Acy夕拾算法 Week1_day5
知识点参考:代码随想录-二叉树理论基础
· 父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i * 2 +1,右孩子就是 i * 2 +2。
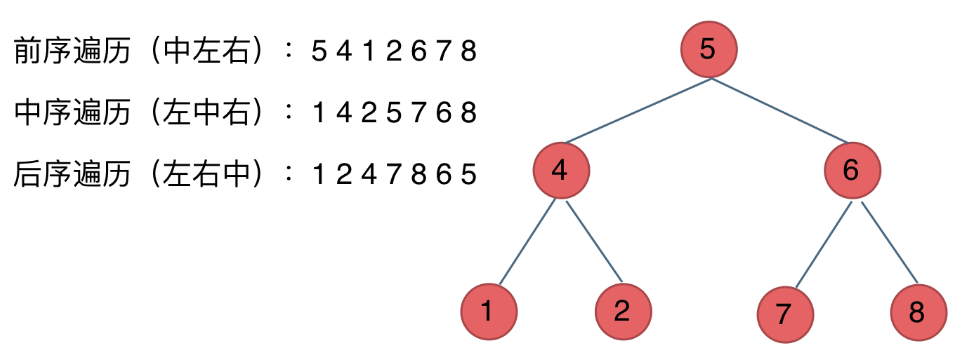
· 深度优先:有前中后序遍历:这里前中后,其实指的就是 中间节点的遍历顺序(位置)
·· 前序遍历:中左右
·· 中序遍历:左中右
·· 后序遍历: 左右中
···· 从“最”开始:从最中开始,从最左开始;左右顺序不变;所有的 中、左都要遍历完,才能开始 左、中/右;左右是指图中的左右,即当中在图中的最左时它为左,eg,中序的5
递归:1.参数和返回值;2.终止条件;3.单层逻辑。
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
/*
整理思路:
前序:中左右;
1.参数:当前节点,数组结果;返回空;2.遍历到当前为空,结束;3.中左右
void preT(TreeNode* cur, vector& res)
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
preT(root, res);
return res;
}
void preT(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& res)
{
if(cur == NULL) return ;
res.push_back(cur->val);
preT(cur->left, res);
preT(cur->right, res);
}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
/*
我的思路:
左中右,把左全部遍历完,再中再全部左…
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
midT(root, res);
return res;
}
void midT(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& res)
{
if(cur == NULL) return;
midT(cur->left, res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
midT(cur->right, res);
}
};
104. 二叉树的最大深度
/*
整理思路:
深度优先搜索:一直向下,返回左右最大+1(根),直到空返回0。
广度优先搜索:
*/
深度优先搜索
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max( maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
广度优先搜索
周日补





















 399
399

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








