01 前言
在Github一个开源项目中(awesome-llm-apps)发现有很多Agent应用都是使用的Agno这个框架构建的,然后发现Agno在Github上有34k+的star,提交也比较活跃,于是上手体验了一番,由此分享。
Agno 是一个高性能的多智能体(Agents)框架。既可构建单一智能体,也能将多个智能体组合成一个Team(在 Agno 中称为 Team),还支持构建稳定输出的工作流。
在构建智能体时,你可以灵活使用多种组件,包括大语言模型(LLM)、存储(会话与状态)、记忆模块、知识库以及工具(支持 MCP)。
官方进行了一项与 LangGraph 的性能对比测试:在实例化 1000 次带工具的智能体测试任务中(测试脚本详见 Github),Agno 在时间和内存使用方面均表现出显著优势。
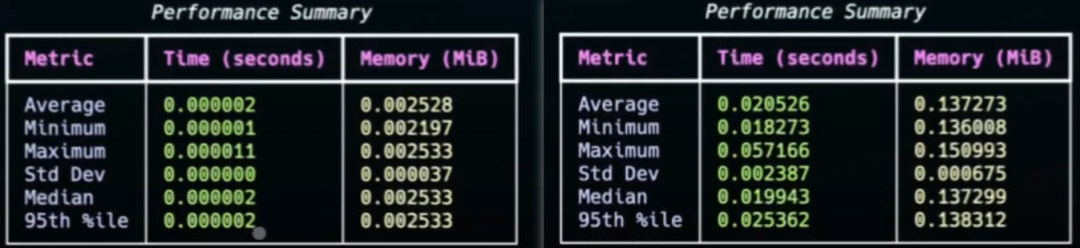
左Agno、右LangGraph
除了性能,该框架的另一大亮点是其 AgentOS 运行时环境。一方面,它可以与 FastApp 结合,快速生成 API 接口;另一方面,Agno 提供了控制面板,方便你连接所开发的 AgentOS 进行实时监控、测试与管理。此外,AgentOS 还具备隐私数据保护能力,确保数据不会通过任何第三方媒介传输(这一点与云厂商产品或 SaaS 系统形成鲜明对比)。
02 单智能体(Agent)
首先看下Agno的基础部分也是核心部分:单智能体(Agent)的构建。Agent可以使用**大语言模型(LLM)、存储(会话与状态)、记忆模块、知识库以及工具(支持 MCP)**等组件。
定义一个Agent
使用Agno定义并执行一个Agent只需要数行代码即可。
from agno.agent import Agent
from agno.models.openai import OpenAILike
open_ai_like_model = OpenAILike(id="Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct",
base_url="https://api-inference.modelscope.cn/v1",
api_key="ms-xxx")
agent = Agent(model=open_ai_like_model)
agent.print_response("自我介绍")
示例通过Agent类进行实例化,并指定model。使用print_response发起对Agent提问,内部使用的是run方法,这里也可以直接使用agent.run(“自我介绍”)。如果要流式响应,指定stream参数为True。
示例中的模型地址是魔塔社区的兼容OpenAI接口URL。模型是千问开源模型,魔塔社区模型详情页复制id。
上文示例,模型定义到一个单独的同层文件中,下文示例使用时导入:
from open_ai_like import open_ai_like_model
存储
如果需要保存历史****对话消息(Session)或者对话过程中的状态信息(State),就需要使用外部数据库进行存储,Agno支持Mysql、Pg、Sqlite、Redis等十多种数据库。
from agno.agent import Agent
from open_ai_like import open_ai_like_model
from agno.db.sqlite import SqliteDb
from agno.session import AgentSession
# set up the database
db = SqliteDb(db_file="tmp/agno_session.db",
session_table="agno_session")
# Run agent andreturn the response as a variable
agent = Agent(description="你是一个小助手",
model=open_ai_like_model,
db=db,
add_history_to_context=True,
num_history_runs=2)
# Retrieve the memories about the user
agent.print_response("自我介绍", user_id="123", session_id="ss-123", show_message=True)
# 最后一次运行的消息
output = agent.get_last_run_output(session_id="ss-123")
messages = output.messages
for item in messages:
print(f"\n=========={item.role}:{item.content}")
示例使用SqliteDb进行session会话的存储。
add_history_to_context:是否要加入历史消息到提示词上下文中,True加入,默认False。
num_history_runs:加入几轮历史对话消息到上下文中。
最后通过get_last_run_output获取输出内容,并通过messages打印包括system、user、assistant三种类型的消息。
工具(支持MCP)
Agent可以通过使用工具扩展模型的能力边界,例如获取当前时间、算数、查询天气、读取文件等等。Agno提供了内置工具调用,同时也支持自定义工具以及MCP。
1、内置工具
Agno内置工具100+个,位于agno.tools包下。
from agno.agent import Agent
from open_ai_like import open_ai_like_model
from agno.tools.duckduckgo import DuckDuckGoTools
agent = Agent(model=open_ai_like_model,
tools=[DuckDuckGoTools()],
markdown=True)
agent.print_response("Whats happening in France?", stream=True)
通过tools指定多个工具。此处使用了duckduckgo工具的web搜索能力,实现新闻信息的实时获取。
Agent会将工具描述以tools参数的方式发给模型。模型判断如果问题需要查询工具,则调用工具并将响应内容返回给模型,模型再组织响应内容。如果有必要会进行多轮工具调用。
2、自定义工具
def web_search(query: str) -> str:
"""Use this function to search some News.
Args:
query(str): query param.
"""
return "Protests Against Budget Cuts: France is experiencing widespread protests and strikes across more than 240 locations. Organized by the CGT union, emonstrators are urging the government to abandon its planned budget cuts."
agent = Agent(description="你是一个小助手",
model=open_ai_like_model,
tools=[web_search],
markdown=True)
run_out_put = agent.run("Whats happening in France?")
通过tools指定自定义的web_search方法。
可以通过如下方式打印提示词及工具参数:
run_out_put = agent.run("Whats happening in France?")
print(f"run_out_put.tools:{run_out_put.tools}")
messages = run_out_put.messages
for item in messages:
print(f"\n=========={item.role}:{item.content}")
示例会返回系统提示词如下:
==========system:你是一个小助手
<additional_information>
- Use markdown to format your answers.
</additional_information>
也可以通过定义Agent时指定参数debug_mode=True输出提示词日志。
3、MCP
MCP即模型上下文协议(Model Context Protocol),Agno支持MCP的三种传输协议:Stdio、SSE、Streamable HTTP。
import asyncio
from agno.agent import Agent
from open_ai_like import open_ai_like_model
from agno.tools.mcp import MCPTools
async def run_agent() -> None:
# Initialize the MCP tools
mcp_tools = MCPTools(url="https://docs.agno.com/mcp", transport="streamable-http")
# Connect to the MCP server
await mcp_tools.connect()
try:
agent = Agent(model=open_ai_like_model, tools=[mcp_tools], markdown=True)
await agent.aprint_response("What is agno?", stream=True)
finally:
# Always close the connection when done
await mcp_tools.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(run_agent())
示例使用MCPTools定义MCP工具,transport使用的是MCP最新版本传输协议Streamable HTTP,并通过connect()进行连接指定的MCP地址。
asyncio是Python中一个用于并发编程标准库
系统提示词
系统提示词在AI应用中至关重要,用于发送给模型作上下文并控制模型的输出。
Agno框架支持设置系统提示词、用户提示词(提问的问题)、历史对话消息以及**根据部分参数补充系统提示词。**如上文中有关session的使用属于增加历史对话;而markdown=True会补充系统提示词使用markdown格式输出。
1、主动设置系统提示词
定义Agent时设置system_message参数,可以明确指定系统提示词。设置此参数会失效其它会生成系统提示词的参数,如markdown=True不再补充系统提示词输出markdown格式。
2、特定参数生成系统提示词
在没有配置system_message参数时,有些参数会默认生成系统提示词。
from agno.agent import Agent
agent = Agent(
description="You are a famous short story writer asked to write for a magazine",
instructions=["You are a pilot on a plane flying from Hawaii to Japan."],
markdown=True,
debug_mode=True, # Set to True to view the detailed logs and see the compiled system message
)
agent.print_response("Tell me a 2 sentence horror story.", stream=True)
生成提示词如下:
You are a famous short story writer asked to write for a magazine
<instructions>
You are a pilot on a plane flying from Hawaii to Japan.
</instructions>
<additional_information>
- Use markdown to format your answers.
</additional_information>
更多生成系统提示词的Agent参数:
# --- Settings for building the default system message ---
# A description of the Agent that is added to the start of the system message.
description: Optional[str] = None
# List of instructions for the agent.
instructions: Optional[Union[str, List[str], Callable]] = None
# Provide the expected output from the Agent.
expected_output: Optional[str] = None
# Additional context added to the end of the system message.
additional_context: Optional[str] = None
# If markdown=true, add instructions to format the output using markdown
markdown: bool = False
# If True, add the agent name to the instructions
add_name_to_context: bool = False
# If True, add the current datetime to the instructions to give the agent a sense of time
# This allows for relative times like "tomorrow" to be used in the prompt
add_datetime_to_context: bool = False
# If True, add the current location to the instructions to give the agent a sense of place
# This allows for location-aware responses and local context
add_location_to_context: bool = False
# Allows for custom timezone for datetime instructions following the TZ Database format (e.g. "Etc/UTC")
timezone_identifier: Optional[str] = None
# If True, resolve session_state, dependencies, and metadata in the user and system messages
resolve_in_context: bool = True
03 多智能体(Team)
在Agno中,多Agent协作的智能体被定义为Team。“Team 是由多个 Agent(或其他子Team)组成的集合,它们通过协作来完成各项任务。”
被执行的Team被称为Team Leader,其它Agent或者子Team被称为Team Member。
与Agent类似,Team支持设置****大语言模型(LLM)、存储(会话)、记忆模块、知识库以及工具(支持 MCP)。
设置大模型(LLM):用于指导Team Leader向Team Member分配任务。其它模块的使用可以类比Agent部分。
from agno.agent import Agent
from agno.utils.pprint import pprint_run_response
from open_ai_like import open_ai_like_model
from agno.team import Team, TeamRunOutput
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
return f"The weather in {city} is sunny and warm."
def get_news(topic: str) -> str:
return f"The latest news about {topic} is HAHAHA"
agent_1 = Agent(model=open_ai_like_model,
role="News agent",
tools=[get_news],
description="get the latest news")
agent_2 = Agent(model=open_ai_like_model,
role="Weather agent",
tools=[get_weather],
description="get the weather for the next 3 days")
# 通过模型来判断要用的agent
team = Team(model=open_ai_like_model, name="News and Weather Team", members=[agent_1, agent_2])
# Synchronous execution 非流式
result: TeamRunOutput = team.run(input="What is the weather in Hangzhou?", debug_mode=True)
pprint_run_response(result)
# Synchronous execution 流式
#for chunk in team.run("What is the weather in Tokyo?", stream=True, stream_intermediate_steps=True):
# print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
示例定义的Team指定了两个Agent成员,分别是新闻Agent和天气Agent,两个Agent分别绑定了各自的工具列表。最后使用team.run进行提问。
如下是Team生成的系统提示词:
You are the leader of a team and sub-teams of AI Agents.
Your task is to coordinate the team to complete the user's request.
Here are the members in your team:
<team_members>
- Agent 1:
- ID: f2b3e3a2-a15e-432a-a465-8cf4de227561
- Role: News agent
- Member tools:
- get_news
- Agent 2:
- ID: be6eaf34-9808-4305-ba24-38960d27d8c7
- Role: Weather agent
- Member tools:
- get_weather
</team_members>
<how_to_respond>
- Your role is to delegate tasks to members in your team with the highest
likelihood of completing the user's request.
- Carefully analyze the tools available to the members and their roles
before delegating tasks.
- You cannot use a member tool directly. You can only delegate tasks to
members.
- When you delegate a task to another member, make sure to include:
- member_id (str): The ID of the member to delegate the task to. Use
only the ID of the member, not the ID of the team followed by the ID of
the member.
- task_description (str): A clear description of the task.
- expected_output (str): The expected output.
- You can delegate tasks to multiple members at once.
- You must always analyze the responses from members before responding to
the user.
- After analyzing the responses from the members, if you feel the task has
been completed, you can stop and respond to the user.
- If you are not satisfied with the responses from the members, you should
re-assign the task.
- For simple greetings, thanks, or questions about the team itself, you
should respond directly.
- For all work requests, tasks, or questions requiring expertise, route to
appropriate team members.
</how_to_respond>
任务会被指派给第二个查询天气的Agent,其系统提示词和用户提示词如下:
========================== system ==========================
get the weather for the next 3 days
<your_role>
Weather agent
</your_role>
=========================== user ===========================
You are a member of a team of agents. Your goal is to complete the
following task:
<task>
Get the current weather information for Hangzhou, China
</task>
<expected_output>
Current weather conditions including temperature, humidity, wind speed,
and general weather description for Hangzhou
</expected_output>
04 最后
整体而言,利用 Agno 构建智能体Agent能够显著降低开发成本与门槛。其有完整详尽的 API 文档大大降低了上手难度,性能则是该框架的另一大亮点。
Agno能力还不止于此,还支持如Human in the loop以及多模态等等,篇幅原因,可以直接借鉴官方文档学习。
最后
为什么要学AI大模型
当下,⼈⼯智能市场迎来了爆发期,并逐渐进⼊以⼈⼯通⽤智能(AGI)为主导的新时代。企业纷纷官宣“ AI+ ”战略,为新兴技术⼈才创造丰富的就业机会,⼈才缺⼝将达 400 万!
DeepSeek问世以来,生成式AI和大模型技术爆发式增长,让很多岗位重新成了炙手可热的新星,岗位薪资远超很多后端岗位,在程序员中稳居前列。

与此同时AI与各行各业深度融合,飞速发展,成为炙手可热的新风口,企业非常需要了解AI、懂AI、会用AI的员工,纷纷开出高薪招聘AI大模型相关岗位。

最近很多程序员朋友都已经学习或者准备学习 AI 大模型,后台也经常会有小伙伴咨询学习路线和学习资料,我特别拜托北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位的鲁为民老师给大家这里给大家准备了一份涵盖了AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频 全系列的学习资料,这些学习资料不仅深入浅出,而且非常实用,让大家系统而高效地掌握AI大模型的各个知识点。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
AI大模型系统学习路线
在面对AI大模型开发领域的复杂与深入,精准学习显得尤为重要。一份系统的技术路线图,不仅能够帮助开发者清晰地了解从入门到精通所需掌握的知识点,还能提供一条高效、有序的学习路径。

但知道是一回事,做又是另一回事,初学者最常遇到的问题主要是理论知识缺乏、资源和工具的限制、模型理解和调试的复杂性,在这基础上,找到高质量的学习资源,不浪费时间、不走弯路,又是重中之重。
AI大模型入门到实战的视频教程+项目包
看视频学习是一种高效、直观、灵活且富有吸引力的学习方式,可以更直观地展示过程,能有效提升学习兴趣和理解力,是现在获取知识的重要途径

光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。

海量AI大模型必读的经典书籍(PDF)
阅读AI大模型经典书籍可以帮助读者提高技术水平,开拓视野,掌握核心技术,提高解决问题的能力,同时也可以借鉴他人的经验。对于想要深入学习AI大模型开发的读者来说,阅读经典书籍是非常有必要的。

600+AI大模型报告(实时更新)
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

AI大模型面试真题+答案解析
我们学习AI大模型必然是想找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题都是总结当前最新、最热、最高频的面试题,并且每道题都有详细的答案,面试前刷完这套面试题资料,小小offer,不在话下


这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】






















 1124
1124

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








