💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
人工势场法(Artificial Potential Field, APF)是一种常用的移动机器人路径规划方法。这种方法通过模拟物理中的势场理论来引导机器人的运动,从而实现从起始点到目标点的导航。使用人工势场的移动机器人路径规划,是通过在目标位置设置引力源产生引力,在障碍物周围设置斥力源产生斥力,机器人在引力与斥力共同作用下确定运动方向和速度。其优点包括实时性好、灵活性高、路径平滑;缺点有局部极小值问题、对环境变化敏感、参数调整困难。该方法在移动机器人导航等领域有广泛应用,且不断发展改进。
📚2 运行结果
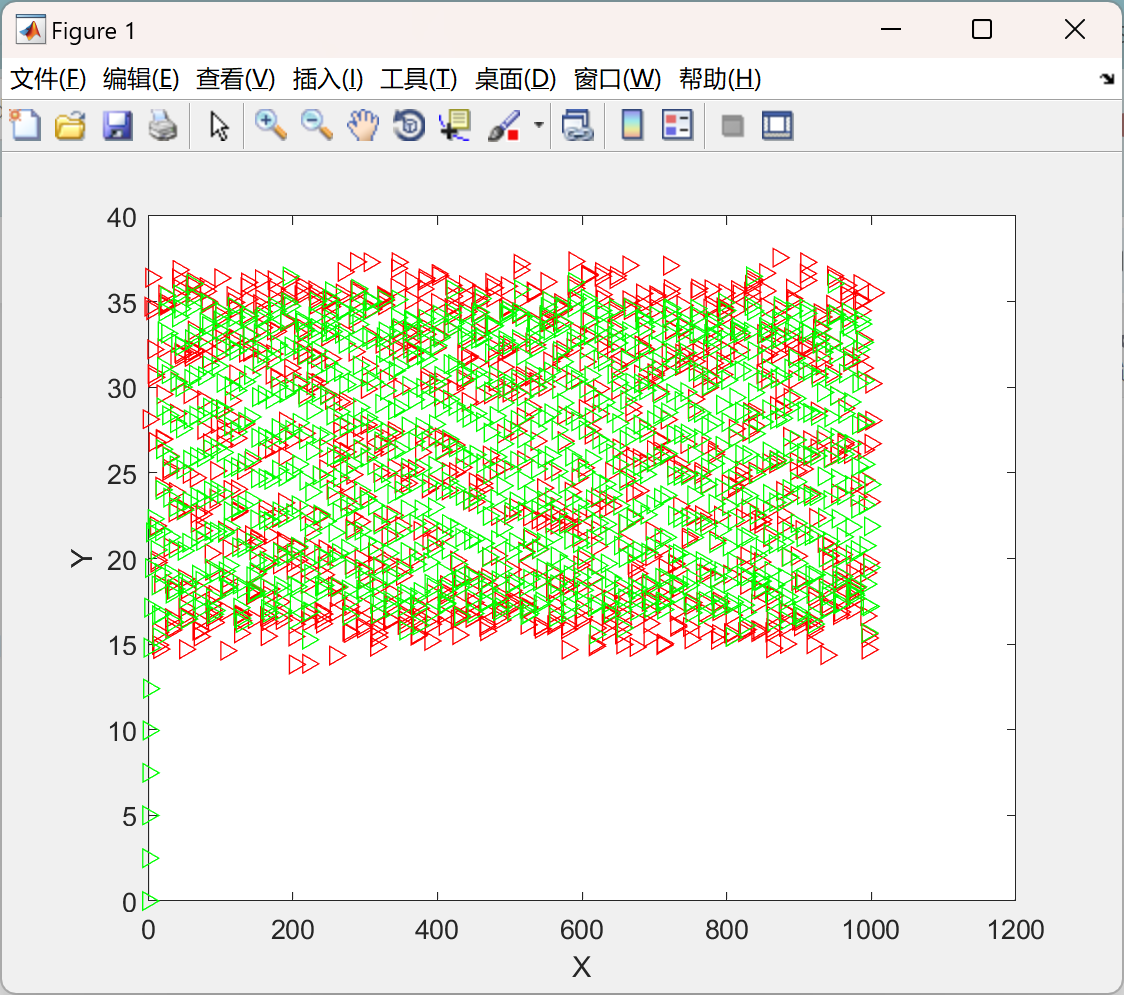
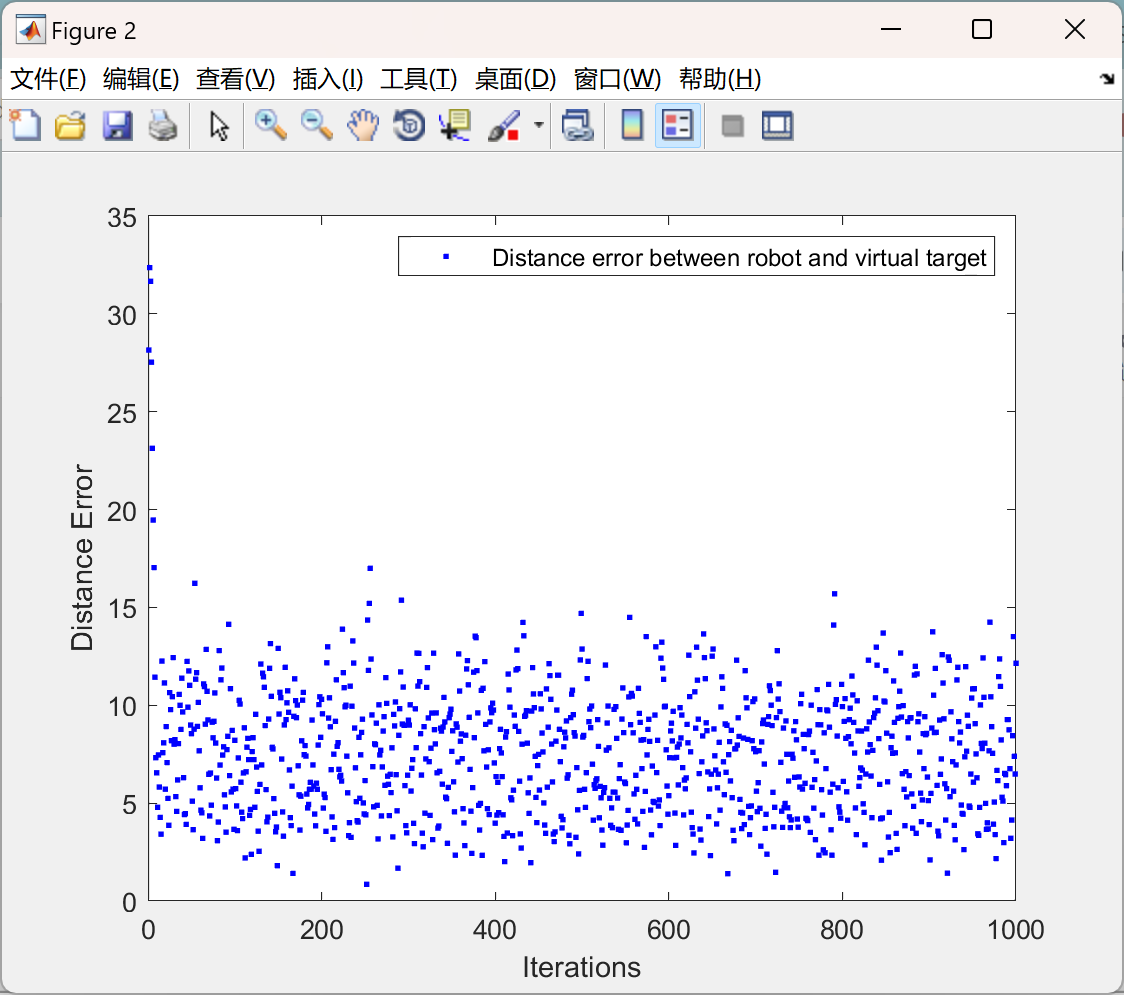
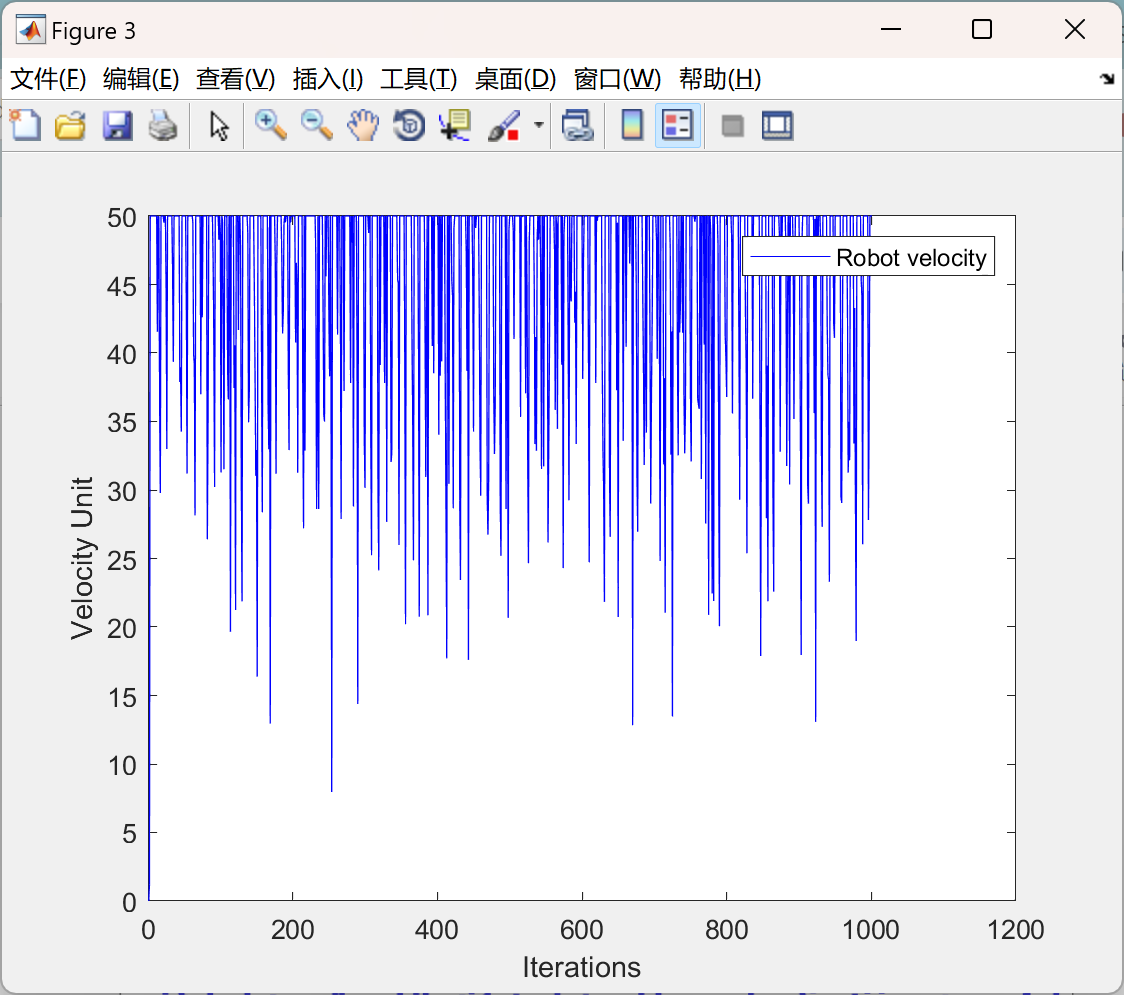
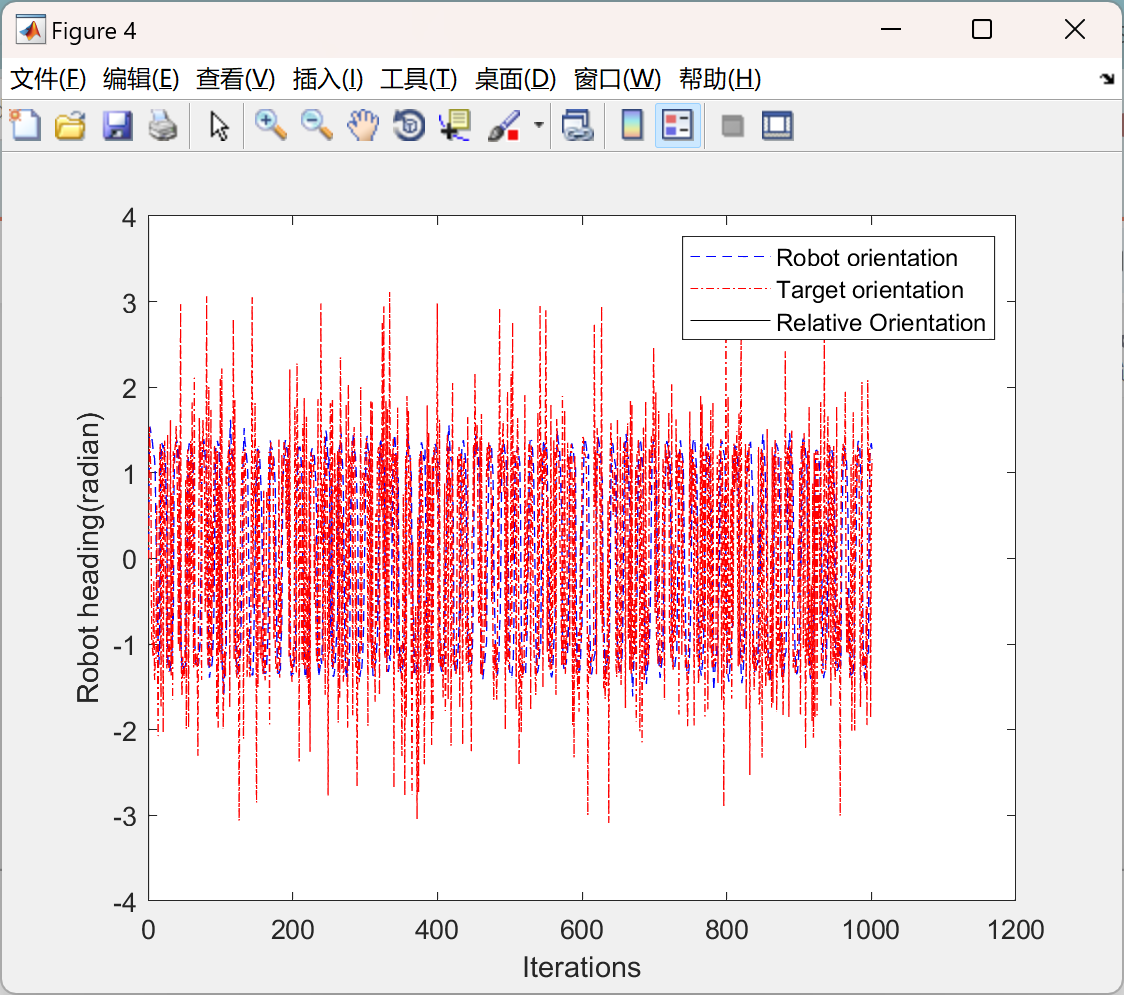
主函数部分代码:
clc,clear
close all
n = 2; % Number of dimensions
delta_t = 0.05; % Set time step
t = 0:delta_t:50;% Set total simulation time 0 0.05 0.1 0.15.....
lambda = 8.5; % Set scaling factor of attractive potential field
vr_max = 50; % Set maximum of robot velocity
%Set Virtual Target
qv = zeros (length(t),n); %Initial positions of virtual target
pv = 1.2; %Set velocity of virtual target
theta_t = zeros (length(t),1); % Initial heading of the virtual target
%Set Robot
qr = zeros (length(t),n); %initial position of robot
vrd = zeros (length(t),1); %Initial velocity of robot
theta_r = zeros (length(t),1); % Initial heading of the robot
qrv = zeros (length(t),n); %Save relative positions between robot and virtual target
prv = zeros(length(t),n); %Save relative velocities between robot and virtual target
qrv(1,:) = qv(1,:) - qr(1,:);%Compute the initial relative position
%Compute the initial relative velocity
prv(1,:) = [pv*cos(theta_t(1))-vrd(1)*cos(theta_r(1)), pv*sin(theta_t(1))-vrd(1)*sin(theta_r(1))];
%====Set noise mean and standard deviation====
noise_mean = 0.8;
noise_std = 0.8;
pause('on')
for i =2:length(t)
%++++++++++CIRCULAR TRAJECTORY+++++++++++
%Set target trajectory moving in CIRCULAR trajectory WITHOUT noise
% qv_x = 60 - 15*cos(t(i));
% qv_y = 30 + 15*sin(t(i));
% qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of virtual target
%Set target trajectory moving in CIRCULAR trajectory WITH noise
% qv_x = 60 - 15*cos(t(i))+ noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
% qv_y = 30 + 15*sin(t(i)) + noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
% qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of target
%++++++++++LINEAR TRAJECTORY+++++++++++
%Set target trajectory moving in Linear trajectory WITHOUT noise
% qv_x = t(i);
% qv_y = qv_x + 100;
% qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of virtual target
%Set target trajectory moving in Linear trajectory WITH noise
% qv_x = i + noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
% qv_y = qv_x + 100 + noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
% qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of target
%++++++++++SINE WAVE TRAJECTORY+++++++++++
%Set target trajectory moving in sine trajectory WITHOUT noise
% qv_x = i;
% qv_y = 10*sin(1/3*qv_x) + 25;
% qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of virtual target
%Set target trajectory moving in sine trajectory WITH noise
qv_x = i + noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
qv_y = 10*sin(1/3*qv_x) + 25 + noise_std * randn + noise_mean;
qv(i,:) = [qv_x, qv_y]; %compute position of target
%Compute the target heading
qt_diff(i,:) =qv(i,:)- qv(i-1,:);
theta_t(i) = atan2(qt_diff(i,2),qt_diff(i,1));
%Calculation
phi=atan2(qrv(i-1,2),qrv(i-1,1));
vrd(i) = sqrt((norm(pv)^2) + 2*lambda*norm(qrv(i-1,:))*abs(cos(theta_t(i)- phi)) + (lambda^2)*(norm(qrv(i-1,:))^2));
if vrd(i)>vr_max
vrd(i)= vr_max;
end
theta_r(i) = phi + asin((norm(pv)*sin(theta_t(i) - phi))/(vrd(i)));
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]葛超,张鑫源,王红,等.改进Informed-RRT*算法的移动机器人路径规划[J/OL].电光与控制:1-11[2024-09-26].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1227.TN.20240925.1741.002.html.
[2]罗济雨,孙丙宇.基于概率运动基元的移动机器人轨迹学习与避障算法研究[J].仪表技术,2024(05):53-56.DOI:10.19432/j.cnki.issn1006-2394.2024.05.007.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现





















 1690
1690

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








