1 简介
随着现代居民居住地愈发集中,供水管网规模不断扩大,水资源供给面临着新的困难和挑战.其中包括水资源调度时的动态变化,管网的突发故障,水资源的不可控流失以及多目标和计算量庞大等问题.BP神经网络因拥有较强的自学习能力和泛化能力而被广泛应用于水资源预测问题中,但其也存在收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部极值的问题.群智能算法作为一种寻优算法,具有操作简单,收敛速度快,全局寻优能力强等优点.为提高BP神经网络在水资源预测方面的收敛速度和预测精度,提出一种基于鲸鱼算法优化的BP神经网络水资源需求预测模型,通过BP神经网络采用WOA算法输出的最优权值,阈值作为初始参数值训练模型.实验验证,WOA-BP神经网络方法相比传统BP方法在收敛速度和预测精度方面都有更优的表现.
BP神经网络是一种多层的前馈神经网络,其主要的特点是:信号是前向传播的,而 误 差 是 反 向 传 播 的。BP神经 网 络的过程主要分为两个阶段,第一阶段是信号的前向传播,即从输入层经过隐藏层,最后再到达输出层;第二阶段是误差的反向传播,将输出层的结果与预期结果做对比,从输出层到隐含层,最后到输入层,依次调节隐含层到输出层的权重和偏置、输入层到隐含层的权重和偏置。BP神经网络具有自学习能力、非线性函数映射能力,且鲁棒性 强。三 层 BP神经 网 络 的结构如图1所示。

2 部分代码
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% 鲸鱼优化算法 %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while t<Max_iter
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<lb;
Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
% Update the leader
if fitness<Leader_score % Change this to > for maximization problem
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
end
3 仿真结果
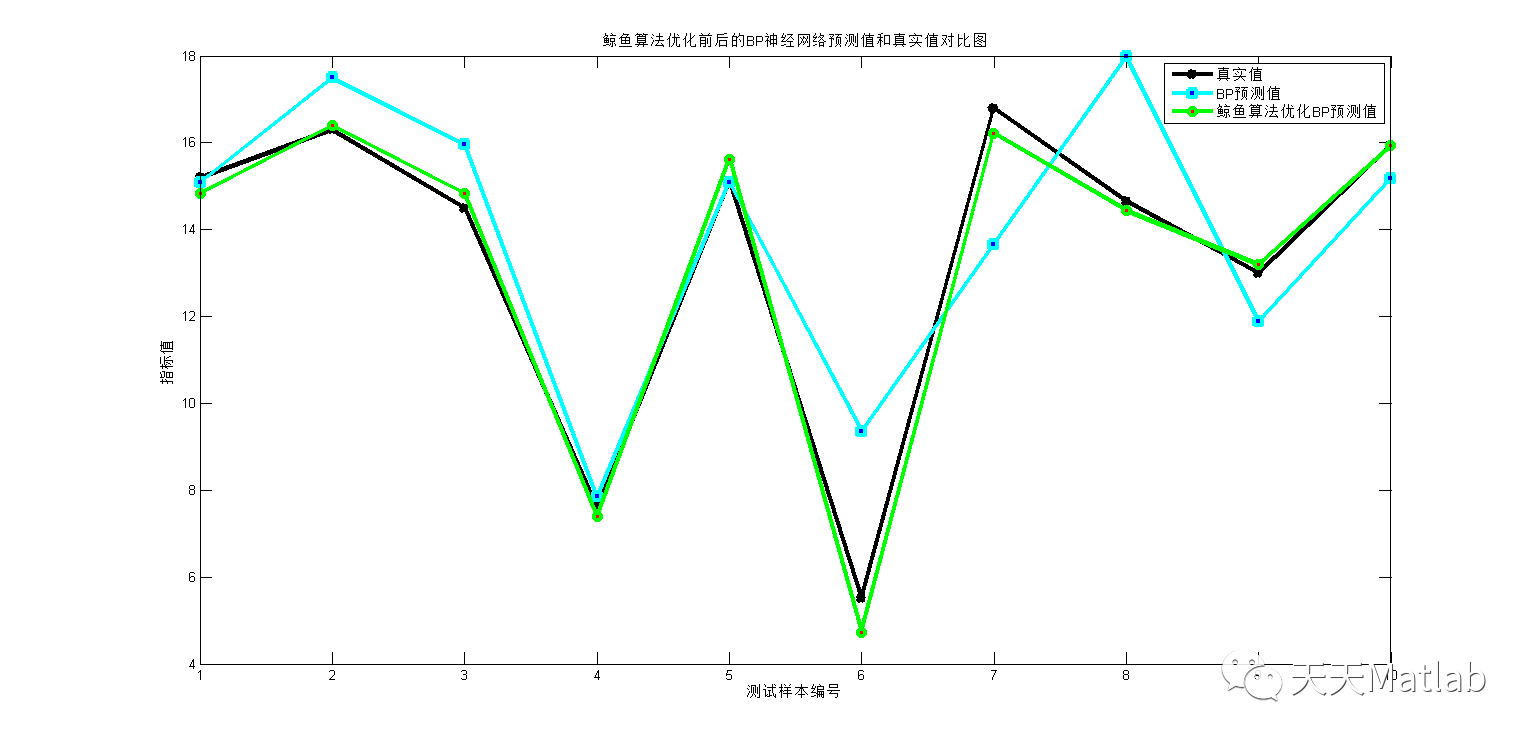
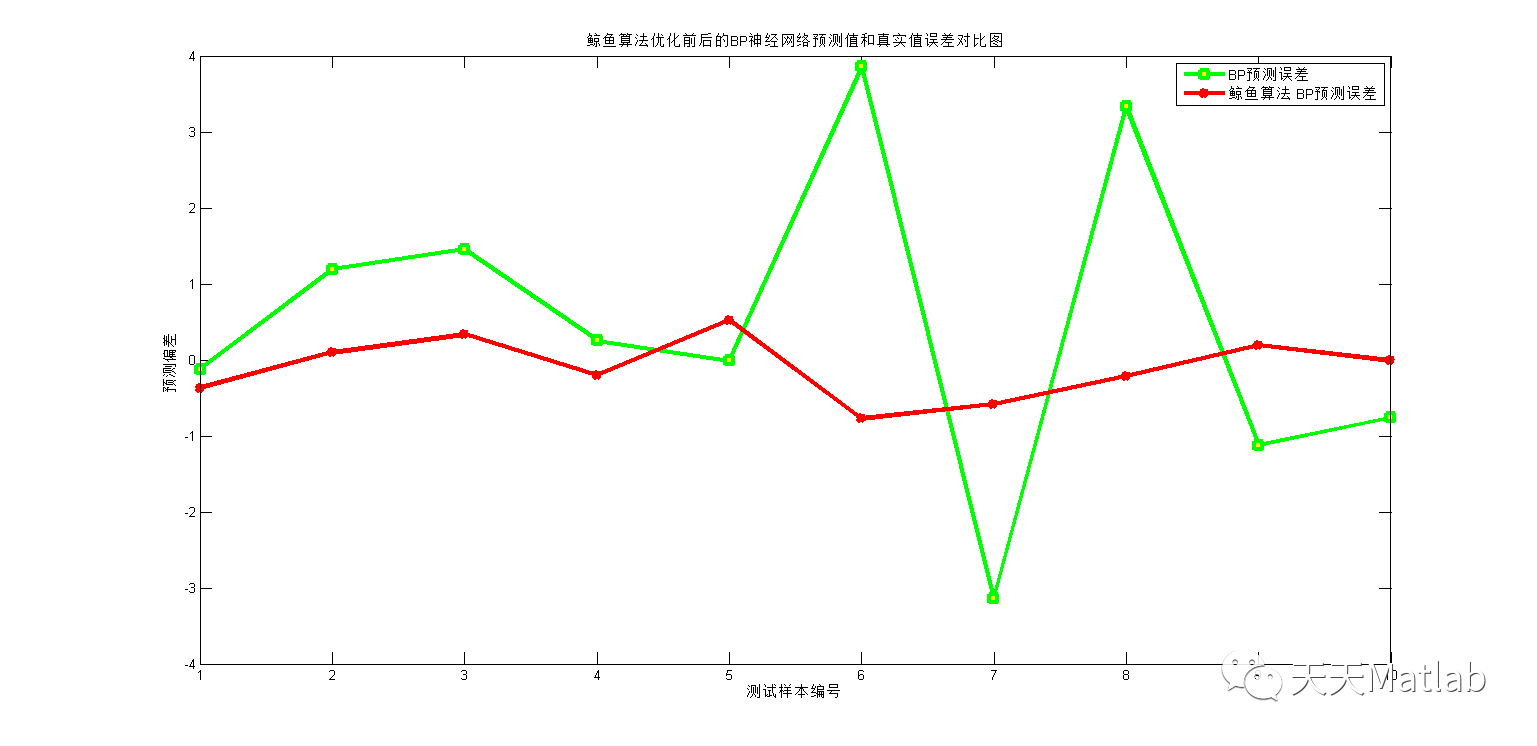
4 参考文献
[1]马创, 周代棋, 张业. 基于改进鲸鱼算法的BP神经网络水资源需求预测方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(S02):5.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

 改进鲸鱼算法优化的BP神经网络在水资源需求预测中的应用,
改进鲸鱼算法优化的BP神经网络在水资源需求预测中的应用,





















 6001
6001

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








