目录
本文是对LPIPS技术的代码解读,原文解读请看LPIPS,本文参考的代码是PYIQA。
原文概要
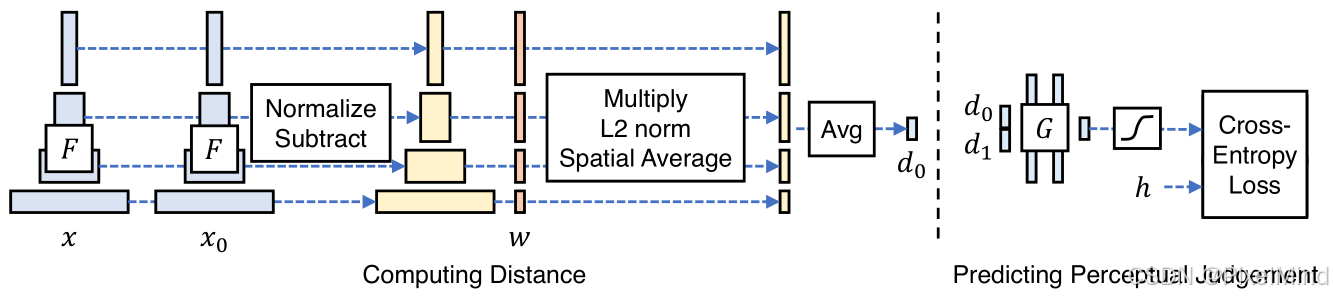
LPIPS通过计算深度网络中不同图像的特征距离来评估感知相似性指标,过程如下图所示。
下面将根据PYIQA的实现来对LPIPS进行代码讲解。
1. 代码讲解
总的来说,LPIPS的计算可以被分为以下5步:
- 图像进行预处理,标准化。
- 通过选定的网络的多个特征层的激活输出作为LPIPS指标的计算输入。
- 逐个特征进行对比,特征首先进行normalize,然后进行MSE计算,normalize是L2范数的归一化,通道上所有值相加为L2范数大小。
- 然后是在空间上做平均,(这里可以选择是否使用LPIPS训练的几个FC层参数,在论文中也有提到)
- 最终的结果由所有层的结果求和得来,多个层的结果权重一样。
代码路径位于pyiqa/archs/lpips_arch.py中,实现如下所示。
@ARCH_REGISTRY.register()
class LPIPS(nn.Module):
"""LPIPS model.
Args:
lpips (Boolean) : Whether to use linear layers on top of base/trunk network.
pretrained (Boolean): Whether means linear layers are calibrated with human
perceptual judgments.
pnet_rand (Boolean): Whether to randomly initialized trunk.
net (String): ['alex','vgg','squeeze'] are the base/trunk networks available.
version (String): choose the version ['v0.1'] is the default and latest;
['v0.0'] contained a normalization bug.
pretrained_model_path (String): Petrained model path.
The following parameters should only be changed if training the network:
eval_mode (Boolean): choose the mode; True is for test mode (default).
pnet_tune (Boolean): Whether to tune the base/trunk network.
use_dropout (Boolean): Whether to use dropout when training linear layers.
"""
def __init__(
self,
pretrained=True,
net='alex',
version='0.1',
lpips=True,
spatial=False,
pnet_rand=False,
pnet_tune=False,
use_dropout=True,
pretrained_model_path=None,
eval_mode=True,
semantic_weight_layer=-1,
**kwargs,
):
super(LPIPS, self).__init__()
self.pnet_type = net
self.pnet_tune = pnet_tune
self.pnet_rand = pnet_rand
self.spatial = spatial
self.lpips = lpips # false means baseline of just averaging all layers
self.version = version
self.scaling_layer = ScalingLayer()
self.semantic_weight_layer = semantic_weight_layer
if self.pnet_type in ['vgg', 'vgg16']:
net_type = vgg16
self.chns = [64, 128, 256, 512, 512]
elif self.pnet_type == 'alex':
net_type = alexnet
self.chns = [64, 192, 384, 256, 256]
elif self.pnet_type == 'squeeze':
net_type = squeezenet
self.chns = [64, 128, 256, 384, 384, 512, 512]
self.L = len(self.chns)
self.net = net_type(pretrained=not self.pnet_rand, requires_grad=self.pnet_tune)
if lpips:
self.lin0 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[0], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lin1 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[1], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lin2 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[2], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lin3 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[3], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lin4 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[4], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lins = [self.lin0, self.lin1, self.lin2, self.lin3, self.lin4]
if self.pnet_type == 'squeeze': # 7 layers for squeezenet
self.lin5 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[5], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lin6 = NetLinLayer(self.chns[6], use_dropout=use_dropout)
self.lins += [self.lin5, self.lin6]
self.lins = nn.ModuleList(self.lins)
if pretrained_model_path is not None:
load_pretrained_network(self, pretrained_model_path, False)
elif pretrained:
load_pretrained_network(
self, default_model_urls[f'{version}_{net}'], False
)
if eval_mode:
self.eval()
def forward(self, in1, in0, retPerLayer=False, normalize=True):
r"""Computation IQA using LPIPS.
Args:
in1: An input tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
in0: A reference tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
retPerLayer (Boolean): return result contains result of
each layer or not. Default: False.
normalize (Boolean): Whether to normalize image data range
in [0,1] to [-1,1]. Default: True.
Returns:
Quality score.
"""
if (
normalize
): # turn on this flag if input is [0,1] so it can be adjusted to [-1, +1]
in0 = 2 * in0 - 1
in1 = 2 * in1 - 1
# v0.0 - original release had a bug, where input was not scaled
in0_input, in1_input = (
(self.scaling_layer(in0), self.scaling_layer(in1))
if self.version == '0.1'
else (in0, in1)
)
outs0, outs1 = self.net.forward(in0_input), self.net.forward(in1_input)
feats0, feats1, diffs = {}, {}, {}
for kk in range(self.L):
feats0[kk], feats1[kk] = (
normalize_tensor(outs0[kk]),
normalize_tensor(outs1[kk]),
)
diffs[kk] = (feats0[kk] - feats1[kk]) ** 2
if self.lpips:
if self.spatial:
res = [
upsample(self.lins[kk](diffs[kk]), out_HW=in0.shape[2:])
for kk in range(self.L)
]
elif self.semantic_weight_layer >= 0:
res = []
semantic_feat = outs0[self.semantic_weight_layer]
for kk in range(self.L):
diff_score = self.lins[kk](diffs[kk])
semantic_weight = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(
semantic_feat,
size=diff_score.shape[2:],
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False,
)
avg_score = torch.sum(
diff_score * semantic_weight, dim=[1, 2, 3], keepdim=True
) / torch.sum(semantic_weight, dim=[1, 2, 3], keepdim=True)
res.append(avg_score)
else:
res = [
spatial_average(self.lins[kk](diffs[kk]), keepdim=True)
for kk in range(self.L)
]
else:
if self.spatial:
res = [
upsample(diffs[kk].sum(dim=1, keepdim=True), out_HW=in0.shape[2:])
for kk in range(self.L)
]
else:
res = [
spatial_average(diffs[kk].sum(dim=1, keepdim=True), keepdim=True)
for kk in range(self.L)
]
val = 0
for i in range(self.L):
val += res[i]
if retPerLayer:
return (val, res)
else:
return val.squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)可以看到,输入的两幅图像会首先进行预处理,标准化,即self.scaling_layer的前向过程,如下所示。
class ScalingLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ScalingLayer, self).__init__()
self.register_buffer(
'shift', torch.Tensor([-0.030, -0.088, -0.188])[None, :, None, None]
)
self.register_buffer(
'scale', torch.Tensor([0.458, 0.448, 0.450])[None, :, None, None]
)
def forward(self, inp):
return (inp - self.shift) / self.scale接下来是计算选定网络的多个特征层的激活输出,代码这里默认是alexnet,计算了5个不同位置的特征输出,则现在我们拥有了2幅图像的5对特征输出,总共10个特征,net按照选定的网络类型进行初始化。
self.net = net_type(pretrained=not self.pnet_rand, requires_grad=self.pnet_tune)前向中,利用这个net进行推理。
outs0, outs1 = self.net.forward(in0_input), self.net.forward(in1_input)然后来到前面讲的第三步,逐个特征进行对比,特征首先进行normalize,然后进行MSE计算,normalize是L2范数的归一化,通道上所有值相加为L2范数大小,代码如下所示:
for kk in range(self.L):
feats0[kk], feats1[kk] = (
normalize_tensor(outs0[kk]),
normalize_tensor(outs1[kk]),
)
diffs[kk] = (feats0[kk] - feats1[kk]) ** 2这里的L是层的数目,在本例子中是5,normalize_tensor实现如下:
def normalize_tensor(in_feat, eps=1e-10):
norm_factor = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(in_feat**2, dim=1, keepdim=True))
return in_feat / (norm_factor + eps)可以看到feat在dim维度上做了L2范数的归一化。
后续来到第四步,即计算空间上的平均,(这里可以选择是否使用LPIPS训练的几个FC层参数),如下所示:
if self.lpips:
if self.spatial:
res = [
upsample(self.lins[kk](diffs[kk]), out_HW=in0.shape[2:])
for kk in range(self.L)
]
elif self.semantic_weight_layer >= 0:
res = []
semantic_feat = outs0[self.semantic_weight_layer]
for kk in range(self.L):
diff_score = self.lins[kk](diffs[kk])
semantic_weight = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(
semantic_feat,
size=diff_score.shape[2:],
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False,
)
avg_score = torch.sum(
diff_score * semantic_weight, dim=[1, 2, 3], keepdim=True
) / torch.sum(semantic_weight, dim=[1, 2, 3], keepdim=True)
res.append(avg_score)
else:
res = [
spatial_average(self.lins[kk](diffs[kk]), keepdim=True)
for kk in range(self.L)
]
else:
if self.spatial:
res = [
upsample(diffs[kk].sum(dim=1, keepdim=True), out_HW=in0.shape[2:])
for kk in range(self.L)
]
else:
res = [
spatial_average(diffs[kk].sum(dim=1, keepdim=True), keepdim=True)
for kk in range(self.L)
]可以看到如果self.LPIPS生效的话,会用到self.lins这几个FC层用于计算LPIPS指标,如果我们只使用特征来进行计算的话是不需要这几个参数的,可以直接到spatial_average函数对本次求取的特征距离进行空间的平均值计算,前面计算的特征只是做了L2范数的归一化,这里是求取最后的res,即LPIPS结果,看最后一个分支,首先特征距离会进行通道的sum,然后再求空间的均值。得到L个res结果,spatial_average的实现如下:
def spatial_average(in_tens, keepdim=True):
return in_tens.mean([2, 3], keepdim=keepdim)最后我们将所有层的结果求和得到最终的值即可。
val = 0
for i in range(self.L):
val += res[i]以上就得到了最终我们使用到的LPIPS指标。
以上针对于LPIPS的代码实现的部分讲解完毕,如果有不清楚的问题欢迎大家提出。























 939
939

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








