noise, updates the estimation of state variables by using the estimated value of the previous time and the observed value at the present time, and obtains the estimated value at the present time.
Kalman filtering algorithm is a recursive filtering algorithm proposed by Kalman et al in the 1960s. Its essence is to find a set of recursive estimation algorithm based on the minimum mean square error as the best criterion. This algorithm uses the state space model of signal and noise, updates the estimation of state variables by using the estimated value of the previous time and the observed value of the current time, and obtains the estimated value of the occurrence time. It is widely used in inertial navigation system. The noise just mentioned refers to the error between the calculated value and the actual value.
So why is Kalman filter applied to inertial navigation system? This is mainly because the “pure inertial” sensor of the inertial navigation system is not enough to achieve the required navigation accuracy. In order to compensate for the shortcomings of the navigation system, other navigation equipment are often used to improve the navigation accuracy and reduce the navigation error. Therefore, using Kalman filtering algorithm, the data from inertial navigation system and other navigation devices (such as the position calculated by inertial navigation system compared with the position information given by GPS receiver) can be mixed to estimate and correct the unknown inertial navigation system error.
Kalman filter algorithm has been widely used for more than 30 years, including robot navigation, control, sensor data fusion, even military radar system and missile tracking.
For example, in radar, people are interested in tracking the target, but the measured values of target position, velocity and acceleration often have noise at any time. Using the dynamic information of the target, Kalman filter tries to remove the influence of noise and obtain an optimal estimation of the target position. This estimation can be the estimation (filtering) of the current target position, the estimation (prediction) of the future position, or the estimation (interpolation or smoothing) of the past position.
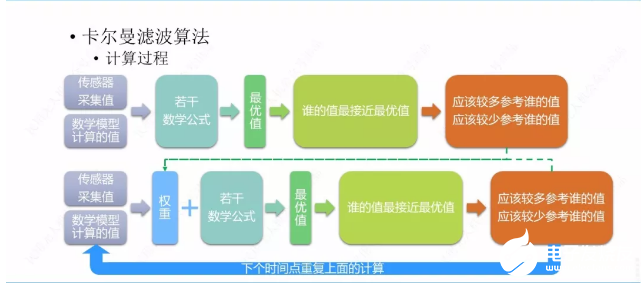
Kalman filter algorithm is a very complex calculation. Let’s briefly talk about its calculation process in combination with the aircraft. For example, the aircraft wants to know its own state, which can be attitude, speed or position information. We know that the sensors of the aircraft can get this information, These information can also be calculated through the mathematical model of inertial navigation, but there is still a certain gap between the value of these two information and the actual value. Putting these two values in several mathematical formulas can get an optimal value. By comparing this optimal value with the value of sensor and mathematical model, we can know which value is close to the optimal value, In the next calculation, we should refer more to the value close to the optimal value. For example, the value of the sensor is closest to the optimal value, so we use a larger weight for the value of the sensor and a smaller weight for the value obtained by the mathematical model. The weight obtained is not given casually, but also obtained through the mathematical formula. The weight will work when I recalculate in the next time period. The value of the sensor and the value of the mathematical model will be put in the mathematical formula with the weight to get the optimal value. Then we compare the optimal value with the value of the sensor and the mathematical model, and then see which value is close to the optimal value. If the value of the sensor is close to the optimal value, We will still generate a weight through the formula and give it to the calculation of the next time period. By repeating this calculation, we can get a relatively better value, which is the approximate process of Kalman filter algorithm.
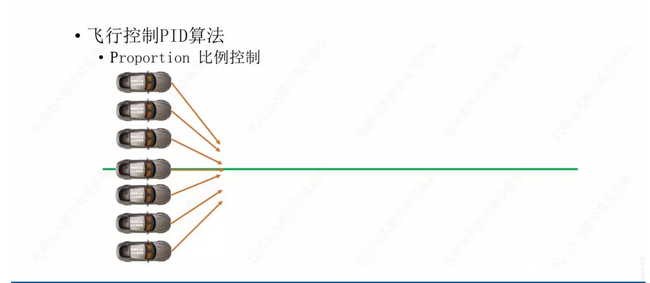
3、 Flight control PID algorithm
PID controller is a linear controller. It mainly forms the control deviation according to the given value and the actual output value, and then uses the deviation to give a reasonable control quantity.
At present, people have obtained many algorithms and theories with excellent control effect through scientific research, but in the field of engineering application, the control algorithm based on classical PID is still the simplest and most effective control scheme.
PID controller is a linear controller. It mainly forms the control deviation according to the given value and the actual output value, and then uses the deviation to give a reasonable control quantity.
At present, among several mainstream open source flight controls, PID control algorithm is used to realize the attitude and trajectory control of UAV without exception.
In PID, P is the initial line of proportion, which means proportion, I is the initial line of integral, which means integral, and D is the initial letter of differential, which means differential.
So what problems can PID controller algorithm solve? Taking the multi rotor as an example, without the control system, if the signal is directly used to drive the motor to drive the propeller to rotate to generate the control force, the dynamic response will be too fast, or too slow, or the control overshoot or insufficient, and the multi rotor can not successfully complete the take-off and suspension actions at all. In order to solve these problems, it is necessary to add PID controller algorithm to the control system loop. The proportional, integral and differential relationship between attitude information and propeller speed is established. By adjusting the parameters of each link, the multi rotor system control can achieve the phenomenon of rapid dynamic response, neither impulse nor lack.
Responsible editor: GT








 本文介绍了无人机飞行控制的三种核心算法:捷联惯导系统、卡尔曼滤波算法和PID控制。捷联惯导系统通过加速度计和陀螺仪测量飞机运动,实现自主导航;卡尔曼滤波用于融合不同导航设备数据,提高精度;PID控制则在飞行控制中调整偏差,确保稳定飞行。这些算法在现代无人机技术中发挥着关键作用。
本文介绍了无人机飞行控制的三种核心算法:捷联惯导系统、卡尔曼滤波算法和PID控制。捷联惯导系统通过加速度计和陀螺仪测量飞机运动,实现自主导航;卡尔曼滤波用于融合不同导航设备数据,提高精度;PID控制则在飞行控制中调整偏差,确保稳定飞行。这些算法在现代无人机技术中发挥着关键作用。
















 1717
1717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








