代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.optimize as op
def plotData(X, y):
index0 = list()
index1 = list()
j = 0
for i in y:
if i == 0:
index0.append(j)
else:
index1.append(j)
j = j + 1
plt.scatter(X[index0, 0], X[index0, 1], marker='o')
plt.scatter(X[index1, 0], X[index1, 1], marker='+')
plt.xlabel('Exam 1 score')
plt.ylabel('Exam 2 score')
plt.legend(['y=0', 'y=1'], loc='upper right')
# plt.show()
def mapFeature(X1, X2):
degree = 6
out = np.ones((X1.shape[0], 1))
for i in range(1, degree + 1):
for j in range(0,i+1):
newColum = (X1 ** (i-j))*(X2 ** j)
out = np.column_stack((out, newColum))
return out
def mapFeature1(x1, x2):
degree = 6
out = np.ones((1, 1))
for i in range(1, degree+1):
for j in range(0, i+1):
newColumn = (x1 ** (i - j))*(x2 ** j)
out = np.column_stack((out, newColumn))
return out
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def costFunctionReg_cost(initial_theta, X, y, Lambda):
m, n = np.shape(X)
initial_theta = initial_theta.reshape((n,1))
h = sigmoid(X.dot(initial_theta))
#theta的第一个不参与正则化,需变为0
theta_temp = initial_theta.copy()
theta_temp[0] = 0
#theta_temp = np.row_stack((0 ,initial_theta[1:])) #用这种方法会出BUG
J = (1/m) * np.sum(-1*y*np.log(h) - (1-y)*np.log(1-h)) +\
(Lambda/(2*m)) * np.dot(theta_temp.T,theta_temp)
return J
def costFunctionReg_grad(initial_theta, X, y, Lambda):
m, n = np.shape(X)
initial_theta = initial_theta.reshape((n,1))
h = sigmoid(X.dot(initial_theta))
theta_temp = initial_theta.copy()
theta_temp[0] = 0
#$theta_temp = np.row_stack((0, initial_theta[1:]))
grad = (X.T).dot(h-y) / m + Lambda/m * theta_temp
return grad.flatten()
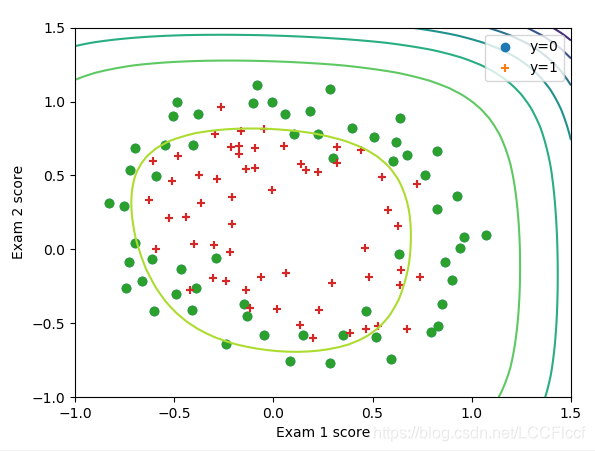
def plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y):
figure = plotData(X[:, 1:], y)
m, n = X.shape
# Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
if n <= 3:
point1 = np.min(X[:, 1])
point2 = np.max(X[:, 1])
point = np.array([point1, point2])
plot_y = -1*(theta[0] + theta[1]*point)/theta[2]
plt.plot(point, plot_y, '-')
plt.legend(['Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Boundary'], loc='lower left')
else:
u = np.linspace(-1, 1.5, 50)
v = u.copy()
z = np.zeros((u.shape[0], v.shape[0]))
for i in range(u.shape[0]):
for j in range(v.shape[0]):
z[i, j] = mapFeature1(u[i], v[j]).dot(theta)
z = z.T
#print(u.shape)
#print(z.shape)
plt.contour(u, v, z)
plt.show()
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ======================load data========================
file = 'ex2data2.txt'
data = np.loadtxt(file, delimiter=',')
X = data[:,:2]
y = data[:,2].reshape((data.shape[0],1))
plotData(X, y)
# =========== Part 1: Regularized Logistic Regression ============
X = mapFeature(X[:,0], X[:,1])
# initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = np.zeros((X.shape[1], 1))
# set regularization parameter lambda to 1
Lambda = 1
cost = costFunctionReg_cost(initial_theta, X, y, Lambda)
grad = costFunctionReg_grad(initial_theta, X, y, Lambda)
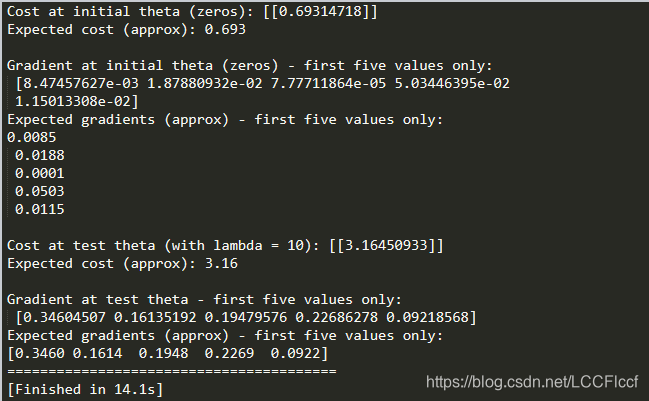
print('Cost at initial theta (zeros):',cost)
print('Expected cost (approx): 0.693\n')
print('Gradient at initial theta (zeros) - first five values only:\n',grad[0:5])
print('Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:')
print('0.0085\n 0.0188\n 0.0001\n 0.0503\n 0.0115\n')
# Compute and display cost and gradient with all-ones theta and lambda = 10
Lambda = 10
test_theta = np.ones((X.shape[1], 1))
cost = costFunctionReg_cost(test_theta, X, y, Lambda)
grad = costFunctionReg_grad(test_theta, X, y, Lambda)
print('Cost at test theta (with lambda = 10):',cost)
print('Expected cost (approx): 3.16\n')
print('Gradient at test theta - first five values only:\n',grad[0:5])
print('Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:')
print('[0.3460\t0.1614\t0.1948\t0.2269\t0.0922]')
print('='*40)
# ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accuracies =============
# Optional Exercise:
# In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
# see how regularization affects the decision coundart
#
# Try the following values of lambda (0, 1, 10, 100).
#
# How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
# the training set accuracy vary?
# Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = np.zeros((X.shape[1], 1))
#set the different lambda
myLambda = 5
#optimize
Result = op.minimize(fun=costFunctionReg_cost, \
x0=initial_theta, \
args=(X,y,myLambda),\
method='TNC',\
jac=costFunctionReg_grad)
theta = Result.x
cost = Result.fun
# Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y)
# end
运行结果
踩到的坑
1、手误把np.ones() 和 np.zeros() 混淆
2、在处理正则化项的theta时出错:自以为是地把theta第一列全部变成0,在合并向量时检索错误(神奇的是,此时计算Lambda=1的结果正确)
正确的做法是把theta的第一项变为0(theta为(n x 1)的列向量)
原因:对正则化理解不透彻
3、array作为参数传入到定义的函数里时,shape可能会改变。这里遇到的坑是:
initial_theta在设定时是(28,1),但到了def costFunctionReg_grad()的肚子里面就变成了(28, ),
如果不reshape一下,就会报错:“ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (28,118) (28,) ”
这是经常踩到的坑!!!!!
























 3108
3108

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








