使用python爬虫爬取小说
喜欢看网络小说的朋友们,经常需要从网上下载小说。有些人不想向正版网页交钱,也不想注册其他网站的账号,那么对于某些比较冷门的小说或者是正在更新的小说来说,就很难下载到txt或者其他格式的小说。我就是不想花太多时间找冷门小说的下载资源,因此稍微学习了python的爬虫知识。
新建scrapy爬虫项目
scrapy是python的爬虫框架。使用以下语句安装scrapy。
pip install scrapy安装完成后,打开命令行窗口,转到你想建立project的目录下,使用下面这句话新建scrapy项目。
scrapy startproject ebook新建后就会出现一些基础代码框架。然后,
cd ebook
scrapy genspider example example.com使用genspider根据模板创建一个爬虫,在项目的spider目录下就会多一个example.py文件
实例一
第一个例子,我选取了起点中文网。在起点上随便选择了一本小说。
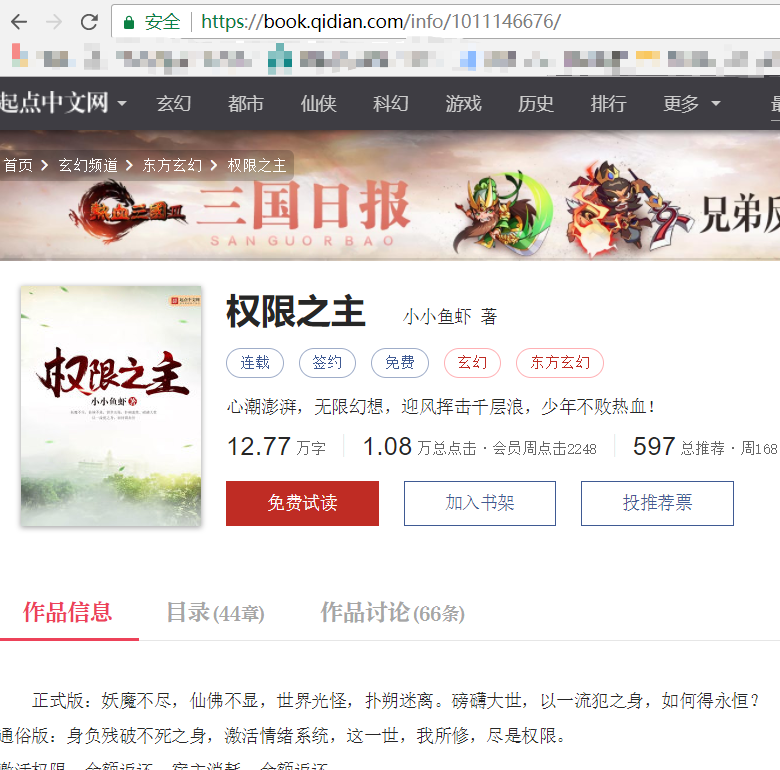
scrapy genspider qxzz qidian.com使用这句话创建了qxzz.py文件。打开后,如下图。
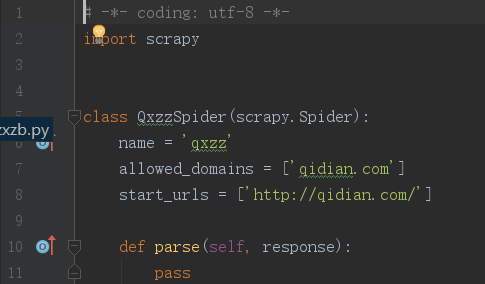
将start_urls中的内容改为这本小说的地址。然后,打开浏览器右上角“更多工具”——>“开发者工具”(chrome)就可以看到下图的样子。
爬取章节地址
打开浏览器右上角“更多工具”——>“开发者工具”(chrome)就可以看到下图的样子。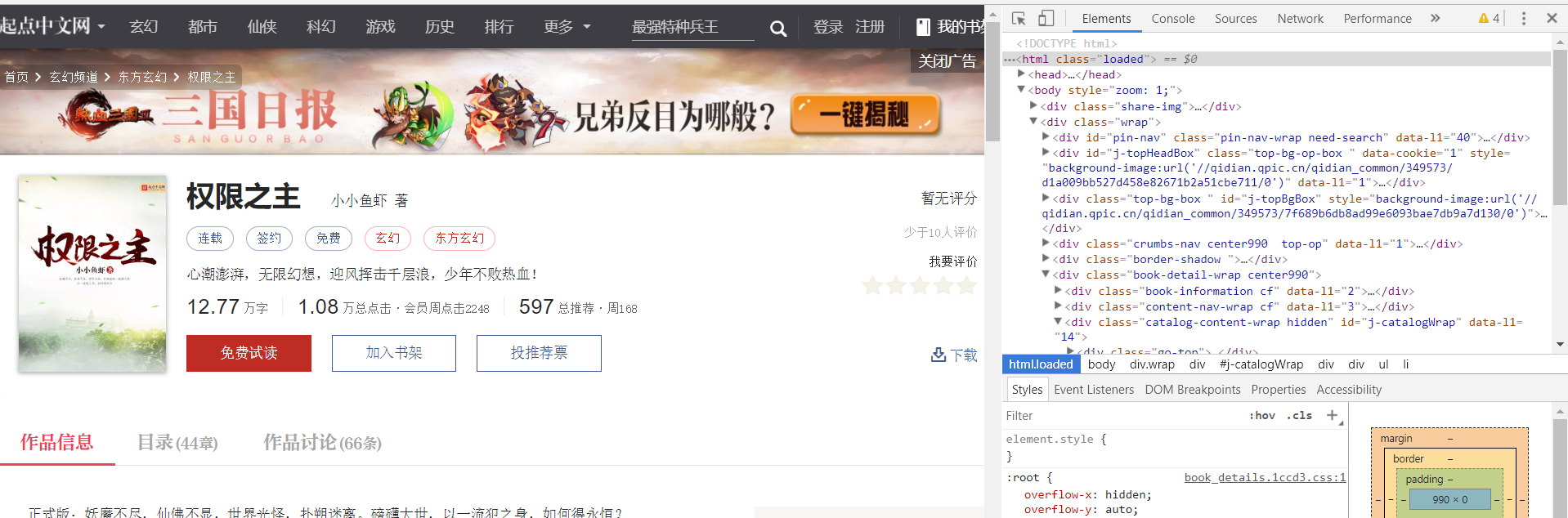
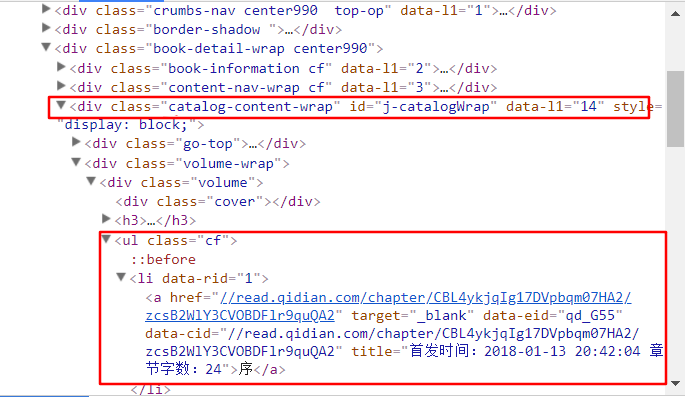
在右边的窗口中找到目录所在的标签。就在下图的第一个方框中,每一章节的内容在第二个方框中。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class QxzzSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'qxzz'
allowed_domains = ['qidian.com']
start_urls = ['https://book.qidian.com/info/1011146676/']
def parse(self, response):
# 获取目录列表
pages = response.xpath('//div[@id="j-catalogWrap"]//ul[@class="cf"]/li')
for page in pages: # 遍历子节点,查询li标签内a子节点的href属性
url = page.xpath('./child::a/attribute::href').extract_first()
print url程序编写完之后,在命令行运行下面语句查看结果
scrapy crawl qxzz输出结果如下
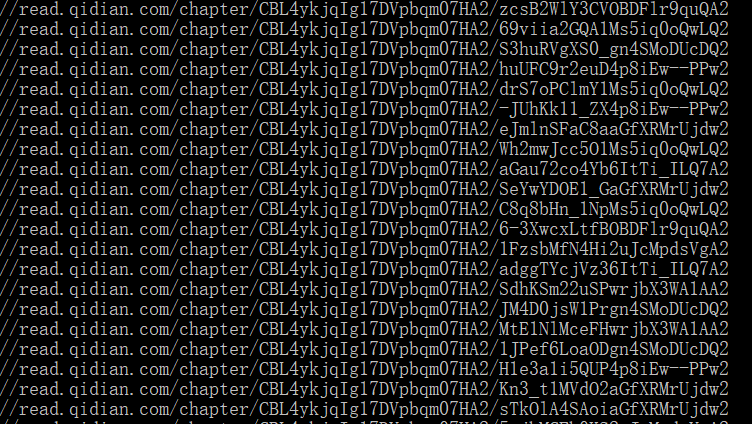
如果你碰到“No module named win32api”的错误,pip install pypiwin32 即可。
爬取每章内容
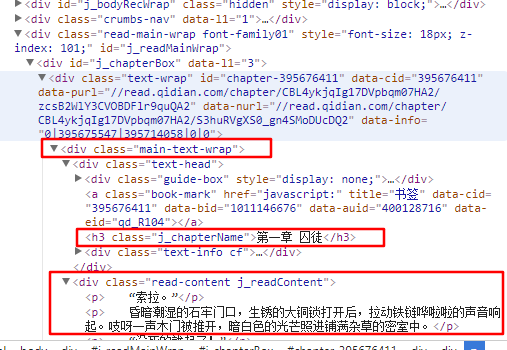
从图中我们可以看出,整个章节在main-text-wrap标签(即第一个框)中,章节名在第二个框中,正文在第三个框中。修改后的代码如下。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class QxzzSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'qxzz'
allowed_domains = ['qidian.com']
start_urls = ['https://book.qidian.com/info/1011146676/']
def parse(self, response):
pages = response.xpath('//div[@id="j-catalogWrap"]//ul[@class="cf"]/li')
for page in pages:
url = page.xpath('./child::a/attribute::href').extract_first()
req = response.follow(url, callback=self.parse_chapter)
yield req
def parse_chapter(self, response):
title = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-text-wrap"]'
'//h3[@class="j_chapterName"]/text()')\
.extract_first().strip()
content = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-text-wrap"]'
'//div[@class="read-content j_readContent"]')\
.extract_first().strip()内容的保存
在爬取内容后,可以以html的形式保存。而为了排序的方便,需要给文件名加一个序号。在起点网上,刚好在li标签内有“data-rid”可以作为序号。修改后代码如下。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
class QxzzSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'qxzz'
allowed_domains = ['qidian.com']
start_urls = ['https://book.qidian.com/info/1011146676/']
def parse(self, response):
pages = response.xpath('//div[@id="j-catalogWrap"]//ul[@class="cf"]/li')
for page in pages:
url = page.xpath('./child::a/attribute::href').extract_first()
idx = page.xpath('./attribute::data-rid').extract_first()
req = response.follow(url, callback=self.parse_chapter)
req.meta['idx'] = idx
yield req
def parse_chapter(self, response):
idx = response.meta['idx']
title = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-text-wrap"]'
'//h3[@class="j_chapterName"]/text()')\
.extract_first().strip()
content = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-text-wrap"]'
'//div[@class="read-content j_readContent"]')\
.extract_first().strip()
filename = './down/%s_%s.html' % (idx, title)
cnt = '<h1>%s</h1> %s' % (title, content)
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(cnt.encode('utf-8'))记住,需要现在目录下新建down文件夹,否则可能会出错。
同一个网站,电子书网页的源代码架构都应该是一样的,因此,只需改变一条网址的语句,就可以爬取该网站的其他电子书。
在爬取结束并且保存后,可以通过Sigil来制作epub电子书,也可以转换成其他格式。
实例二
第二个例子没有新的知识,只是为了更加熟悉这些内容。
第二个例子选择的是下面这本小说。
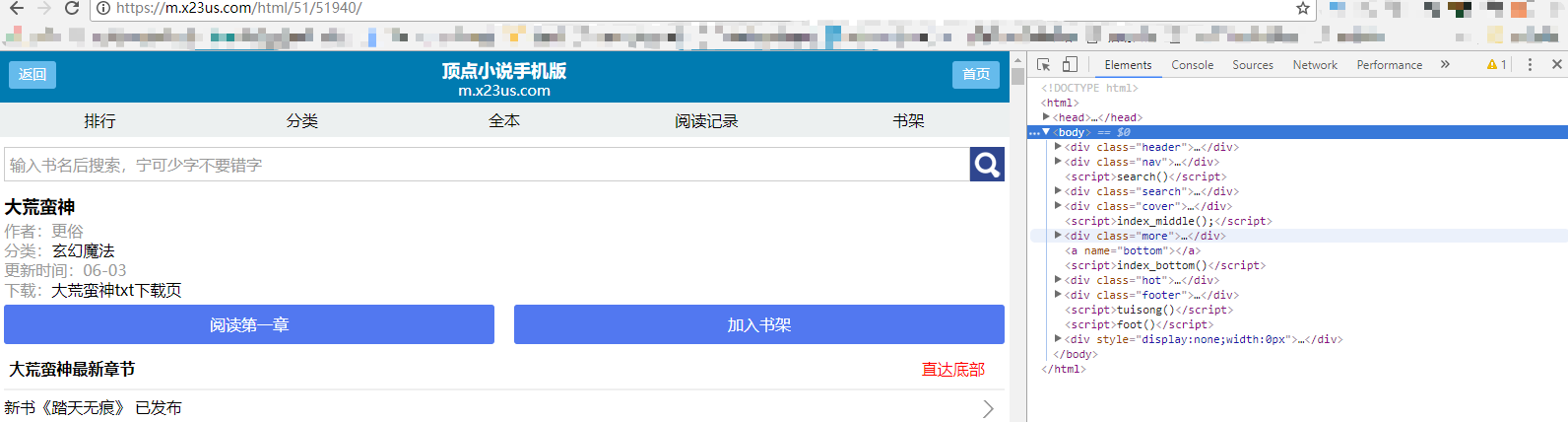
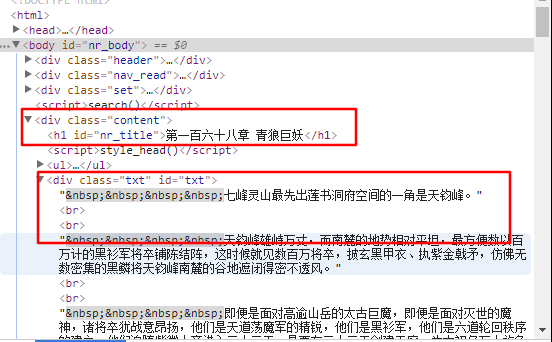
目录和正文内容所在的标签都在下面的图中框出。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from numpy import *
class DmhsSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'dmhs'
allowed_domains = ['m.x23us.com']
start_urls = ['https://m.x23us.com/html/51/51940/']
def parse(self, response):
pages = response.xpath('//div[@class="cover"]//ul[@class="chapter"]/li')
# pages = response.xpath('//ul[@class="chapter"]/li')
for page in pages:
url = page.xpath('./child::a/attribute::href').extract_first()
idx = str(url[0:8])
req = response.follow(url, callback=self.parse_chapter)
req.meta['idx'] = idx
yield req
def parse_chapter(self, response):
idx = response.meta['idx']
title = response.xpath('//div[@class="content"]//h1[@id="nr_title"]/text()')\
.extract_first().strip()
content = response.xpath('//div[@class="content"]//div[@class = "txt"]')\
.extract_first().strip()
filename = './down/%s_%s.html' % (idx, title)
cnt = '<h1>%s</h1> %s' % (title, content)
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(cnt.encode('utf-8'))在这个网站中,没有类似“data-rid”的东西,但又发现每章节的网页地址的数字是随章节号而递增的,因此截取网页地址中的数字来排序保存后的html文件。其他都与例子一相同。
结语
需求才是学习的动力啊。
版本信息
1.0 20180209

本作品采用知识共享署名-相同方式共享 3.0 未本地化版本许可协议进行许可。





















 5070
5070










