目的:实现分频器设计。
1. 设计一个分频器实现将原信号进行8分频,所得信号占空比为50%。
分频是将单一频率信号的频率降为原来的1/N,就叫N分频。将信号进行8分频,即所得信号频率是原信号频率的1/8,则其所得信号的1个周期等于原始信号的8个周期。
占空比是高电平持续时间占整个周期的比值。占空比为50%意思是高低电平持续时间一样,均为半个周期的时间长。
程序
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity frequency_divider is
port(
clk :in std_logic; --原始信号
fp_out :out std_logic --经过分频后的输出信号
);
end frequency_divider;
architecture behave of frequency_divider is
begin
process(clk)
variable count :integer := 0; --integer决定分频数N
begin
if(clk'event and clk = '1') then --上升沿
count := count + 1; --对上升沿的个数进行计数,其实就是对原始信号的周期进行计数
if(count < 5) then
fp_out <= '1'; --输出信号在原始信号的前四个周期内保持高电平
elsif(count <8) then
fp_out <= '0'; --输出信号在原始信号的后四个周期内保持低电平
end if;
if(count = 8) then --因为是8分频,所以当计数到8时要将计数值清0
count := 0;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end behave;
波形仿真图
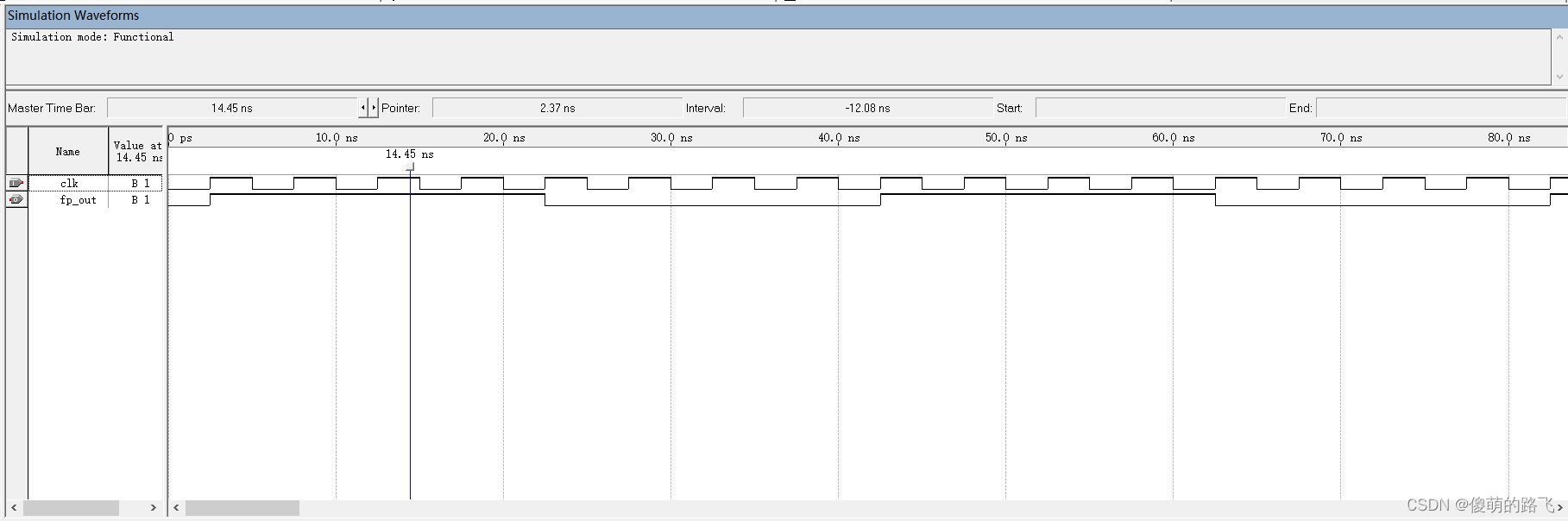
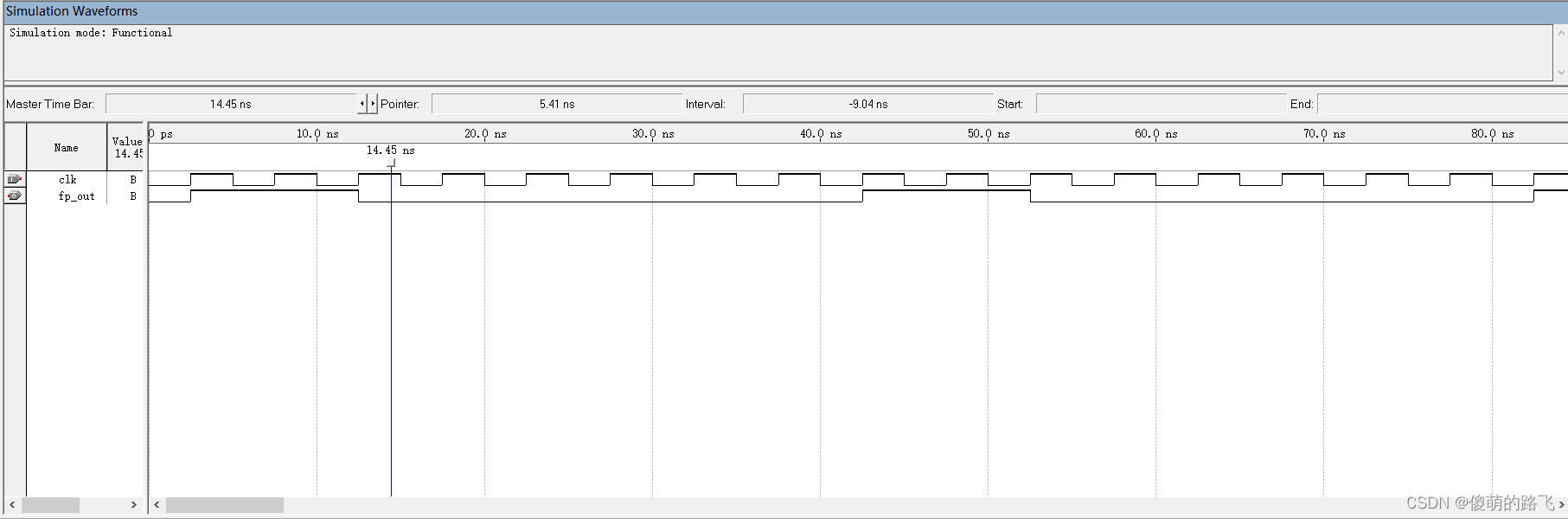
2. 设计一个分频器实现将原信号进行8分频,所得信号占空比为25%。
在上个程序的基础上,对高电平持续时间进行修改,即可实现占空比的修改。
程序
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity frequency_divider is
port(
clk :in std_logic; --原始信号
fp_out :out std_logic --经过分频后的输出信号
);
end frequency_divider;
architecture behave of frequency_divider is
begin
process(clk)
variable count :integer := 0; --integer决定分频数N
begin
if(clk'event and clk = '1') then --上升沿
count := count + 1; --对上升沿的个数进行计数,其实就是对原始信号的周期进行计数
if(count < 3) then
fp_out <= '1'; --输出信号在原始信号的前两个周期内保持高电平
elsif(count <8) then
fp_out <= '0'; --输出信号在原始信号的后六个周期内保持低电平
end if;
if(count = 8) then --因为是8分频,所以当计数到8时要将计数值清0
count := 0;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end behave;
波形仿真图





 本文是VHDL语言学习笔记的第七部分,主要介绍如何设计8分频器。首先,设计了一个8分频器,其输出信号占空比为50%,即高低电平各占半个周期。接着,在此基础上调整,实现了占空比为25%的8分频器,通过波形仿真验证了设计效果。
本文是VHDL语言学习笔记的第七部分,主要介绍如何设计8分频器。首先,设计了一个8分频器,其输出信号占空比为50%,即高低电平各占半个周期。接着,在此基础上调整,实现了占空比为25%的8分频器,通过波形仿真验证了设计效果。


















 2554
2554

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










