人工智能混合编程实践:C++调用Python ONNX进行YOLOv8推理
前言
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv10训练自己的数据集(交通标志检测)
- YOLO11训练自己的数据集(吸烟、跌倒行为检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
相关介绍
Python简介
Python 是一种高级编程语言,因其代码的可读性和简洁性而广受欢迎。它支持多种编程范式,包括面向对象、命令式和函数式编程或过程式编程。Python的设计哲学强调代码的可读性,并且其语法允许程序员用比C++或Java等语言更少的代码行表达概念。Python拥有一个庞大的标准库,涵盖了诸如文件I/O、系统调用、网络接口等众多领域,极大地提升了开发效率。
C++简介
C++ 是一种广泛使用的编程语言,最初由丹麦计算机科学家Bjarne Stroustrup于1979年在贝尔实验室开发,作为C语言的扩展。C++的设计目标是提供一种能够高效利用硬件资源,同时支持面向对象编程(OOP)特性的语言。随着时间的发展,C++也引入了泛型编程和函数式编程的支持,使其成为一种多范式编程语言。
ONNX简介
ONNX(Open Neural Network Exchange) 是一个开放的生态系统,旨在促进不同框架之间深度学习模型的互操作性。通过ONNX,开发者可以更容易地在不同的深度学习框架(如PyTorch、TensorFlow等)间共享和部署模型。ONNX定义了一种通用的模型文件格式,使得训练好的模型可以在各种硬件平台上高效运行,无论是服务器端还是边缘设备。这有助于加速机器学习技术的研发和应用。
YOLOv8简介
YOLOv8 实际上是基于YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列目标检测算法的一个版本,YOLO系列算法以其快速、准确的目标检测能力著称,广泛应用于实时物体识别场景中。
[1] YOLOv8 源代码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git.
[2] YOLOv8 官方文档:https://docs.ultralytics.com/
前提条件
- 熟悉Python
- 熟悉C++
- 熟悉VS2019
实验环境
Package Version
------------------- -----------
colorama 0.4.6
coloredlogs 15.0.1
contourpy 1.1.1
cycler 0.12.1
flatbuffers 24.3.25
fonttools 4.55.3
humanfriendly 10.0
imageio 2.35.1
importlib_resources 6.4.5
kiwisolver 1.4.7
lazy_loader 0.4
matplotlib 3.7.5
mpmath 1.3.0
networkx 3.1
numpy 1.24.4
onnxruntime-gpu 1.15.0
open2d 5.2.21
opencv-python 4.10.0.84
packaging 24.2
pillow 10.4.0
pip 24.3.1
protobuf 5.29.1
pyparsing 3.1.4
pyreadline3 3.5.4
python-dateutil 2.9.0.post0
PyWavelets 1.4.1
scikit-image 0.21.0
scipy 1.10.1
setuptools 41.2.0
six 1.17.0
sympy 1.13.3
tifffile 2023.7.10
tqdm 4.67.1
zipp 3.20.2
项目结构
cxx_py_infer_yolov8
├─Cxx_PythonModule
│ └─x64
│ └─Release
│ └─Cxx_PythonModule.tlog
├─cxx_py_infer_call
│ └─x64
│ └─Release
│ └─cxx_py_i.f08a3daa.tlog
├─cxx_py_infer.sln
└─x64
└─Release
├─dst
├─Python38
├─src
│ └─1.png
├─weights
│ └─yolov8s.onnx
└─yolov8_py_infer.py

注:yolov8_py_infer.py的代码,请查阅人工智能混合编程实践:Python ONNX进行YOLOv8推理
C++调用Python ONNX进行YOLOv8推理

C++调用Python的相关dll代码
framework.h
#pragma once
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN // 从 Windows 头文件中排除极少使用的内容
// Windows 头文件
#include <windows.h>
pch.h
// pch.h: 这是预编译标头文件。
// 下方列出的文件仅编译一次,提高了将来生成的生成性能。
// 这还将影响 IntelliSense 性能,包括代码完成和许多代码浏览功能。
// 但是,如果此处列出的文件中的任何一个在生成之间有更新,它们全部都将被重新编译。
// 请勿在此处添加要频繁更新的文件,这将使得性能优势无效。
#ifndef PCH_H
#define PCH_H
// 添加要在此处预编译的标头
#include "framework.h"
#include "cxx_pythonModule.h"
cxx_pythonModule cxx_python_module;
extern "C" _declspec(dllexport) bool algorithmPythonInit(const std::string yolo_model_path);
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) bool algorithmPyDetectYOLO(const cv::Mat image, const std::string image_name, std::vector<int>&classID, std::vector<float>&confidenceVal, std::vector<cv::Rect>&rectangles);
#endif //PCH_H
cxx_pythonModule.h
#pragma once
#include <Python.h>
#include <numpy/arrayobject.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <tuple>
#include <opencv2/core/utils/filesystem.hpp> // For cv::glob
#include <chrono> // For measuring time
using namespace cv;
class cxx_pythonModule
{
public:
cxx_pythonModule();
~cxx_pythonModule();
//整体初始化
void PythonInitialize(const std::string yolo_model_path);
void YOLOPyDetection(const cv::Mat image, const std::string image_name, std::vector<int>& classID, std::vector<float>& confidenceVals, std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles);
private:
// 全局或静态变量来存储Python模块和函数
PyObject* g_pONNXInferencer = nullptr;
PyObject* g_pModule = nullptr;
//PyObject* pyArray = nullptr;
PyObject* g_pONNXInferencer_YOLO = nullptr;
PyObject* g_pModule_YOLO = nullptr;
//PyObject* pyArray_YOLO = nullptr;
std::string model_path ;
std::string metadata_path;
int input_width;
int input_height;
std::tuple<std::vector<int>, std::vector<float>, std::vector<cv::Rect>> yolo_infer_and_parse(const cv::Mat& image, const std::string& image_name);
PyObject* mat_to_numpy(const cv::Mat& mat);
void check_python_error();
std::vector<int> parse_numpy_array_to_int_vector(PyObject* pArray);
std::vector<float> parse_numpy_array_to_float_vector(PyObject* pArray);
std::vector<cv::Rect>parse_numpy_array_to_rectangles(PyObject* pValue);
cv::Mat parse_numpy_to_mat(PyObject* pReturnValue);
void print_rectangles(const std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles);
void print_classids(const std::vector<int>& classID);
void print_scores(const std::vector<float>& confidenceVals);
void cleanup_python();
};
#pragma once
dllmain.cpp
// dllmain.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的入口点。
#include "pch.h"
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HMODULE hModule,
DWORD ul_reason_for_call,
LPVOID lpReserved
)
{
switch (ul_reason_for_call)
{
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
break;
}
return TRUE;
}
pch.cpp
// pch.cpp: 与预编译标头对应的源文件
#include "pch.h"
// 当使用预编译的头时,需要使用此源文件,编译才能成功。
bool algorithmPythonInit(const std::string yolo_model_path)
{
cxx_python_module.PythonInitialize(yolo_model_path);
return true;
}
bool algorithmPyDetectYOLO(const cv::Mat image, const std::string image_name, std::vector<int>& classID, std::vector<float>& confidenceVals, std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles)
{
cxx_python_module.YOLOPyDetection(image, image_name, classID, confidenceVals, rectangles);
return true;
}
cxx_pythonModule.cpp
// pch.h: 这是预编译标头文件。
// 下方列出的文件仅编译一次,提高了将来生成的生成性能。
// 这还将影响 IntelliSense 性能,包括代码完成和许多代码浏览功能。
// 但是,如果此处列出的文件中的任何一个在生成之间有更新,它们全部都将被重新编译。
// 请勿在此处添加要频繁更新的文件,这将使得性能优势无效。
#include "pch.h"
#include "cxx_pythonModule.h"
cxx_pythonModule::cxx_pythonModule()
{
}
cxx_pythonModule::~cxx_pythonModule()
{
cleanup_python();
}
void cxx_pythonModule::PythonInitialize(const std::string yolo_model_path)
{
Py_SetPythonHome((wchar_t*)L"./Python38");
if (Py_IsInitialized()) return;
Py_Initialize();
// 初始化 NumPy C API
import_array();
// 设置Python路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('.')");
//获取当前 Python 环境信息
PyRun_SimpleString(
"print('Python version:', sys.version)\n"
"print('Python executable:', sys.executable)\n"
"print('Python path:', sys.path)"
);
//YOLOv8
// 导入Python模块
g_pModule_YOLO = PyImport_ImportModule("yolov8_py_infer"); // python脚本
if (g_pModule_YOLO == NULL) {
check_python_error();
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to import Python module 'yolov8_py_infer'");
}
// 获取Python类
PyObject* g_pClassInferencer_YOLO = PyObject_GetAttrString(g_pModule_YOLO, "YOLOv8ObjectDetector");
if (g_pClassInferencer_YOLO == NULL || !PyType_Check(g_pClassInferencer_YOLO)) {
check_python_error();
Py_DECREF(g_pClassInferencer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(g_pModule_YOLO);
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to get class 'YOLOv8ObjectDetector'");
}
// 构建参数
PyObject* pArgs_YOLO = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs_YOLO, 0, PyUnicode_FromString(yolo_model_path.c_str()));
// 创建 ONNXInferencer 实例
g_pONNXInferencer_YOLO = PyObject_CallObject(g_pClassInferencer_YOLO, pArgs_YOLO);
if (g_pONNXInferencer_YOLO == NULL) {
check_python_error();
Py_DECREF(pArgs_YOLO);
//Py_DECREF(g_pClassInferencer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(g_pModule_YOLO);
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to create instance of 'YOLOv8'");
}
}
void cxx_pythonModule::YOLOPyDetection(const cv::Mat image, const std::string image_name, std::vector<int>& classID, std::vector<float>& confidenceVals, std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles)
{
// 调用 infer_and_parse 函数
std::tie(classID, confidenceVals, rectangles) = yolo_infer_and_parse(image, image_name);
// 返回的框大小需要重新映射会原图大小
std::cout << "YOLOPyDetection" << std::endl;
/*cxx_pythonModule::print_classids(classID);
cxx_pythonModule::print_scores(confidenceVal);
cxx_pythonModule::print_rectangles(rectangles);*/
// 打印结果
for (size_t i = 0; i < classID.size(); ++i) {
std::cout << "Class ID: " << classID[i]
<< ", Score: " << confidenceVals[i]
<< ", Box: (" << rectangles[i].x << ", " << rectangles[i].y
<< ", " << rectangles[i].width << ", " << rectangles[i].height << ")" << std::endl;
}
}
// 调用 Python 的 yolo 方法并解析结果
std::tuple<std::vector<int>, std::vector<float>, std::vector<cv::Rect>> cxx_pythonModule::yolo_infer_and_parse(const cv::Mat& image, const std::string& image_name) {
// 构建参数
PyObject* pArgsInfer_YOLO = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgsInfer_YOLO, 0, mat_to_numpy(image)); // 传递图像的 NumPy 表示
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgsInfer_YOLO, 1, PyUnicode_FromString(image_name.c_str()));
// 确保获取 GIL
PyGILState_STATE gstate = PyGILState_Ensure();
// 获取 detect_object 方法
PyObject* pMethodInfer_YOLO = PyObject_GetAttrString(g_pONNXInferencer_YOLO, "detect_object");
if (pMethodInfer_YOLO && !PyCallable_Check(pMethodInfer_YOLO)) {
check_python_error();
Py_DECREF(pMethodInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pArgsInfer_YOLO);
PyGILState_Release(gstate); // 释放 GIL
throw std::runtime_error("Method 'detect_object' is not callable");
}
// 调用 Python 方法
PyObject* pReturnValueInfer_YOLO = PyObject_CallObject(pMethodInfer_YOLO, pArgsInfer_YOLO);
if (pReturnValueInfer_YOLO == NULL) {
check_python_error(); // 打印 Python 错误信息
PyErr_Clear(); // 清除 Python 异常状态
Py_DECREF(pMethodInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pArgsInfer_YOLO);
PyGILState_Release(gstate); // 释放 GIL
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to call Python method 'detect_object'");
}
// 检查返回值是否为元组且包含三个元素
if (!PyTuple_Check(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO) || PyTuple_Size(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO) != 3) {
check_python_error();
Py_DECREF(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pMethodInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pArgsInfer_YOLO);
PyGILState_Release(gstate); // 释放 GIL
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid return value from Python method 'detect_object'");
}
// 获取元组中的第一个元素(类别ID)
PyObject* pClassIds_YOLO = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO, 0);
std::vector<int> class_ids_YOLO = parse_numpy_array_to_int_vector(pClassIds_YOLO);
// 获取元组中的第二个元素(置信度)
PyObject* pScores_YOLO = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO, 1);
std::vector<float> scores_YOLO = parse_numpy_array_to_float_vector(pScores_YOLO);
// 获取元组中的第三个元素(检测框)
PyObject* pBoxes_YOLO = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO, 2);
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes_YOLO = parse_numpy_array_to_rectangles(pBoxes_YOLO);
// 释放 Python 对象
Py_DECREF(pReturnValueInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pMethodInfer_YOLO);
Py_DECREF(pArgsInfer_YOLO);
PyGILState_Release(gstate); // 释放 GIL
return std::make_tuple(class_ids_YOLO, scores_YOLO, boxes_YOLO);
}
// 解析 Python 返回值并转换为 cv::Mat
cv::Mat cxx_pythonModule::parse_numpy_to_mat(PyObject* pReturnValue) {
if (!PyArray_Check(pReturnValue)) {
throw std::runtime_error("Return value from Python is not a NumPy array.");
}
// 获取 NumPy 数组的指针和信息
PyArrayObject* pArray = reinterpret_cast<PyArrayObject*>(pReturnValue);
void* data = PyArray_DATA(pArray);
int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(pArray);
npy_intp* shape = PyArray_SHAPE(pArray);
int type = PyArray_TYPE(pArray);
//// 检查维度是否正确
//if (ndims != 3) {
// throw std::runtime_error("NumPy array must have 3 dimensions (height, width, channels).");
//}
// 获取图像的高度、宽度和通道数
int rows = shape[0];
int cols = shape[1];
int channels;
if (ndims != 3) {
channels = 1;
}
else {
channels = shape[2];
}
// 根据数据类型创建 cv::Mat
cv::Mat result;
if (type == NPY_UINT8) {
result = cv::Mat(rows, cols, CV_8UC(channels), data).clone();
}
else if (type == NPY_UINT16) {
result = cv::Mat(rows, cols, CV_16UC(channels), data).clone();
}
else {
throw std::runtime_error("Unsupported NumPy array data type.");
}
return result;
}
// 将 cv::Mat 转换为 PyArrayObject * ,支持 8 位和 16 位图像
PyObject * cxx_pythonModule::mat_to_numpy(const cv::Mat & mat) {
if (mat.empty()) {
throw std::runtime_error("Input cv::Mat is empty.");
}
// 确保 Mat 是连续的
cv::Mat continuous_mat;
if (!mat.isContinuous()) {
continuous_mat = mat.clone();
}
else {
continuous_mat = mat;
}
// 获取 Mat 的尺寸和类型
int dims[] = { continuous_mat.rows, continuous_mat.cols, continuous_mat.channels() };
npy_intp shape[3] = { dims[0], dims[1], dims[2] };
// 根据 cv::Mat 的数据类型选择 NumPy 数据类型
int numpy_type;
switch (continuous_mat.depth()) {
case CV_8U: numpy_type = NPY_UINT8; break;
case CV_16U: numpy_type = NPY_UINT16; break;
default:
throw std::runtime_error("Unsupported cv::Mat data type.");
}
// 创建 NumPy 数组,不设置 NPY_ARRAY_OWNDATA
PyObject* pArray = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(3, shape, numpy_type, continuous_mat.data);
// 确保 NumPy 不会释放数据
Py_INCREF(pArray); // 增加引用计数,防止 NumPy 销毁数据
return pArray;
}
// 辅助函数:检查Python错误并打印
void cxx_pythonModule::check_python_error() {
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
PyErr_Print();
std::cerr << "Python error occurred." << std::endl;
}
}
// 解析 NumPy 数组为 std::vector<int>(类别ID)
std::vector<int> cxx_pythonModule::parse_numpy_array_to_int_vector(PyObject* pArray) {
if (!PyArray_Check(pArray)) {
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid NumPy array for class IDs");
}
PyArrayObject* np_array = (PyArrayObject*)pArray;
int length = PyArray_SIZE(np_array);
std::vector<int> result(length);
memcpy(result.data(), PyArray_DATA(np_array), length * sizeof(int));
return result;
}
// 解析 NumPy 数组为 std::vector<float>(置信度)
std::vector<float> cxx_pythonModule::parse_numpy_array_to_float_vector(PyObject* pArray) {
if (!PyArray_Check(pArray)) {
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid NumPy array for scores");
}
PyArrayObject* np_array = (PyArrayObject*)pArray;
int length = PyArray_SIZE(np_array);
std::vector<float> result(length);
memcpy(result.data(), PyArray_DATA(np_array), length * sizeof(float));
return result;
}
// 解析 NumPy 数组为 std::vector<cv::Rect>(检测框)
std::vector<cv::Rect> cxx_pythonModule::parse_numpy_array_to_rectangles(PyObject* pArray) {
if (!PyArray_Check(pArray)) {
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid NumPy array for boxes");
}
PyArrayObject* np_array = (PyArrayObject*)pArray;
int num_boxes = PyArray_DIMS(np_array)[0];
std::vector<cv::Rect> result(num_boxes);
for (int i = 0; i < num_boxes; ++i) {
int x = ((int*)PyArray_GETPTR2(np_array, i, 0))[0];
int y = ((int*)PyArray_GETPTR2(np_array, i, 1))[0];
int w = ((int*)PyArray_GETPTR2(np_array, i, 2))[0];
int h = ((int*)PyArray_GETPTR2(np_array, i, 3))[0];
result[i] = cv::Rect(x, y, w, h);
}
return result;
}
// 打印矩形框信息
void cxx_pythonModule::print_rectangles(const std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < rectangles.size(); ++i) {
const cv::Rect& rect = rectangles[i];
std::cout << "Rectangle " << i + 1 << ": "
<< "x=" << rect.x << ", "
<< "y=" << rect.y << ", "
<< "width=" << rect.width << ", "
<< "height=" << rect.height << std::endl;
}
}
void cxx_pythonModule::print_classids(const std::vector<int>& classID) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < classID.size(); ++i) {
const int id = classID[i];
std::cout << "id=" << id << std::endl;
}
}
void cxx_pythonModule::print_scores(const std::vector<float>& confidenceVals) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < confidenceVals.size(); ++i) {
const float score = confidenceVals[i];
std::cout << "score=" << confidenceVals[i] << std::endl;
}
}
// 清理Python环境
void cxx_pythonModule::cleanup_python() {
if (g_pONNXInferencer != NULL) {
Py_DECREF(g_pONNXInferencer);
g_pONNXInferencer = NULL;
}
if (g_pModule != NULL) {
Py_DECREF(g_pModule);
g_pModule = NULL;
}
if (Py_IsInitialized()) {
Py_Finalize();
}
}
C++调用Python代码的主函数
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 定义函数指针类型
//python模块初始化
typedef bool(*algorithmPythonInit)(const std::string yolo_model_path);
//yolov8模块
typedef bool (*algorithmPyDetectYOLO)(const cv::Mat image, const std::string image_name, std::vector<int>& classID, std::vector<float>& confidenceVal, std::vector<cv::Rect>& rectangles);
algorithmPythonInit alg_PythonInit;
algorithmPyDetectYOLO alg_PyDetectYOLO;
int main() {
//load dll
HINSTANCE hdll1 = LoadLibrary(L"Cxx_PythonModule.dll");
std::cout << GetLastError() << endl;
if (hdll1 == NULL)
{
FreeLibrary(hdll1);
printf("dll miss %d \n", __LINE__);
return -1;
}
//环境初始化
alg_PythonInit = (algorithmPythonInit)GetProcAddress(hdll1, "algorithmPythonInit");
//yolov8检测
alg_PyDetectYOLO = (algorithmPyDetectYOLO)GetProcAddress(hdll1, "algorithmPyDetectYOLO");
string yolo_model_path = "./weights/yolov8s.onnx";
//初始化python模块相关环境
alg_PythonInit(yolo_model_path);
clock_t start = clock();
// 图片路径
string dataPath = "./src";
//结果路径
string DesPath = "./dst/";
//glob
std::string pattern = dataPath + "/*.png";
vector<cv::String> fileNames;
cv::glob(pattern, fileNames, true);
cout << "fileNames.size=" << fileNames.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < fileNames.size(); i++)
{
String ImgName = fileNames[i];
//-1 在OpenCV中对应的是 cv::IMREAD_UNCHANGED 标志,表示以原始格式读取图像,包括其原有的色彩通道和深度。
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(fileNames[i], -1);
//1.获取不带路径的文件名
string::size_type iPos = fileNames[i].find_last_of('\\') + 1;
string filename = fileNames[i].substr(iPos, fileNames[i].length() - iPos);
cout << "filename:" << filename << endl;
cout << " line " << __LINE__ << " file " << __FILE__ << endl;
//2.获取不带后缀的文件名
string name = filename.substr(0, filename.rfind("."));
cout << "name:" << name << endl;
string image_name = name;
if (image.empty())
continue;
clock_t start = clock();
int result = 0;
cv::Mat img = image.clone();
vector<cv::Rect> rectangles;
std::vector<int> classID;
std::vector<float> confidenceVals;
result = alg_PyDetectYOLO(img, filename, classID, confidenceVals, rectangles);
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "result = " << result << " , time = " << end - start << " ms" << endl;
cout << " line " << __LINE__ << " file " << __FILE__ << std::endl;
}
cout << "===============================" << endl;
cout << " 遍历结束 " << endl;
cout << "===============================" << endl;
return 0;
}
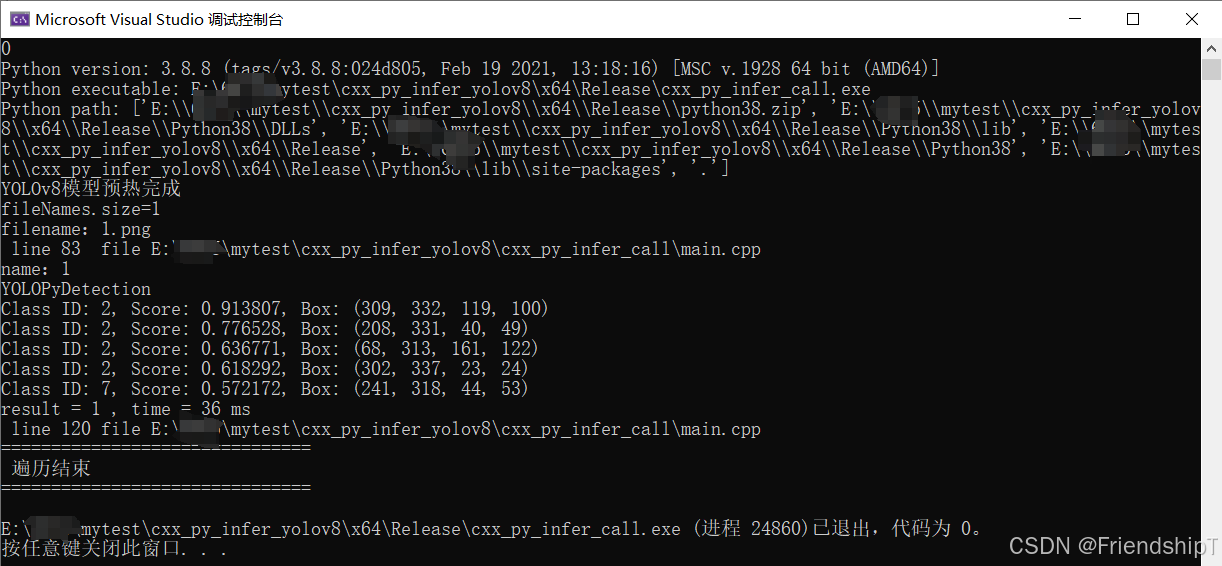
YOLOv8模型预热完成
fileNames.size=1
filename:1.png
name:1
YOLOPyDetection
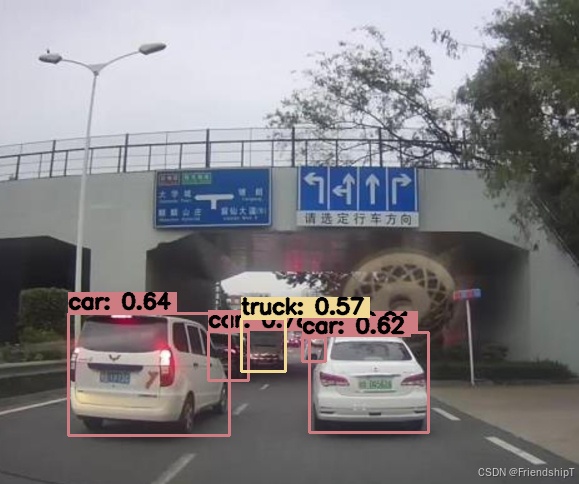
Class ID: 2, Score: 0.913807, Box: (309, 332, 119, 100)
Class ID: 2, Score: 0.776528, Box: (208, 331, 40, 49)
Class ID: 2, Score: 0.636771, Box: (68, 313, 161, 122)
Class ID: 2, Score: 0.618292, Box: (302, 337, 23, 24)
Class ID: 7, Score: 0.572172, Box: (241, 318, 44, 53)
result = 1 , time = 36 ms

参考文献
[1] YOLOv8 源代码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git.
[2] YOLOv8 官方文档:https://docs.ultralytics.com/
[3] YOLO11 源代码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git
[4] YOLO11 官方文档:https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolo11/
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv10训练自己的数据集(交通标志检测)
- YOLO11训练自己的数据集(吸烟、跌倒行为检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目

























 267
267

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










