Build a circuit that has two 3-bit inputs that computes the bitwise-OR of the two vectors, the logical-OR of the two vectors, and the inverse (NOT) of both vectors. Place the inverse of in the upper half of (i.e., bits [5:3]), and the inverse of in the lower half. bout_nota
Bitwise vs. Logical Operators
Earlier, we mentioned that there are bitwise and logical versions of the various boolean operators (e.g., norgate). When using vectors, the distinction between the two operator types becomes important. A bitwise operation between two N-bit vectors replicates the operation for each bit of the vector and produces a N-bit output, while a logical operation treats the entire vector as a boolean value (true = non-zero, false = zero) and produces a 1-bit output.
Look at the simulation waveforms at how the bitwise-OR and logical-OR differ.
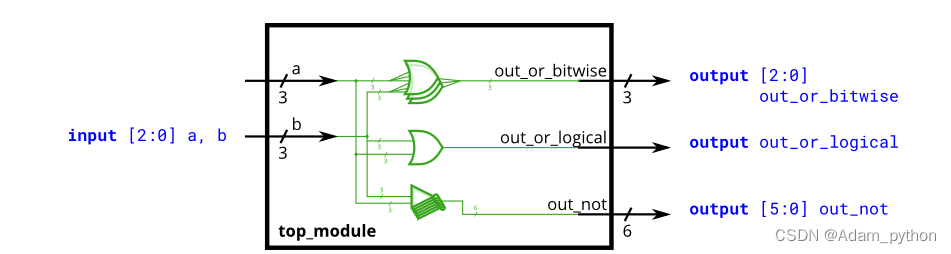
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise[0] = a[0] | b[0];
assign out_or_bitwise[1] = a[1] | b[1];
assign out_or_bitwise[2] = a[2] | b[2];
assign out_or_logical = a[0]|a[1]|a[2]|b[0]|b[1]|b[2];
assign out_not[0] = ~a[0];
assign out_not[1] = ~a[1];
assign out_not[2] = ~a[2];
assign out_not[3] = ~b[0];
assign out_not[4] = ~b[1];
assign out_not[5] = ~b[2];
endmodule




 这篇博客探讨了位操作和逻辑操作的区别,以3位输入向量为例,展示了如何构建一个电路来计算位向量的位OR、逻辑OR以及NOT操作。位操作在每个位上独立执行,而逻辑操作则将整个向量视为一个布尔值。文章通过示例代码展示了在Verilog中实现这些操作的方法,并用波形图对比了位OR和逻辑OR的不同。
这篇博客探讨了位操作和逻辑操作的区别,以3位输入向量为例,展示了如何构建一个电路来计算位向量的位OR、逻辑OR以及NOT操作。位操作在每个位上独立执行,而逻辑操作则将整个向量视为一个布尔值。文章通过示例代码展示了在Verilog中实现这些操作的方法,并用波形图对比了位OR和逻辑OR的不同。

















 2835
2835

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








