[Matlab-5]Laplace变换
Laplace 变换(数学)

Laplace 变换和逆变换


Laplace 变换与Fourier变换的关系

极点(pole)与零点(zero)


由图上可以看出是否stable
//First order poles on real axis (a=0,w=1)
//H1(s)=1/(s+0.1) H2(s)=1/s H3(s)=1/(s-0.1)
clear;clf;
b = 1;
t = 0:0.001:60;
a = [1,0.1];
sys1 = tf(b,a);
subplot(3,2,2);plot(t,impluse(sys1,t),'g');xlabel('t');ylabel('h1(t)');
a = [1,0];
sys1 = tf(b,a);
subplot(3,2,4);plot(t,impluse(sys2,t),'r');xlabel('t');ylabel('h2(t)');
a = [1,-0.1];
sys3 = tf(b,a);
subplot(3,2,6);plot(t,impluse(sys3,t),'b');xlabel('t');ylabel('h3(t)');
subplot(3,2,[1 3 5]);
pzplot(sys1,'g');hold on;
pzplot(sys2,'r');
pzplot(sys3,'b');hold off;
作3D曲面图(surface plot)
标题会用到的函数
颜色挑选
栗子

给定微分方程求Laplace变换

零状态响应
拿上面的Y(s)来举例,就是只保留后面的项,分母和左边式子系数相对应。否则就是有初始态的,和上面一样
一些栗子

clear;
syms s;
F = (s^3+5*s^2+9*s+7)/(s^2+3*s+2);
ft = ilaplace(F)

clear;clf;
syms s t;
% L(RHS) = 6
%f = diff(heaviside(t));
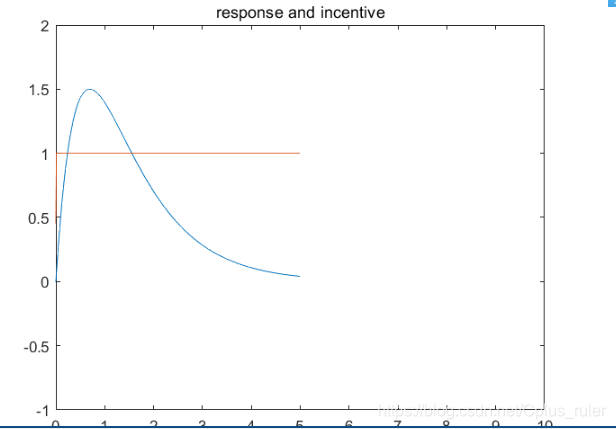
F = 6/(s^2 + 3*s + 2);
ft = ilaplace(F);
fplot(t,ft);hold on;
xlabel('t');
title('response and incentive');
xlim([0,10]);
ylim([-1,2]);
fs = heaviside(t);
fplot(t,fs);

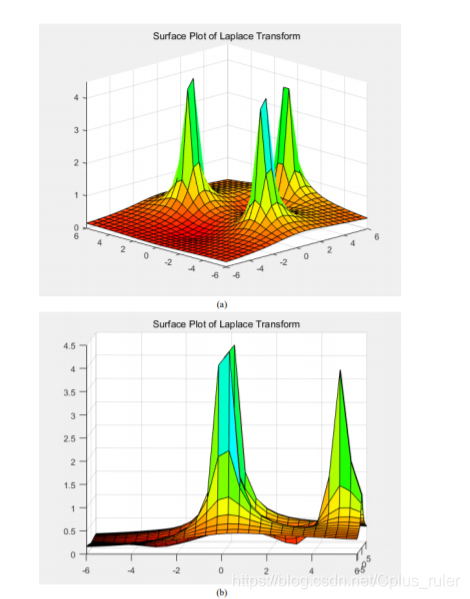
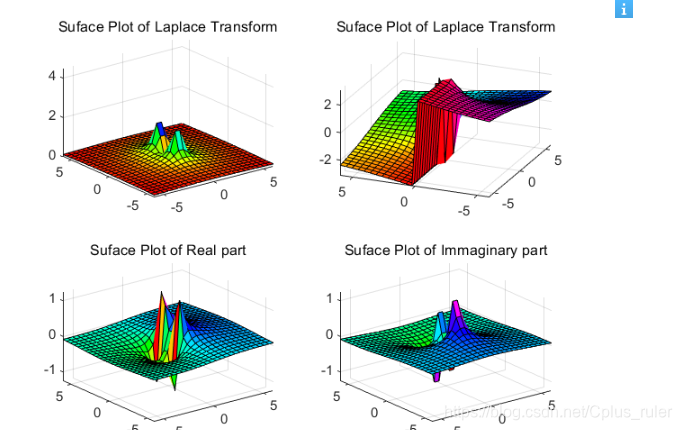
clear;clf;
x = -6:0.48:6;y=x;
[sigma,omega] = meshgrid(x,y);
s = sigma +1j*omega;
Fs = s./(s.*s + 1);
Fsabs = abs(Fs);
subplot(2,2,1);
surf(sigma,omega,Fsabs);
axis([-6,6,-6,6,0,4.5]);
title('Suface Plot of Laplace Transform');
colormap(hsv);
rotate3d on;
subplot(2,2,2);
Fphase = angle(Fs);
surf(sigma,omega,Fphase);
%axis([-6,6,-6,6,0,4.5]);
title('Suface Plot of Laplace Transform');
colormap(hsv);
rotate3d on;
subplot(2,2,3);
Freal =real(Fs);
surf(sigma,omega,Freal);
%axis([-6,6,-6,6,0,4.5]);
title('Suface Plot of Real part');
colormap(hsv);
rotate3d on;
subplot(2,2,4);
Fim = imag(Fs);
surf(sigma,omega,Fim);
title('Suface Plot of Immaginary part');
colormap(hsv);
rotate3d on;```
 Matlab实现Laplace变换与信号处理
Matlab实现Laplace变换与信号处理





 本文介绍了Laplace变换的数学原理及其在Matlab中的应用,包括Laplace变换、逆变换、与Fourier变换的关系,以及如何通过3D曲面图分析系统稳定性。同时,展示了如何利用Laplace变换求解微分方程,并给出了零状态响应的计算方法及实例。
本文介绍了Laplace变换的数学原理及其在Matlab中的应用,包括Laplace变换、逆变换、与Fourier变换的关系,以及如何通过3D曲面图分析系统稳定性。同时,展示了如何利用Laplace变换求解微分方程,并给出了零状态响应的计算方法及实例。

















 1512
1512

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








