FROM
- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
我的环境
- 语言环境:Python 3.10.12
- 开发工具:Jupyter Lab
- 深度学习环境:
- torch==2.3.1+cu121
- torchvision==0.18.1+cu121
一、本周内容
1. DenseNet
DenseNet(密集连接卷积网络)凭借其独特的连接方式和高效的特征传递机制脱颖而出。在传统卷积网络中,随着网络深度的增加,特征图往往会丢失部分信息。而DenseNet通过将每个卷积层的输出特征图与后续所有层的输入特征图进行拼接,实现了特征的密集连接。这种设计使得网络中的每一层都能直接访问前面所有层的特征,极大地增强了特征的复用性和传递效率,有效缓解了深层网络中的梯度消失和特征丢失问题。
在处理复杂的图像分类任务时,DenseNet能够更好地捕捉到图像中的细节特征,并将这些特征有效地传递到网络的深层,从而提高了模型的分类准确率。此外,DenseNet的这种连接方式还减少了网络参数的数量,使得模型在保持高性能的同时,具有更高的计算效率和更小的内存占用,这对于实际应用中的模型部署具有重要意义。
2. SE模块
SE模块作为一种轻量级的注意力机制,其核心思想是通过学习通道间的权重关系,对特征图的通道进行加权,从而增强重要特征的表达,抑制不重要特征的影响。在DenseNet中引入SE模块,可以进一步提升模型对特征的感知能力,使模型更加关注于对分类任务有关键作用的特征。
在实现SE模块的过程中,通过全局平均池化对特征图进行压缩,得到一个通道描述子,然后通过两个全连接层(瓶颈结构)学习通道间的权重关系,并利用sigmod函数将权重归一化到0到1之间,最后将这些权重应用于原始特征图的通道上。
3. 整合
在DenseNet的每个DenseBlock之后添加SE模块,需要确保SE模块的输入和输出特征图的尺寸和通道数与DenseBlock相匹配,这涉及到对特征图尺寸和通道数的精确计算和调整。
二、核心代码及运行截图
dense.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, blocks, num_channels, growth_rate, bn_axis):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn_axis = bn_axis
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(blocks):
self.layers.append(ConvBlock(num_channels, growth_rate, bn_axis))
num_channels += growth_rate
def forward(self, x):
for layer in self.layers:
x = torch.cat([x, layer(x)], dim=self.bn_axis)
num_channels = x.size(self.bn_axis) # 更新num_channels
return x
class ConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, growth_rate, bn_axis):
super(ConvBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn_axis = bn_axis
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels, eps=1.001e-5)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 4 * growth_rate, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(4 * growth_rate, eps=1.001e-5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(4 * growth_rate, growth_rate, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = F.relu(self.bn1(x))
x1 = self.conv1(x1)
x1 = F.relu(self.bn2(x1))
x1 = self.conv2(x1)
return x1
class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, reduction, bn_axis):
super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn_axis = bn_axis
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels, eps=1.001e-5)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, int(num_channels * reduction), kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0) # 严格减半
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn(x))
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.pool(x)
return x
class SqueezeExcitationLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, filter_sq, num_channels):
super(SqueezeExcitationLayer, self).__init__()
self.filter_sq = filter_sq
self.num_channels = num_channels
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(num_channels, filter_sq)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(filter_sq, num_channels)
def forward(self, inputs):
squeeze = self.avgpool(inputs)
squeeze = squeeze.view(squeeze.size(0), -1)
excitation = F.relu(self.fc1(squeeze))
excitation = torch.sigmoid(self.fc2(excitation))
excitation = excitation.view(excitation.size(0), self.num_channels, 1, 1)
scale = inputs * excitation
return scale
class DenseNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, blocks, input_shape=None, classes=1000):
super(DenseNet, self).__init__()
self.bn_axis = 1 if input_shape[0] == 3 else -1 # 根据输入形状确定bn_axis
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_shape[0], 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1.001e-5)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.dense_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
self.transition_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
num_channels = 64
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
self.dense_blocks.append(DenseBlock(block, num_channels, growth_rate=32, bn_axis=self.bn_axis))
num_channels += block * 32
if i < len(blocks) - 1:
self.transition_blocks.append(TransitionBlock(num_channels, reduction=0.5, bn_axis=self.bn_axis))
num_channels = int(num_channels * 0.5)
self.se = SqueezeExcitationLayer(16, num_channels)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels, eps=1.001e-5)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(num_channels, classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool1(x)
for i in range(len(self.dense_blocks)):
x = self.dense_blocks[i](x)
if i < len(self.dense_blocks) - 1:
x = self.transition_blocks[i](x)
x = self.se(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn(x))
x = self.avg_pool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def DenseNet121(input_shape=[3, 224, 224], classes=1000):
return DenseNet([6, 12, 24, 16], input_shape, classes)
def DenseNet169(input_shape=[3, 224, 224], classes=1000):
return DenseNet([6, 12, 32, 32], input_shape, classes)
def DenseNet201(input_shape=[3, 224, 224], classes=1000):
return DenseNet([6, 12, 48, 32], input_shape, classes)
输出:
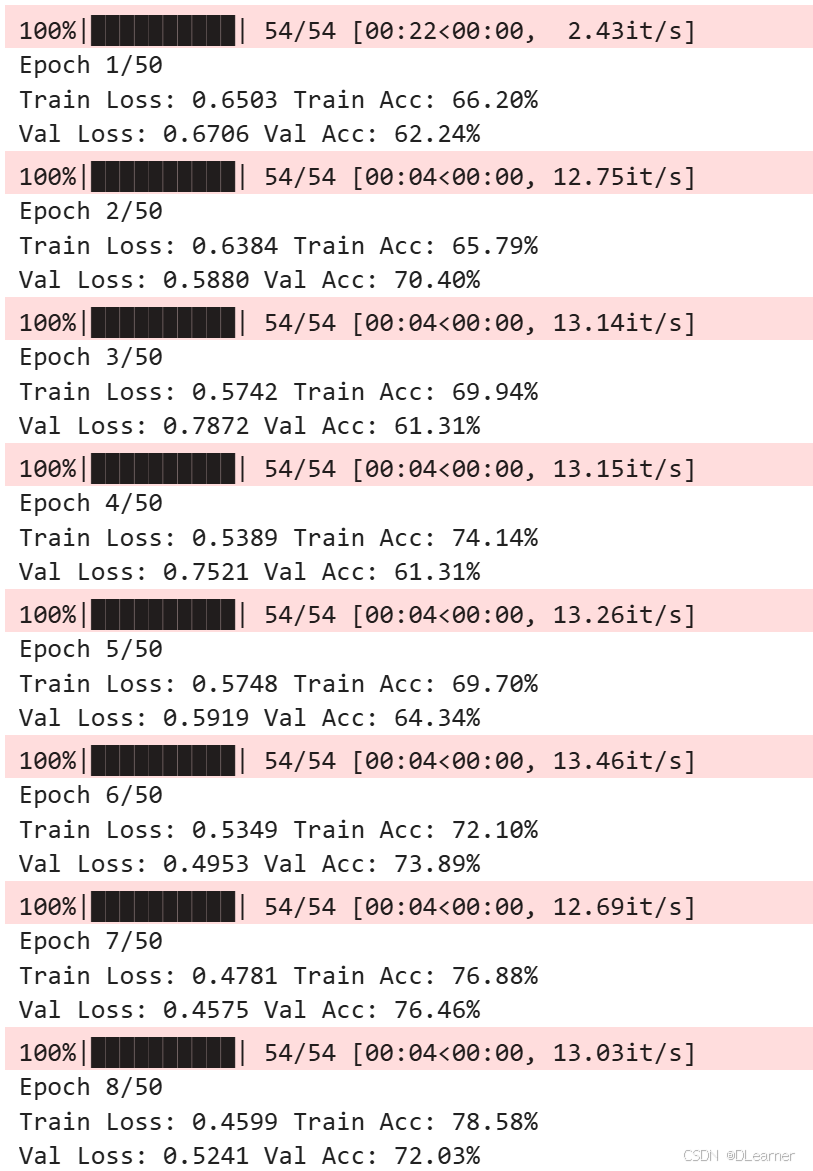
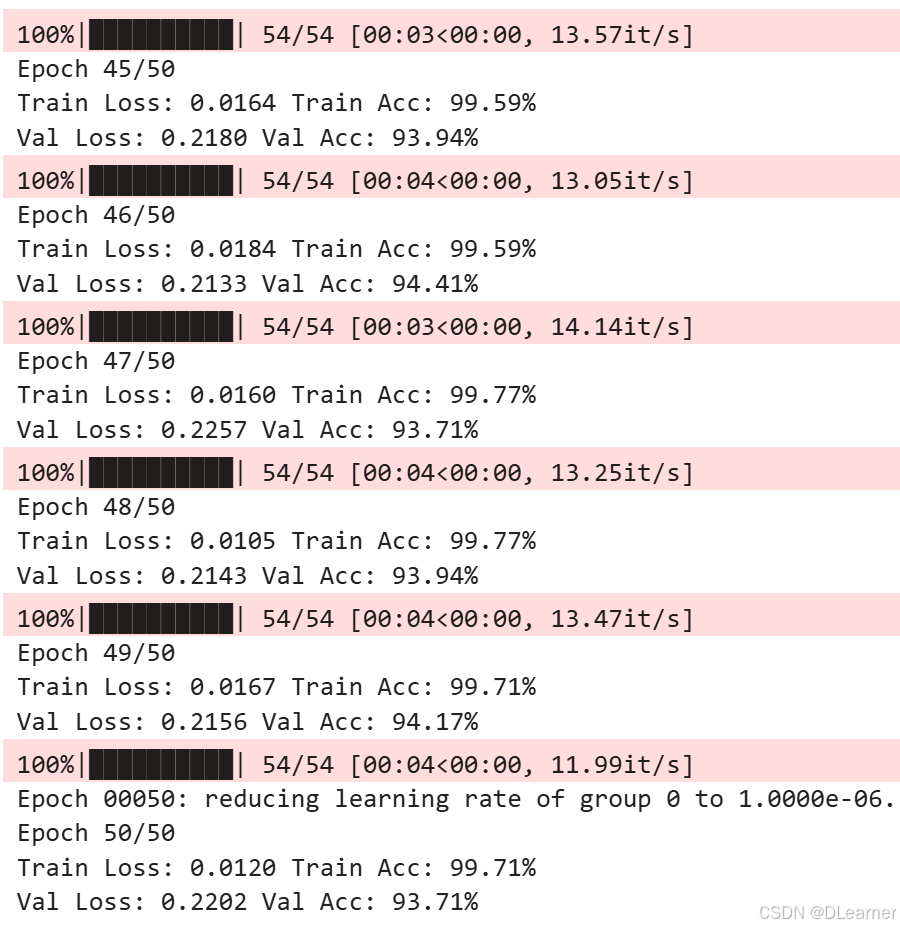
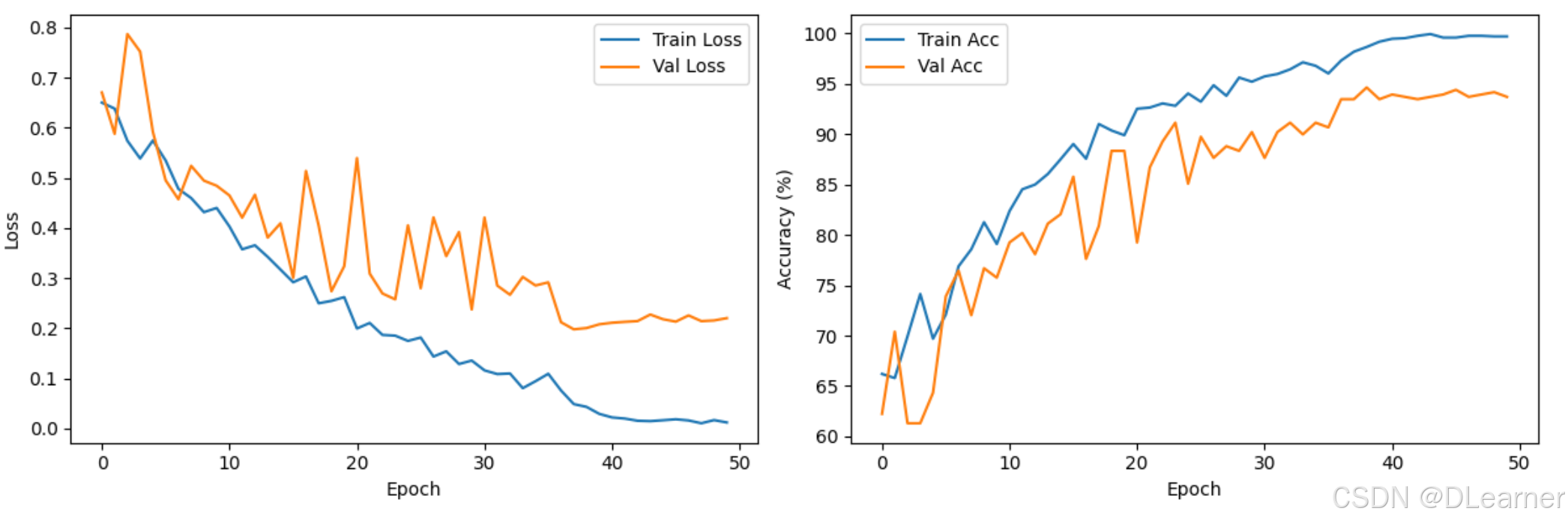
绘制训练历史
输出:






















 1145
1145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








