一、简介
1 粒子群算法的概念
粒子群优化算法(PSO:Particle swarm optimization) 是一种进化计算技术(evolutionary computation)。源于对鸟群捕食的行为研究。粒子群优化算法的基本思想:是通过群体中个体之间的协作和信息共享来寻找最优解.
PSO的优势:在于简单容易实现并且没有许多参数的调节。目前已被广泛应用于函数优化、神经网络训练、模糊系统控制以及其他遗传算法的应用领域。
2 粒子群算法分析
2.1基本思想
粒子群算法通过设计一种无质量的粒子来模拟鸟群中的鸟,粒子仅具有两个属性:速度和位置,速度代表移动的快慢,位置代表移动的方向。每个粒子在搜索空间中单独的搜寻最优解,并将其记为当前个体极值,并将个体极值与整个粒子群里的其他粒子共享,找到最优的那个个体极值作为整个粒子群的当前全局最优解,粒子群中的所有粒子根据自己找到的当前个体极值和整个粒子群共享的当前全局最优解来调整自己的速度和位置。下面的动图很形象地展示了PSO算法的过程: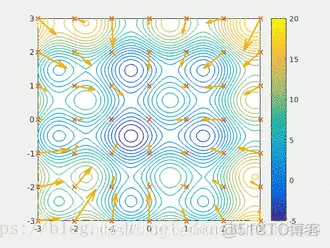
2 更新规则
PSO初始化为一群随机粒子(随机解)。然后通过迭代找到最优解。在每一次的迭代中,粒子通过跟踪两个“极值”(pbest,gbest)来更新自己。在找到这两个最优值后,粒子通过下面的公式来更新自己的速度和位置。
公式(1)的第一部分称为【记忆项】,表示上次速度大小和方向的影响;公式(1)的第二部分称为【自身认知项】,是从当前点指向粒子自身最好点的一个矢量,表示粒子的动作来源于自己经验的部分;公式(1)的第三部分称为【群体认知项】,是一个从当前点指向种群最好点的矢量,反映了粒子间的协同合作和知识共享。粒子就是通过自己的经验和同伴中最好的经验来决定下一步的运动。以上面两个公式为基础,形成了PSO的标准形式。
公式(2)和 公式(3)被视为标准PSO算法。
3 PSO算法的流程和伪代码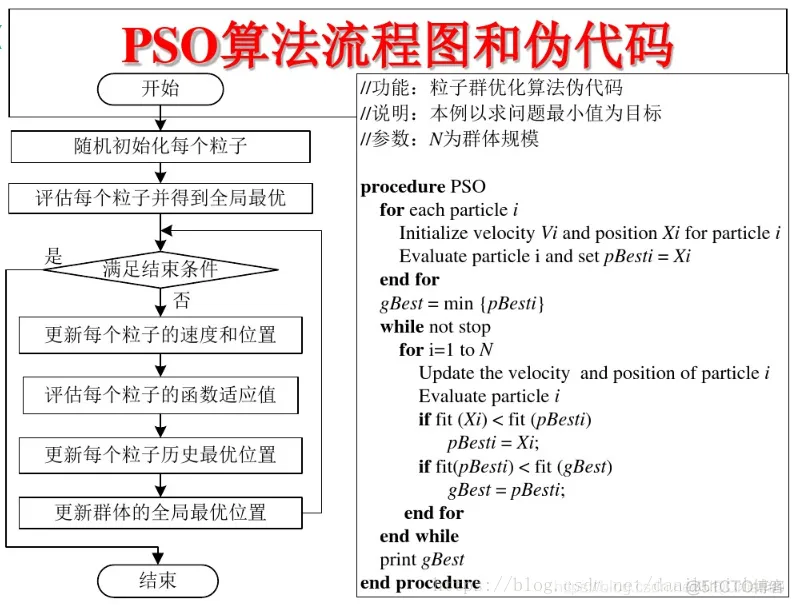
二、源代码
function [L_best,xx,tourGbest]=main(data)
%% 下载数据
% data=load('coor.txt');
% cityCoor=data;%城市坐标矩阵
cityCoor=data;
%% 计算城市间距离
n=size(cityCoor,1); %城市数目
cityDist=zeros(n,n); %城市距离矩阵
for i=1:n
for j=1:n
if i~=j
cityDist(i,j)=((cityCoor(i,1)-cityCoor(j,1))^2+...
(cityCoor(i,2)-cityCoor(j,2))^2+(cityCoor(i,3)-cityCoor(j,3))^2)^0.5;
end
cityDist(j,i)=cityDist(i,j);
end
end
nMax=10; %进化次数
indiNumber=400; %个体数目
individual=zeros(indiNumber,n);
%^初始化粒子位置
for i=1:indiNumber
individual(i,:)=randperm(n);
end
%% 计算种群适应度
indiFit=fitness(individual,cityDist);
[value,index]=min(indiFit);
tourPbest=individual; %当前个体最优
tourGbest=individual(index,:) ; %当前全局最优
recordPbest=inf*ones(1,indiNumber); %个体最优记录
recordGbest=indiFit(index); %群体最优记录
xnew1=individual;
%% 循环寻找最优路径
L_best=zeros(1,nMax);
for N=1:nMax
N
%计算适应度值
indiFit=fitness(individual,cityDist);
% %% 精英复制
% [bad good order]=elite(individual,cityCoor,cityDist,0.1); %提取10%的精英粒子
% elitenum=size(bad,2);
% individual(bad,:)=individual(good,:);
%% 精英复制学习
[bad good order]=elite(individual,cityCoor,cityDist,0.1); %提取10%的精英粒子
elitenum=size(bad,2);
%随机调整
for i=1:elitenum
% better(i,:)=tsp(cityCoor,n,cityDist);
better(i,:)=goodchange(individual(good(i),:),cityDist);
end
individual(bad,:)=better;
%更新当前最优和历史最优
for i=1:indiNumber
if indiFit(i)<recordPbest(i)
recordPbest(i)=indiFit(i);
tourPbest(i,:)=individual(i,:);
end
if indiFit(i)<recordGbest
recordGbest=indiFit(i);
tourGbest=individual(i,:);
end
end
[value,index]=min(recordPbest);
recordGbest(N)=recordPbest(index);
%% 交叉操作
for i=1:indiNumber
% 与个体最优进行交叉
c1=unidrnd(n-1); %产生交叉位
c2=unidrnd(n-1); %产生交叉位
while c1==c2
c1=round(rand*(n-2))+1;
c2=round(rand*(n-2))+1;
end
chb1=min(c1,c2);
chb2=max(c1,c2);
cros=tourPbest(i,chb1:chb2);
ncros=size(cros,2);
%删除与交叉区域相同元素
for j=1:ncros
for k=1:n
if xnew1(i,k)==cros(j)
xnew1(i,k)=0;
for t=1:n-k
temp=xnew1(i,k+t-1);
xnew1(i,k+t-1)=xnew1(i,k+t);
xnew1(i,k+t)=temp;
end
end
end
end
%插入交叉区域
xnew1(i,n-ncros+1:n)=cros;
%新路径长度变短则接受
dist=0;
for j=1:n-1
dist=dist+cityDist(xnew1(i,j),xnew1(i,j+1));
end
dist=dist+cityDist(xnew1(i,1),xnew1(i,n));
if indiFit(i)>dist
individual(i,:)=xnew1(i,:);
end
% 与全体最优进行交叉
c1=round(rand*(n-2))+1; %产生交叉位
c2=round(rand*(n-2))+1; %产生交叉位
while c1==c2
c1=round(rand*(n-2))+1;
c2=round(rand*(n-2))+1;
end
chb1=min(c1,c2);
chb2=max(c1,c2);
cros=tourGbest(chb1:chb2);
ncros=size(cros,2);
%删除与交叉区域相同元素
for j=1:ncros
for k=1:n
if xnew1(i,k)==cros(j)
xnew1(i,k)=0;
for t=1:n-k
temp=xnew1(i,k+t-1);
xnew1(i,k+t-1)=xnew1(i,k+t);
xnew1(i,k+t)=temp;
end
end
end
end
%插入交叉区域
xnew1(i,n-ncros+1:n)=cros;
%新路径长度变短则接受
dist=0;
for j=1:n-1
dist=dist+cityDist(xnew1(i,j),xnew1(i,j+1));
end
function path = tsp(loc,NumCity,distance)
% NumCity = length(loc); %城市个数
% distance = zeros(NumCity); %初始化距离矩阵,30行30列
%
% %装填距离矩阵
% for i = 1:NumCity,
% for j = 1:NumCity,
% %城市i和城市j之间的距离,既为两点间的二阶范数
% distance(i, j) = norm(loc(i, :) - loc(j, :));
% end
% end
%
% %通过目标函数从路径中生成能量值,既为各个城市之间距离的和
% %path = randperm(NumCity);
% %energy = sum(distance((path-1)*NumCity + [path(2:NumCity) path(1)]));
count = 1000;
all_dE = zeros(count, 1);
for i = 1:count
path = randperm(NumCity); %随机的生成一个路径,数字为30以内
%把距离定义成能量值,把所有城市之间的距离相加
energy = sum(distance((path-1)*NumCity + [path(2:NumCity) path(1)]));
new_path = path;
index = round(rand(2,1)*NumCity+.5);
inversion_index = (min(index):max(index));
new_path(inversion_index) = fliplr(path(inversion_index));
all_dE(i) = abs(energy - ...
sum(sum(diff(loc([new_path new_path(1)],:))'.^2)));
end
dE = max(all_dE);%记录20组能量差里面的最大值
dE = max(all_dE);
temp = 10*dE; %选择一个最大差值作为起始温度值
MaxTrialN = NumCity*100; % 最大的试验温度值 ,既试验解的最大个数
MaxAcceptN = NumCity*10; % 最大的可接受的温度值,既可接受的解的最大个数
StopTolerance = 0.005; %容忍度,既为终止温度值
StopTolerance = 0.005;
TempRatio = 0.4; %温度下降比率
minE = inf; %初始化最小能量值
maxE = -1; %初始化最大能量值- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 176.
- 177.
- 178.
- 179.
- 180.
- 181.
- 182.
- 183.
- 184.
- 185.
- 186.
- 187.
- 188.
- 189.
- 190.
- 191.
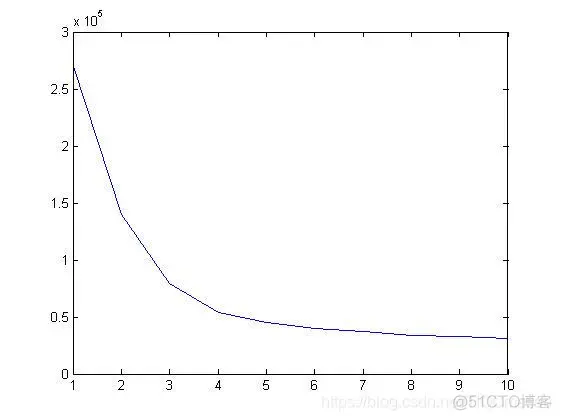
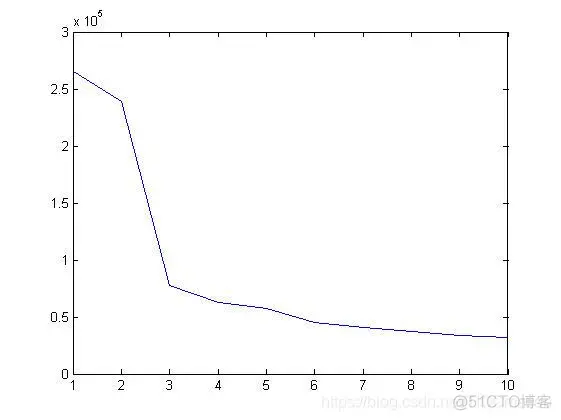
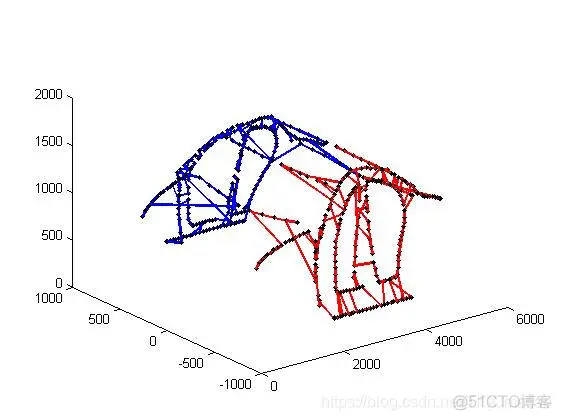
三、运行结果




















 422
422

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








