文章介绍Agent设计中的并行化模式,通过同时执行独立任务提升效率。并行化适用于任务间无依赖场景,特别适合处理延迟高的外部服务。LangChain、LangGraph和Google ADK等框架提供并行执行机制,文中以Python代码示例展示如何使用RunnableParallel实现并行处理。虽然并行化可降低延迟并加快响应速度,但也会增加系统复杂性,是优化大模型Agent工作流的关键技术。
并行化概述
基于“提示词链”的Agent虽然可以把一个复杂的任务拆分成多个小任务,但拆分的任务非常多时会出现执行效率上的问题。因为,任务是串行执行的。为了提升Agent任务执行的效率,并行化模式就显得非常重要了。并行化,并不是一个新的概念,在传统编程范式中也非常常用。
并行化,会同时执行多个组件:比如:调用LLM,使用工具,或使用子Agent等。并行执行不需要等待上一个步骤完成后再执行后面的步骤。这样可以大大提升Agent整体的性能。
设想以下场景:我希望从网络上不同链接爬取数据,并综合这些信息来完成一个综述。那么,顺序流程是:
- 爬取url1的数据
- 爬取url2的数据
- 爬取url3的数据
- 综合123的数据,并生成综述
若通过以上流程一步一步的执行,则效率可能不会太高。而并行化方法如下:
1.同时并行爬取url1,url2,url3的数据
2.再根据1的数据,生成综述
其核心思想是识别工作流中不依赖于其他部分输出的部分,然后并行执行它们。这在处理具有延迟的外部服务(例如 API 或数据库)时尤其有效,因为您可以并行发出多个请求。
实现并行化通常需要支持异步执行或多线程/多处理(asynchronous execution or multi-threading/multi-processing)的框架。现代智能体框架在设计时就考虑了异步操作,这样就可以轻松定义可并行运行的步骤。
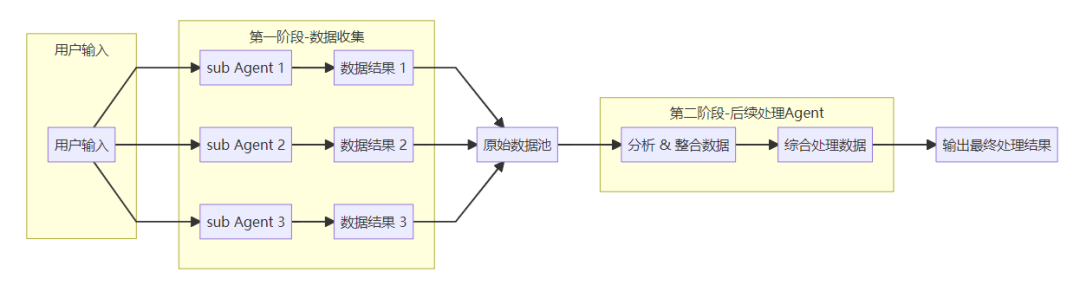
LangChain 、LangGraph 和 Google ADK 等框架提供了并行执行机制。在 LangChain 表达式语言 (LCEL) 中,您可以通过使用 |(表示顺序)等运算符组合可运行对象,并构建链或图以使其包含并发执行的分支来实现并行执行。
LangGraph 凭借其图结构,允许您定义可从单个状态转换执行的多个节点,从而有效地在工作流中实现并行分支。
Google ADK 提供了强大的原生机制来促进和管理智能体的并行执行,从而显著提升了复杂多智能体系统的效率和可扩展性。 ADK 框架内的这种固有功能允许开发人员设计和实施多个智能体可以同时而不是顺序运行的解决方案。并行化模式对于提升智能体系统的效率和响应能力至关重要,尤其是在处理涉及多个独立查找、计算或与外部服务交互的任务时。它是优化复杂智能体工作流性能的关键技术。
与传统多线程设计的模式一样,当处理流程不相互依赖时,就可以使用并行化处理模式。而在实际使用时,往往会把并行模式和其他模式一起结合使用。
代码实战
该Python 代码实现了一个 LangChain 应用程序,通过并行执行高效地处理给定主题。需要注意的是,asyncio 提供的是并发,而非并行。它通过使用事件循环在单线程上实现并发,当一个任务空闲时(例如,等待网络请求),事件循环会智能地在任务之间切换。这会产生多个任务同时进行的效果,但代码本身仍然只由一个线程执行,并受到 Python 全局解释器锁 (GIL) 的限制。
初始化一个 ChatOpenAI 实例,具体使用硅基流动的提供的大模型,定义三个独立的 LangChain“链”,每个链针对输入主题执行不同的任务。
第一个链:用于简明扼要地概括主题,使用包含主题占位符的系统消息和用户消息。第二个链:配置为生成三个与主题相关的有趣问题。第三个链:设置为从输入主题中识别 5 到 10 个关键词,并要求它们以逗号分隔。每个独立的链都包含一个针对其特定任务定制的 ChatPromptTemplate,然后是初始化的语言模型和一个用于将输出格式化为字符串的 StrOutputParser。
然后构建一个 RunnableParallel 块来绑定这三个链,使它们能够同时执行。这个并行 Runnable 还包含一个 RunnablePassthrough 块,以确保原始输入主题可用于后续步骤。为最终的综合步骤定义了一个单独的 ChatPromptTemplate 模板,它将摘要、问题、关键词和原始主题作为输入,生成一个综合答案。完整的端到端处理链名为 full_parallel_chain,它是通过将 map_chain(并行块)按顺序排列到综合提示中,然后是语言模型和输出解析器来创建的。
importos
importasyncio
fromtypingimportOptional
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
fromlangchain_core.promptsimportChatPromptTemplate
fromlangchain_core.output_parsersimportStrOutputParser
fromlangchain_core.runnablesimportRunnable, RunnableParallel, RunnablePassthrough
# --- 配置 ---
local_llm="Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct"
base_url="https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1"
# Initialize the LLM model (using OpenAI in this example)
llm=ChatOpenAI(model=local_llm, base_url=base_url, api_key="sk-xxx")
# --- 定义独立的处理链 ---
# These three chains represent distinct tasks that can be executed in parallel.
summarize_chain: Runnable= (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Summarize the following topic concisely:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
|llm
|StrOutputParser()
)
questions_chain: Runnable= (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Generate three interesting questions about the following topic:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
|llm
|StrOutputParser()
)
terms_chain: Runnable= (
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Identify 5-10 key terms from the following topic, separated by commas:"),
("user", "{topic}")
])
|llm
|StrOutputParser()
)
# --- 构建并行和综合处理链 ---
# 定义并行处理的任务块。每个任务块的处理结果会传递到下一个步骤。
map_chain=RunnableParallel(
{
"summary": summarize_chain,
"questions": questions_chain,
"key_terms": terms_chain,
"topic": RunnablePassthrough(), # Pass the original topic through
}
)
# 2. 定义最后的综合提示词,合并并行结果。
synthesis_prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """Based on the following information:
Summary: {summary}
Related Questions: {questions}
Key Terms: {key_terms}
Synthesize a comprehensive answer."""),
("user", "Original topic: {topic}")
])
# 3. 通过将并行结果直接传送到综合提示中,然后传送到 LLM 和输出解析器来构建完整链。
full_parallel_chain=map_chain|synthesis_prompt|llm|StrOutputParser()
# --- Run the Chain ---
asyncdefrun_parallel_example(topic: str) ->None:
"""
Asynchronously invokes the parallel processing chain with a specific topic
and prints the synthesized result.
Args:
topic: The input topic to be processed by the LangChain chains.
"""
ifnotllm:
print("LLM not initialized. Cannot run example.")
return
print(f"\n--- Running Parallel LangChain Example for Topic: '{topic}' ---")
try:
# The input to `ainvoke` is the single 'topic' string,
# then passed to each runnable in the `map_chain`.
response=awaitfull_parallel_chain.ainvoke(topic)
print("\n--- Final Response ---")
print(response)
exceptExceptionase:
print(f"\nAn error occurred during chain execution: {e}")
if__name__=="__main__":
test_topic="The history of space exploration"
# In Python 3.7+, asyncio.run is the standard way to run an async function.
asyncio.run(run_parallel_example(test_topic))
结果输出如下
--- Running Parallel LangChain Example for Topic: 'The history of space exploration'---
--- Final Response ---
The history of space exploration is a fascinating narrative of human achievement and innovation, reflecting the philosophical and cultural influences of different countries. This journey from early observations to advanced missions has been shaped by both competition and collaboration among nations.
### Philosophical and Cultural Influences
- **The USSR (now Russia)**: The USSR's space program was driven by a desire to showcase technological prowess and ideological superiority. Sergei Korolev, the father of Soviet cosmonautics, was instrumental in the development of early space technology. The launch of Sputnik 1 in 1957 marked the beginning of the Space Age and underscored the USSR's leading position in space.
- **The United States**: The US space program was heavily influenced by Cold War tensions and the need to demonstrate technological superiority over the USSR. The success of NASA's Mercury program, with Alan Shepard being the first American astronaut to reach space in 1961, was a significant milestone. The Apollo missions, particularly Apollo 11’s moon landing in 1969, represented a monumental achievement that showcased American ingenuity and technological advancement.
- **International Cooperation and Competition**: The Enlightenment concept of progress and the push for scientific advancement have also played crucial roles. The Skylab program, for example, demonstrated international cooperation, with American astronauts and Soviet cosmonauts participating in joint missions. Conversely, the Space Race was characterized by numerous conflicts that spurred technological innovation and fueled a desire to achieve notable milestones first.
### Technological Advancements
- **Rockets**: The development of rocket technology by scientists like Konstantin Tsiolkovsky and Robert H. Goddard laid the groundwork for modern space exploration. Sergei Korolev’s work on creating an ICBM that could be adapted for space missions was crucial. NASA’s Saturn V rocket, used in the Apollo missions, was a pinnacle of this technology, enabling the successful moon landings.
- **Satellites**: The launch of Sputnik 1set the stage for the proliferation of satellites, which have become essential for communication, navigation, and Earth observation. Modern satellites, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, have provided unprecedented views of the cosmos and advanced our understanding of the universe.
- **Mars Rovers**: Developments like the Mars Rovers (e.g., Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance) exemplify the integration of advanced engineering and robotics in exploring distant planets. These rovers have provided valuable data about the Martian surface and its potential for supporting life.
### Ongoing Innovations and Private Sector Involvement
The 1990s and 2000s saw significant advancements in space technology and missions. The International Space Station (ISS), a collaborative effort involving multiple countries, has been a cornerstone of modern space exploration. It has enabled extensive research in microgravity, materials science, and biology.
In recent years, the space sector has been profoundly influenced by the involvement of private companies. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are redefining space travel through reusable rockets, reducing costs, and pushing the boundaries of private spaceflight. SpaceX’s missions to the ISS and plans for future Mars missions are hallmarks of this new era.
### Conclusion
Space exploration has been a labyrinth of philosophical, cultural, and technological dimensions that have shaped human progress. From early observations and the early Soviet and American space races to current private sector involvement, the journey continues. The legacy of figures like Sergei Korolev, Alan Shepard, and Neil Armstrong exemplifies the spirit of human endeavor in venturing into the unknown. As we continue to explore and understand the cosmos, the influence of these milestones and key figures will undoubtedly play a lasting role in the future of space exploration.
总结
并行化是一种同时执行独立任务以提高效率的模式。并行化有助于减少总体延迟并使智能体系统对复杂任务的响应更快。采用并发或并行架构会带来相当大的复杂性和成本,影响设计、调试和系统日志记录等关键开发阶段。但LangChain 和 Google ADK 等框架为定义和管理并行执行提供了内置支持。在 LangChain 表达语言 (LCEL) 中,RunnableParallel 是并行运行多个可运行对象的关键构造。
并行化模式是一种通过并发执行独立子任务来优化计算工作流的方法。这种方法可以降低整体延迟,尤其是在涉及多个模型推理或调用外部服务的复杂操作中。
各种框架提供了不同的机制来实现此模式。在 LangChain 中,像 RunnableParallel 这样的结构用于显式定义并同时执行多个处理链。相比之下,像 Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 这样的框架可以通过多智能体委托实现并行化,其中主协调器模型将不同的子任务分配给可以并发操作的专门智能体。
我们如何系统学习掌握AI大模型?
AI大模型作为人工智能领域的重要技术突破,正成为推动各行各业创新和转型的关键力量。抓住AI大模型的风口,掌握AI大模型的知识和技能将变得越来越重要。
学习AI大模型是一个系统的过程,需要从基础开始,逐步深入到更高级的技术。
这里给大家精心整理了一份
全面的AI大模型学习资源,包括:AI大模型全套学习路线图(从入门到实战)、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习、面试题等,资料免费分享!

1. 成长路线图&学习规划
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
这里,我们为新手和想要进一步提升的专业人士准备了一份详细的学习成长路线图和规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习成长路线。

2. 大模型经典PDF书籍
书籍和学习文档资料是学习大模型过程中必不可少的,我们精选了一系列深入探讨大模型技术的书籍和学习文档,它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。(书籍含电子版PDF)

3. 大模型视频教程
对于很多自学或者没有基础的同学来说,书籍这些纯文字类的学习教材会觉得比较晦涩难以理解,因此,我们提供了丰富的大模型视频教程,以动态、形象的方式展示技术概念,帮助你更快、更轻松地掌握核心知识。

4. 大模型行业报告
行业分析主要包括对不同行业的现状、趋势、问题、机会等进行系统地调研和评估,以了解哪些行业更适合引入大模型的技术和应用,以及在哪些方面可以发挥大模型的优势。

5. 大模型项目实战
学以致用 ,当你的理论知识积累到一定程度,就需要通过项目实战,在实际操作中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作和职业发展打下坚实的基础。

6. 大模型面试题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。
在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我们将提供精心整理的大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以
微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码,免费领取【保证100%免费】





















 778
778

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








