

1. Period Jitter
file:///Users/ssong/Downloads/AN10007-Jitter-and-measurement%20(3).pdf
1.1 Period jitter is the deviation in cycle time of a clock signal with respect to the ideal period over a number of randomly selected cycles. Period jitter is useful in calculating timing margins in digital systems.
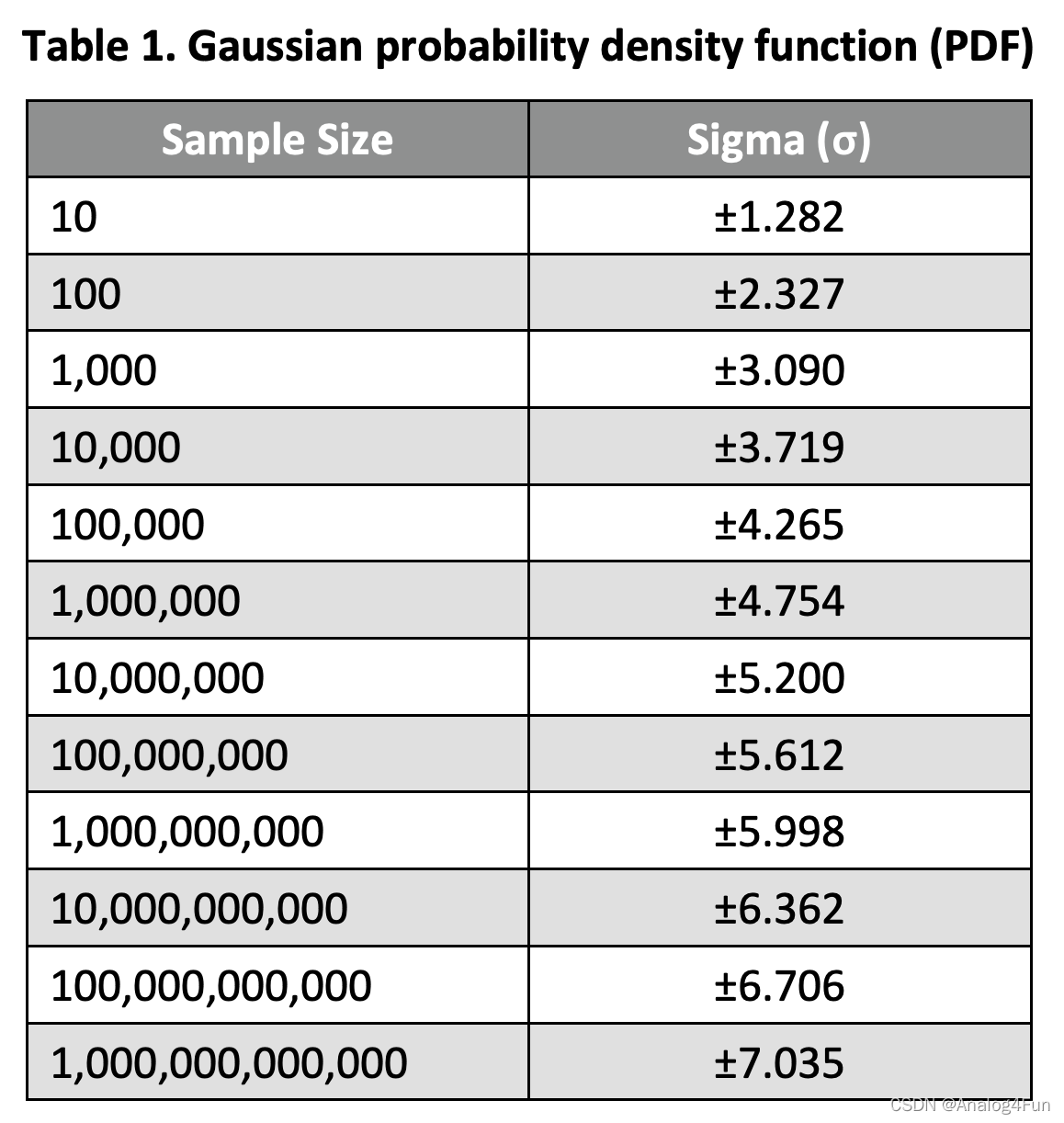
1.2 Because the period jitter from a clock is random in nature with Gaussian distribution, it can be completely expressed in terms of its Root Mean Square (RMS) value in pico-seconds (ps). However, the peak-to-peak value is more relevant in calculating setup and hold time budgets.
1.3 To convert the RMS jitter to peak-to-peak (Pk-Pk) jitter for a sample size of 10,000, the reader can use the following equation:
𝑃𝑒𝑎𝑘‒ 𝑡𝑜‒ 𝑝𝑒𝑎𝑘 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑗𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑟 = ±3.719 𝑥 (𝑅𝑀𝑆 𝑗𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑟)
2. Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter
2.1 C2C jitter is the variation in cycle time of a signal between adjacent cycles, over a random sample of adjacent cycle pairs. There is no reference to an ideal cycle.
2.2 C2C jitter is typically reported as a peak value in ps which defines the maximum deviation between the rising edges of any two consecutive clocks. And it is sometimes expressed as a RMS value in ps as well.
2.3 This type of jitter specification is commonly used to illustrate the stability of spread spectrum clocks because the period jitter is more sensitive to the frequency spreading feature while C2C jitter is not.
2.4 The peak value is the largest absolute (T1-T2) number in the data set.
3. Long-term Jitter
3.1 Deviation of N-consecutive periods of the actual clock from ideal clock. The actual number of cycles used in the measurement is application dependent. It represents the cumulative effect of jitter on a continuous stream of clock cycles over a long time interval.
3.2 Long-term jitter is typically useful in graphics/video displays and long-range telemetry applications such as range finders.
3.3 TIE measurements are especially useful when examining the behavior of transmitted data streams, where the reference clock is typically recovered from the data signal using a Clock/Data Recovery (CDR) circuit. A large TIE value may indicate that the PLL in the CDR is too slow in responding to the data stream’s changing bit rate.
4. Jitter's Relationship
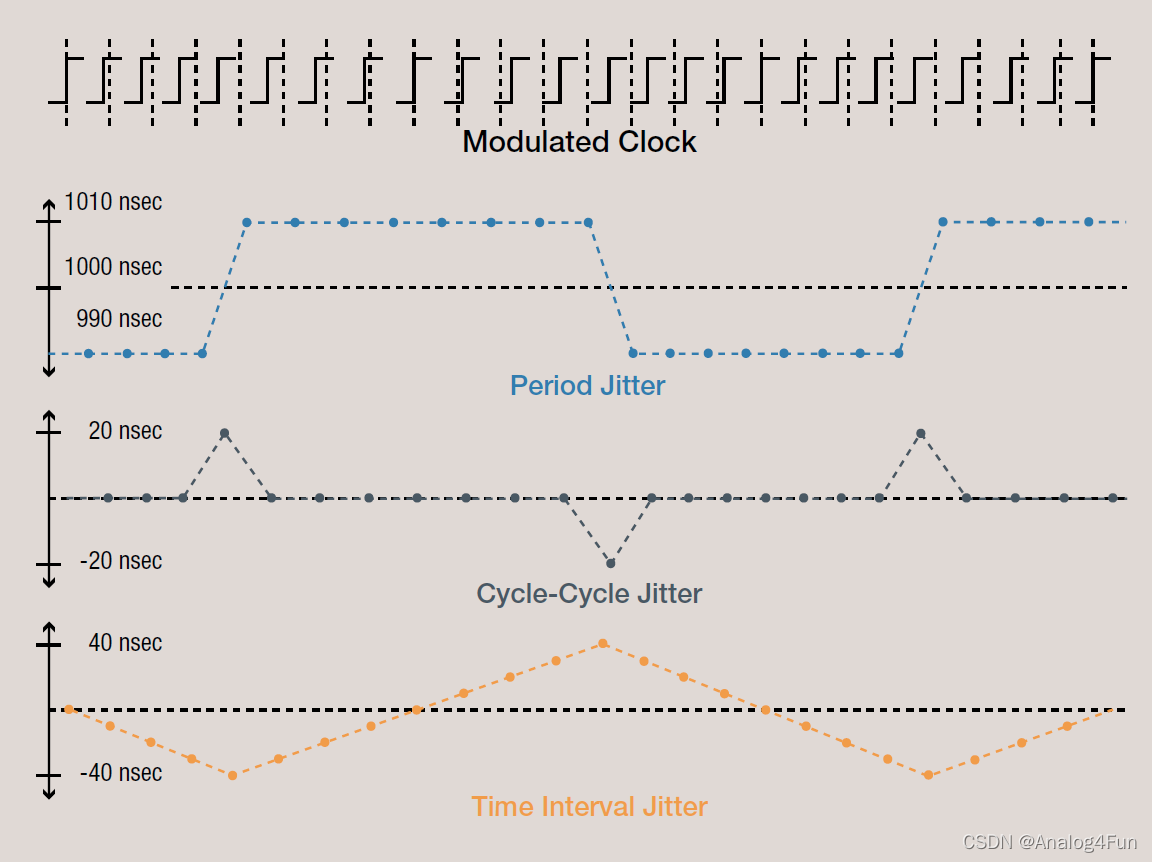
4.1 From the plot: 1) TIE is obtained by integrating the period jitter. 2) C2C is obtained by differentiating the period jitter. 3) Fixed period (or frequency) offset results in phase error accumulation (ramp in TIE).
4.2 PJ(j) = TIE(j)–TIE(j-1) ---> PJ(z)= TIE(z)*(1-z^-1)
Period jitter is first order high pass filtered TIE. Mostly high frequency jitter
4.3 Frequency/Period modulated by RTS noise in the comparator ---> period jitter
TIE shows ramp/saw-tooth behavior ---> integration of the PJ
 Jitter的类型、特性及相互关系
Jitter的类型、特性及相互关系






 本文详细介绍了时钟信号的三种抖动类型:周期抖动(Period Jitter)、周期间抖动(Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter)和长期抖动(Long-term Jitter)。周期抖动是相对于理想周期的时钟周期偏差,通常以RMS值表示。周期间抖动是相邻周期之间的变化,峰值值定义了连续时钟边沿的最大偏差。长期抖动则关注连续时钟周期在长时间间隔内的累积效应,适用于图形/视频显示和远程遥测应用。文章还探讨了这些抖动类型之间的关系,如周期抖动是周期间抖动的积分,而固定频率偏移导致相位误差积累。
本文详细介绍了时钟信号的三种抖动类型:周期抖动(Period Jitter)、周期间抖动(Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter)和长期抖动(Long-term Jitter)。周期抖动是相对于理想周期的时钟周期偏差,通常以RMS值表示。周期间抖动是相邻周期之间的变化,峰值值定义了连续时钟边沿的最大偏差。长期抖动则关注连续时钟周期在长时间间隔内的累积效应,适用于图形/视频显示和远程遥测应用。文章还探讨了这些抖动类型之间的关系,如周期抖动是周期间抖动的积分,而固定频率偏移导致相位误差积累。

















 3781
3781

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








