彩色空间转换实验
基本原理
RGB与YUV色彩空间的基础知识
RGB
RGB计色系统
RGB计色系统的创立是为了准确地对颜色进行表述和计算。1931年CIE对三基色做了统一规定,如下表:
| 标准色光 | 波长 |
|---|---|
| 红基色光 | 700nm |
| 绿基色光 | 546.1nm |
| 蓝基色光 | 435.8nm |
至于为什么选择它们,则是因为它们的获取方法简单,色度稳定准确,而且可以混配出来的颜色较多。
为了计算方便,还要规定基色的单位。
物理计色系统规定:各以1各单位的三种基色光混合后,恰能产出等能白光。经过实验,选取了如下基色单位:
- 700nm,光通量1光瓦的红光作为1个红基色单位。
- 546.1nm,光通量4.5907光瓦的绿光为1个绿基色单位。
- 435.9nm,光通量0.0601光瓦的蓝光为1个蓝基色单位。
至此,任何一个色光均可以表示为:
F = R ( R ) + G ( G ) + B ( B ) F=R(R)+G(G)+B(B) F=R(R)+G(G)+B(B)
其中 ( R ) , ( G ) , ( B ) (R),(G),(B) (R),(G),(B)即为上面提到的基色单位。
XYZ计色系统
在XYZ计色系统中,三个基色单位为 ( X ) , ( Y ) , ( Z ) (X),(Y),(Z) (X),(Y),(Z),任何一个颜色均可以表示为:
F = X ( x ) + Y ( Y ) + Z ( Z ) F=X(x)+Y(Y)+Z(Z) F=X(x)+Y(Y)+Z(Z)
XYZ系统的建立是为了克服RGB计色系统的缺点,它有以下特点:
- 用他们配出实际颜色时,XYZ均为正值。
- 合成光的亮度仅由Y决定,并规定1(Y)的光通量为1光瓦。
- 当 X = Y = Z X=Y=Z X=Y=Z,且大于零时,代表等能白光即E白。
根据特点,列出方程可以计算得到:
( Y ) = 0.4185 ( R ) − 0.0192 ( G ) + 0.0009 ( B ) (Y) = 0.4185(R) - 0.0192(G) + 0.0009(B) (Y)=0.4185(R)−0.0192(G)+0.0009(B)
(X),(Z)同理。通过这组方程联立可以得到系数X,Y,Z与R,G,B的关系。
显像三基色计色系统
以上两个计色系统均是用来进行理论分析的,实际上我们指通常所指的R,G,B并不是RGB计色系统中的三基色,而是取决于的荧光粉,称为电视三基色,分别用 ( R e ) , ( G e ) , ( G b ) (R_e),(G_e),(G_b) (Re),(Ge),(Gb)表示,并且NTSC制中有:
1 ( R e ) + 1 ( G e ) + 1 ( B e ) = 1 C 白 1(R_e)+1(G_e)+1(B_e)=1C白 1(Re)+1(Ge)+1(Be)=1C白
通过计算可以得到对应的亮度公式:
Y = 0.2990 R + 0.5870 G + 0.1140 B Y=0.2990R+0.5870G+0.1140B Y=0.2990R+0.5870G+0.1140B
这就是我们最常用的亮度公式。
YUV
YUV中的Y其实是来自于XYZ标准记色系统中的Y。
YUV与RGB的转换
模拟信号
Y = 0.2990 R + 0.5870 G + 0.1140 B Y=0.2990R+0.5870G+0.1140B Y=0.2990R+0.5870G+0.1140B
U = B − Y = − 0.2990 R − 0.5870 G + 0.8860 B U=B-Y=-0.2990R-0.5870G+0.8860B U=B−Y=−0.2990R−0.5870G+0.8860B
V = R − Y = 0.7010 R − 0.5870 G − 0.1140 B V=R-Y=0.7010R-0.5870G-0.1140B V=R−Y=0.7010R−0.5870G−0.1140B
数字信号
为了便于处理,模拟信号变为数字信号时需要进行归一化处理,使得色差信号的动态范围控制在-0.5-0.5之间。
归一化之后有:
U ′ = 0.564 ( B − Y ) = − 0.1684 R − 0.3316 G + 0.5 B U'=0.564(B-Y)=-0.1684R-0.3316G+0.5B U′=0.564(B−Y)=−0.1684R−0.3316G+0.5B
V ′ = 0.713 ( V − Y ) = 0.5 R − 0.4187 G − 0.0813 B V'=0.713(V-Y)=0.5R-0.4187G-0.0813B V′=0.713(V−Y)=0.5R−0.4187G−0.0813B
亮度信号量化后的电平分配
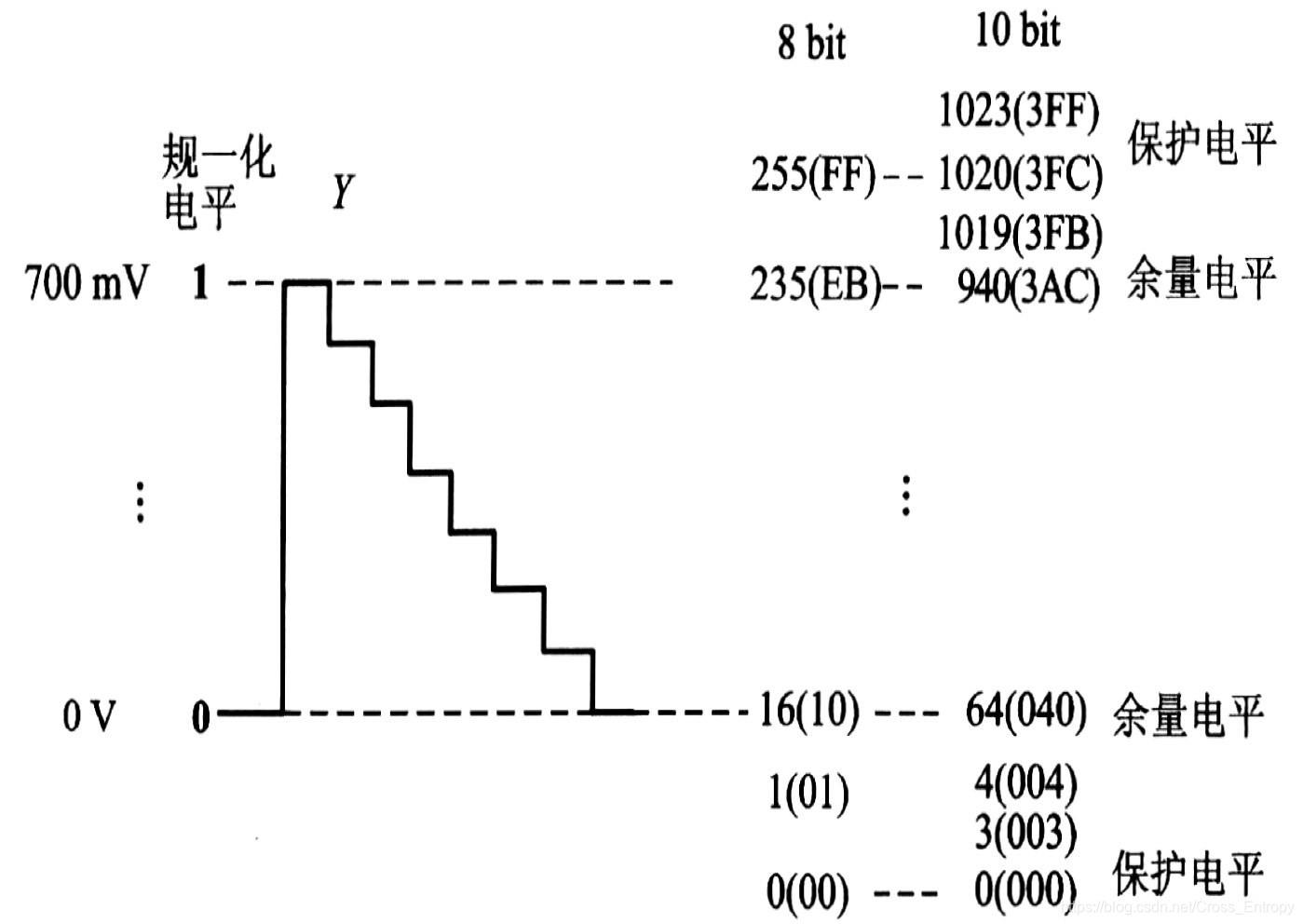
如图所示,在8bit均匀量化中,亮度信号占220个量化级,峰值电平对应235,消隐电平对应16。为了防止信号变动造成过载,在256级上端留20级,下端留16级作为信号超越动态范围的保护带。 其中0与255为保护电平,不允许出现在视频数据流中。
色差信号量化后的电平分配
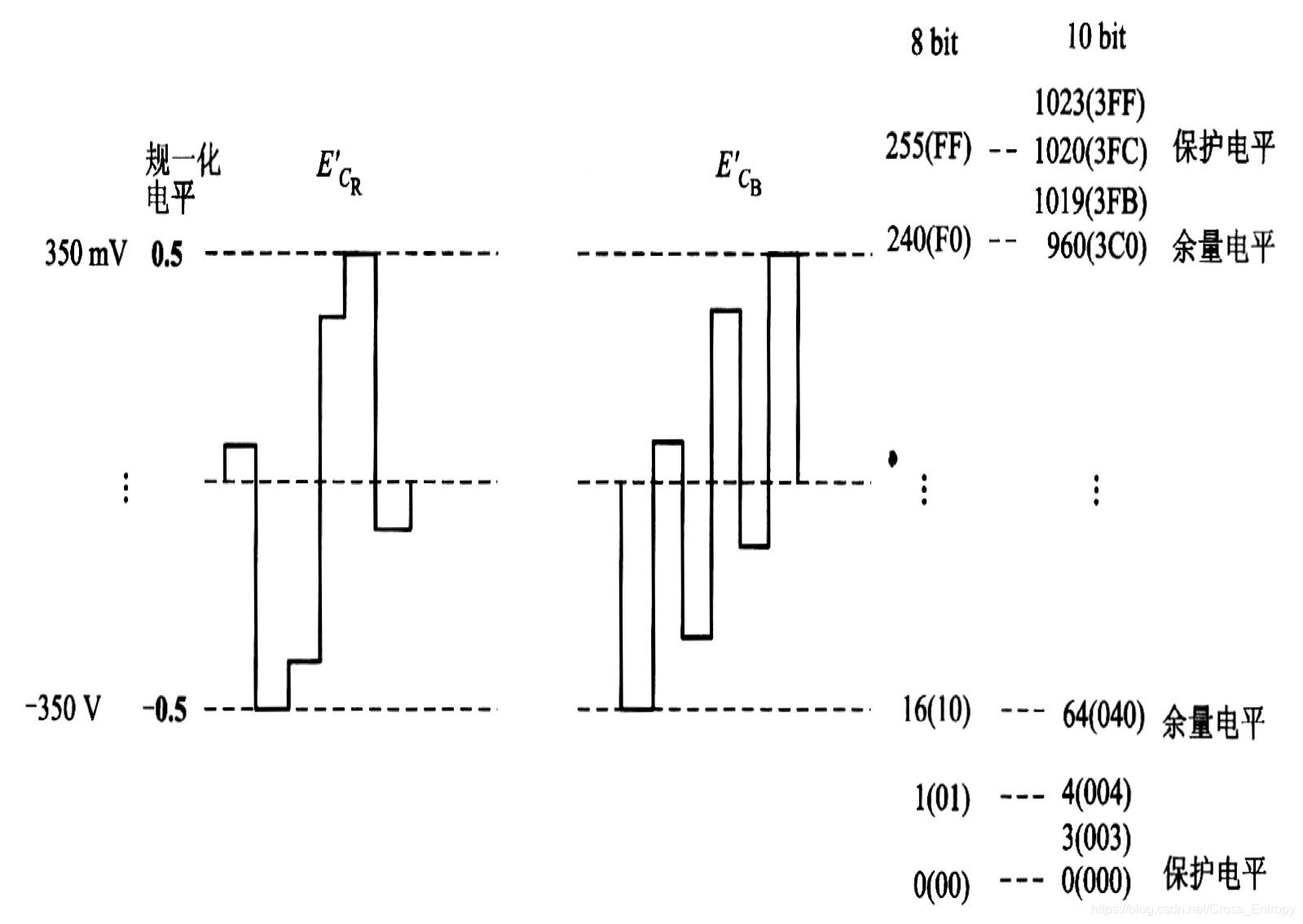
以8bit为例,色差信号经过归一化处理后,动态范围为-0.5-0.5,让色差零电平对应码电平128,色差信号总共占225个量化级。在256级上端留15级,下端留16级作为信号超越动态范围的保护带。
表达式
基于上述分析,可以得到表达式:
D Y = I N T ( 219 Y + 16 ) × 2 n − 8 D_Y=INT(219Y+16)\times{2^{n-8}} DY=INT(219Y+16)×2n−8
D U = I N T ( 224 U ′ + 128 ) × 2 n − 8 D_U=INT(224U'+128)\times{2^{n-8}} DU=INT(224U′+128)×2n−8
D V = I N T ( 224 V ′ + 128 ) × 2 n − 8 D_V=INT(224V'+128)\times{2^{n-8}} DV=INT(224V′+128)×2n−8
其中 D Y , D U , D V D_Y,D_U,D_V DY,DU,DV即为计算机(数字信号)中的数值, I N T ( ) INT() INT()为向下取整, n n n为量化比特数。
上述过程中默认r、g、b的值为0-1之间的,而计算机中的数据则是在0-255范围内,所以修需要将上述公式中r、g、b的从0-255映射到0-1。
即:
D Y = I N T ( 219 Y 225 + 16 ) × 2 n − 8 D_Y=INT(\frac{219Y}{225} + 16)\times{2^{n-8}} DY=INT(225219Y+16)×2n−8
D U = I N T ( 224 U ′ 225 + 128 ) × 2 n − 8 D_U=INT(\frac{224U'}{225}+128)\times{2^{n-8}} DU=INT(225224U′+128)×2n−8
D V = I N T ( 224 V 225 ′ + 128 ) × 2 n − 8 D_V=INT(\frac{224V}{225}'+128)\times{2^{n-8}} DV=INT(225224V′+





 本文详细介绍RGB与YUV色彩空间的基本原理,包括色彩系统的创立、亮度公式、色彩转换及量化过程。并通过实验验证了不同色彩空间的转换效果,分析了转换过程中的误差来源。
本文详细介绍RGB与YUV色彩空间的基本原理,包括色彩系统的创立、亮度公式、色彩转换及量化过程。并通过实验验证了不同色彩空间的转换效果,分析了转换过程中的误差来源。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 255
255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








