Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 14750 Accepted Submission(s): 4241
Problem Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
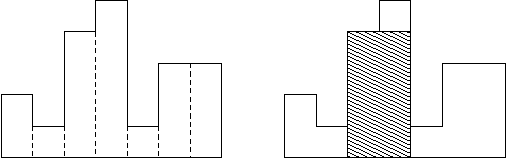
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
Source
【题意】:给出每个矩形高度,宽相同,求出最大矩形面积
【思路】:可以把所有点从左到右将连续比其大的点的长度扫一遍得到l[i],同理从右到左也扫一遍得到r[i],将(r[i]-l[i]+1)*h[i]就是该点的矩形的面积
【新东西】:可以将l[i]和r[i]存起来,这样扫的时候就不用一个一个扫,可以直接跳到l[t-1]的点继续扫,大大优化了程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#define F first
#define S second
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define E exp(1.0)
#define INF 0xFFFFFFF
#define MAX -INF
#define len(a) (__int64)strlen(a)
#define mem0(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
#define mem1(a) (memset(a,-1,sizeof(a)))
using namespace std;
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) {
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) {
return a < b ? a : b;
}
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
__int64 l[100010],r[100010],h[100010];
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
__int64 n,i,t;
while(scanf("%I64d",&n)!=EOF&&n)
{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&h[i]);
}
l[1]=1;r[n]=n;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
t=i;
while(t>1&&h[i]<=h[t-1])//求每个点左边连续比它大的最左边的下标,保存在l[]数组里
{
t=l[t-1];
}
l[i]=t;
}
for(i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
{
t=i;
while(t<n&&h[i]<=h[t+1])//求每个点右边连续比它大的最右边的下标,保存在r[]数组里
{
t=r[t+1];
}
r[i]=t;
}
__int64 maxx=0,temp;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
temp=(r[i]-l[i]+1)*h[i];
if(temp>maxx)maxx=temp;
}
printf("%I64d\n",maxx);
}
}





 本文探讨了如何解决HDU 1506问题,即在直方图中找到最大的矩形区域。通过动态规划(DP)方法,详细解析了寻找最大子矩阵的思路和步骤。
本文探讨了如何解决HDU 1506问题,即在直方图中找到最大的矩形区域。通过动态规划(DP)方法,详细解析了寻找最大子矩阵的思路和步骤。
















 417
417

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








