BFS: Shortest Reach in a Graph
Challenge Name: BFS: Shortest Reach in a Graph
Consider an undirected graph consisting of n n nodes where each node is labeled from to n n and the edge between any two nodes is always of length . We define node s s to be the starting position for a BFS. Given a graph, determine the distances from the start node to each of its descendants and return the list in node number order, ascending. If a node is disconnected, it’s distance should be .
For example, there are n=6 n = 6 nodes in the graph with a starting node s=1 s = 1 . The list of edges=[[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,5]] e d g e s = [ [ 1 , 2 ] , [ 2 , 3 ] , [ 3 , 4 ] , [ 1 , 5 ] ] , and each has a weight of 6 6 .
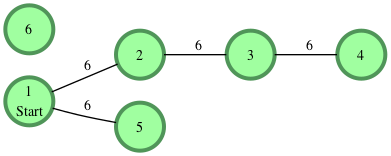
Starting from node and creating a list of distances, for nodes 2 2 through we have distances=[6,12,18,6,−1] d i s t a n c e s = [ 6 , 12 , 18 , 6 , − 1 ] .
Function Description
Define a Graph class with the required methods to return a list of distances.
这道题要求用广度优先遍历图,找到两个节点的最短路径。之前复习了广度优先,实现的办法是引入一个队列。至于图的实现办法,就是用一个二维矩阵,建立两点的映射,两点相连的话该值就为1,不相连为0。
在HackerRank上面做题很头疼的一点是它会给出一些巨大的测试集,无脑用vector的话很容易timeout,就像Merge Sort Counting Inversions里面经历的,这次我也经历了timeout,好在最后都解决了。这一次导致超时的地方是在bfs中,我们会检测节点是否已经经过。最开始我无脑的把整个图复制了vector<vector<int>> seen(graph),而这显然是没有必要的,我们只需要一个长度为n的vector就足够。
做题过程中遇到的另一个问题是distances的记录,最初我用一个count变量,每pop一次就+1,但这会导致count记录的是经过的全部节点数,而不是节点的层数。
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
public:
Graph(int n) {
vector<int> tmp(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.push_back(tmp);
}
this->n = n;
}
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
graph[u][v] = 1;
graph[v][u] = 1;
}
int bfs(int start, int end) {
vector<int> seen(n);
queue<int> que;
que.push(start);
seen[start] = 1;
int distances[n] = {0};
while (!que.empty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (graph[que.front()][i] == 1 && seen[i]==0) {
distances[i] = distances[que.front()]+6;
if (i == end) return distances[i];
que.push(i);
seen[i] = 1;
}
}
que.pop();
}
return -1;
}
vector<int> shortest_reach(int start) {
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res.push_back(bfs(start, i));
}
return res;
}
};
int main() {
int queries;
cin >> queries;
for (int t = 0; t < queries; t++) {
int n, m;
cin >> n;
// Create a graph of size n where each edge weight is 6:
Graph graph(n);
cin >> m;
// read and set edges
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
u--, v--;
// add each edge to the graph
graph.add_edge(u, v);
}
int startId;
cin >> startId;
startId--;
// Find shortest reach from node s
vector<int> distances = graph.shortest_reach(startId);
for (int i = 0; i < distances.size(); i++) {
if (i != startId) {
cout << distances[i] << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}






 本文介绍了一个关于图论的挑战,利用BFS算法寻找从起始节点到图中所有节点的最短距离。题目中给出了一个包含6个节点的无向图,起始节点为1,边长均为6。通过优化广度优先搜索避免超时问题,正确记录每个节点的距离。
本文介绍了一个关于图论的挑战,利用BFS算法寻找从起始节点到图中所有节点的最短距离。题目中给出了一个包含6个节点的无向图,起始节点为1,边长均为6。通过优化广度优先搜索避免超时问题,正确记录每个节点的距离。
















 449
449

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








