CAS( compare and swap)
多个线程修改一个数据时,要比较修改前的值是否变化,如果变化了则不能修改
compare and exchange
ABA
数据已经被其他线程修改过,只不过又变回原先的值。导致线程不知道数据的变化。
线程是调度CPU的最小单元,也叫轻量级进程LWP(Light Weight Process)
两种线程模型
-
用户级线程
-
内核级线程
-
ULT:用户程序实现,不依赖操作系统核心,应用提供创建、同步、调度和管理线程的函数来控制用户线程。不需要用户态\内核态切换,速度快。内核对UTL无感知,线程阻塞则进程(包括它的所有线程)阻塞。
-
KLT:系统内核管理线程,内核保存线程的状态和上下文信息,线程阻塞不会引起进程的阻塞。在多处理器系统上,多线程并行运行。线程的创建、调度和管理由内核完成,效率比ULT高,比进程操作快。
Java虚拟机使用的是KTL。
Java线程创建依赖于系统内核,通过JVM调用系统库创建的内核线程,内核线程与Java-Thread是1:1的映射关系。
Why Java Thread Pool?
线程池的意义
线程是稀缺资源,它的创建与销毁使用个相对偏重且耗费资源的操作,而Java线程依赖于内核线程,创建线程需要进行操作系统状态切换,为避免资源过度消耗需要设法重用线程执行多个任务。线程池就是一个线程缓存,负责对线程进行统一分配、调优与监控。
什么时候使用线程池?
- 单个任务处理时间比较短
- 需要处理的任务量很大
线程池的优势?
重用存在的线程,减少线程创建、销毁的开销,提高性能。
提高响应速度。当任务到达时,无需新建线程就能立即执行。
提高线程的可管理性,可统一分配线程,调优和监控。
用户空间和内核空间

Java线程和内核线程的关系

线程池线程的执行过程

线程池的五种状态

package test.testThread;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 创建三百个线程来证明,Java虚拟机使用的是KTL
*/
public class ThreadModel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// for (int i = 0; i <300 ; i++) {
// Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// while (true){
// try {
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// }
// });
// t.start();
// }
final ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(5),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
for (int i = 0; i <9 ; i++) {
pool.execute(new Task(i));
}
pool.shutdown();
}
}
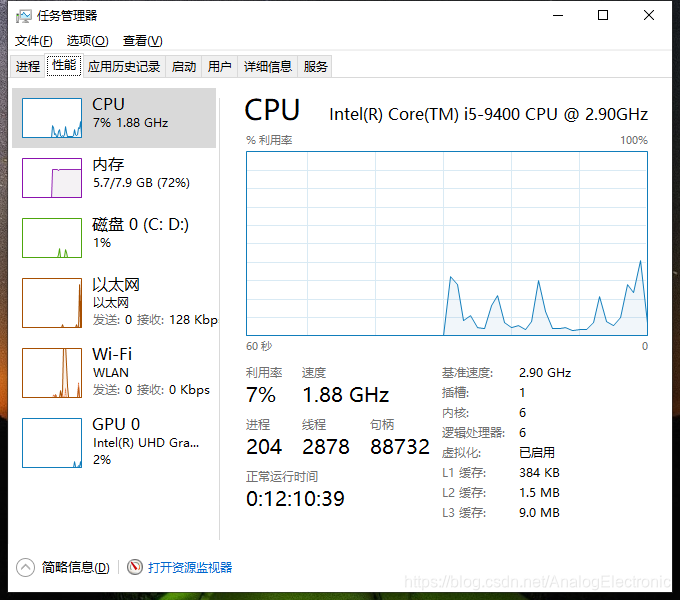
当三百个线程创建完成后,打开任务管理器发现,线程数比之前增加300个

package test.testThread;
public class Task implements Runnable {
private int nov;
public Task(int i){
this.nov = i;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行当前任务的线程是:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务"+nov+"正在执行...");
}
}

ThreadPoolExecutor
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
//参数合法性检查
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//检查线程阻塞队列、线程工厂、退出策略是否为空
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//赋值
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}





















 578
578

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








