本文翻译自https://github.com/kgrzybek/modular-monolith-with-ddd,项目采用MIT宽松许可
文章目录
2.架构
2.4 模块请求处理CQRS
首先是命令和查询职责分离:

命令基于写入模型,根据DDD战术模式(Tactical Patterns)实现:
internal class CreateNewMeetingGroupCommandHandler : ICommandHandler<CreateNewMeetingGroupCommand>
{
private readonly IMeetingGroupRepository _meetingGroupRepository;
private readonly IMeetingGroupProposalRepository _meetingGroupProposalRepository;
internal CreateNewMeetingGroupCommandHandler(
IMeetingGroupRepository meetingGroupRepository,
IMeetingGroupProposalRepository meetingGroupProposalRepository)
{
_meetingGroupRepository = meetingGroupRepository;
_meetingGroupProposalRepository = meetingGroupProposalRepository;
}
public async Task<Unit> Handle(CreateNewMeetingGroupCommand request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var meetingGroupProposal = await _meetingGroupProposalRepository.GetByIdAsync(request.MeetingGroupProposalId);
var meetingGroup = meetingGroupProposal.CreateMeetingGroup();
await _meetingGroupRepository.AddAsync(meetingGroup);
return Unit.Value;
}
}
查询基于读取模型,在数据库视图上执行原始SQL语句:
internal class GetAllMeetingGroupsQueryHandler : IQueryHandler<GetAllMeetingGroupsQuery, List<MeetingGroupDto>>
{
private readonly ISqlConnectionFactory _sqlConnectionFactory;
internal GetAllMeetingGroupsQueryHandler(ISqlConnectionFactory sqlConnectionFactory)
{
_sqlConnectionFactory = sqlConnectionFactory;
}
public async Task<List<MeetingGroupDto>> Handle(GetAllMeetingGroupsQuery request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var connection = _sqlConnectionFactory.GetOpenConnection();
const string sql = "SELECT " +
"[MeetingGroup].[Id], " +
"[MeetingGroup].[Name], " +
"[MeetingGroup].[Description], " +
"[MeetingGroup].[LocationCountryCode], " +
"[MeetingGroup].[LocationCity]" +
"FROM [meetings].[v_MeetingGroups] AS [MeetingGroup]";
var meetingGroups = await connection.QueryAsync<MeetingGroupDto>(sql);
return meetingGroups.AsList();
}
}
命令和查询职责分离的优缺点如下:
优点:
- 解决方案适用于问题:读取和写入需求不一样;
- 满足SRP:一个处理器只做一件事;
- 满足ISP:每个处理器只实现接口的一个方法;
- 命令和接口都是objects(参数object模式),方便序列化和反序列化;
- 简单的方式实现装饰者模式来处理交叉关注点;
- 松散耦合:引入中介者模式将请求处理器和请求调用者解除耦合;
缺点:
- 引入中介更难弄明白哪个类处理哪类请求;
2.5 域模型的规则和标签
领域模型是这个系统中最关键的部分,设计时需要额外的注意。这里有几个关键要点:
2.5.1 站在上层进行封装
所有的成员默认都是私有的,然后是内部(internal),最后才考虑public。
2.5.2 上层PI(Persistence Ignorance)
不依赖基础设施和数据库等,所有类都是POCO;
2.5.3 行为丰富
所有的业务逻辑都封装在领域模型内,不能出现在应用层和其他地方;
2.5.4 Low level of primitive obsession(不知道怎么翻译,请懂的大佬指教)
使用ValueObjects将实体的基本属性组织在一起;
2.5.5 业务语言
在限定上下文环境以业务语言命名所有类、方法和成员;
2.5.6 可测试
领域模型是系统中最为重要的部分,所以必须是容易测试的;
相关代码如下:
public class MeetingGroup : Entity, IAggregateRoot
{
public MeetingGroupId Id { get; private set; }
private string _name;
private string _description;
private MeetingGroupLocation _location;
private MemberId _creatorId;
private List<MeetingGroupMember> _members;
private DateTime _createDate;
private DateTime? _paymentDateTo;
internal static MeetingGroup CreateBasedOnProposal(
MeetingGroupProposalId meetingGroupProposalId,
string name,
string description,
MeetingGroupLocation location, MemberId creatorId)
{
return new MeetingGroup(meetingGroupProposalId, name, description, location, creatorId);
}
public Meeting CreateMeeting(
string title,
MeetingTerm term,
string description,
MeetingLocation location,
int? attendeesLimit,
int guestsLimit,
Term rsvpTerm,
MoneyValue eventFee,
List<MemberId> hostsMembersIds,
MemberId creatorId)
{
this.CheckRule(new MeetingCanBeOrganizedOnlyByPayedGroupRule(_paymentDateTo));
this.CheckRule(new MeetingHostMustBeAMeetingGroupMemberRule(creatorId, hostsMembersIds, _members));
return new Meeting(this.Id,
title,
term,
description,
location,
attendeesLimit,
guestsLimit,
rsvpTerm,
eventFee,
hostsMembersIds,
creatorId);
}
2.6 交叉关注点
为了满足单一职责原则和不重复原则,使用装饰者模式实现交叉关注点,使用三个装饰者来包装命令处理类:日志、验证和单元工作(unit of work,如下图所示:

2.6.1 日志
日志相关的代码如下:
internal class LoggingCommandHandlerDecorator<T> : ICommandHandler<T> where T:ICommand
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
private readonly IExecutionContextAccessor _executionContextAccessor;
private readonly ICommandHandler<T> _decorated;
public LoggingCommandHandlerDecorator(
ILogger logger,
IExecutionContextAccessor executionContextAccessor,
ICommandHandler<T> decorated)
{
_logger = logger;
_executionContextAccessor = executionContextAccessor;
_decorated = decorated;
}
public async Task<Unit> Handle(T command, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if (command is IRecurringCommand)
{
return await _decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
}
using (
LogContext.Push(
new RequestLogEnricher(_executionContextAccessor),
new CommandLogEnricher(command)))
{
try
{
this._logger.Information(
"Executing command {Command}",
command.GetType().Name);
var result = await _decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
this._logger.Information("Command {Command} processed successful", command.GetType().Name);
return result;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
this._logger.Error(exception, "Command {Command} processing failed", command.GetType().Name);
throw;
}
}
}
private class CommandLogEnricher : ILogEventEnricher
{
private readonly ICommand _command;
public CommandLogEnricher(ICommand command)
{
_command = command;
}
public void Enrich(LogEvent logEvent, ILogEventPropertyFactory propertyFactory)
{
logEvent.AddOrUpdateProperty(new LogEventProperty("Context", new ScalarValue($"Command:{_command.Id.ToString()}")));
}
}
private class RequestLogEnricher : ILogEventEnricher
{
private readonly IExecutionContextAccessor _executionContextAccessor;
public RequestLogEnricher(IExecutionContextAccessor executionContextAccessor)
{
_executionContextAccessor = executionContextAccessor;
}
public void Enrich(LogEvent logEvent, ILogEventPropertyFactory propertyFactory)
{
if (_executionContextAccessor.IsAvailable)
{
logEvent.AddOrUpdateProperty(new LogEventProperty("CorrelationId", new ScalarValue(_executionContextAccessor.CorrelationId)));
}
}
}
}
2.6.2 验证
验证装饰者执行命令数据验证,使用FluentValidation库:
internal class ValidationCommandHandlerDecorator<T> : ICommandHandler<T> where T:ICommand
{
private readonly IList<IValidator<T>> _validators;
private readonly ICommandHandler<T> _decorated;
public ValidationCommandHandlerDecorator(
IList<IValidator<T>> validators,
ICommandHandler<T> decorated)
{
this._validators = validators;
_decorated = decorated;
}
public Task<Unit> Handle(T command, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var errors = _validators
.Select(v => v.Validate(command))
.SelectMany(result => result.Errors)
.Where(error => error != null)
.ToList();
if (errors.Any())
{
var errorBuilder = new StringBuilder();
errorBuilder.AppendLine("Invalid command, reason: ");
foreach (var error in errors)
{
errorBuilder.AppendLine(error.ErrorMessage);
}
throw new InvalidCommandException(errorBuilder.ToString(), null);
}
return _decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
}
}
2.6.3 单元工作
每条命令处理都有副作用。使用UnitOfWorkCommandHandlerDecorator装饰器类来达到不在每个处理器(handler)上调用提交(Commit)。 如果是内部命令则会额外标记InternalCommand为已处理,并且分派所有领域事件(作为工作单元的一部分)。
public class UnitOfWorkCommandHandlerDecorator<T> : ICommandHandler<T> where T:ICommand
{
private readonly ICommandHandler<T> _decorated;
private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
private readonly MeetingsContext _meetingContext;
public UnitOfWorkCommandHandlerDecorator(
ICommandHandler<T> decorated,
IUnitOfWork unitOfWork,
MeetingsContext meetingContext)
{
_decorated = decorated;
_unitOfWork = unitOfWork;
_meetingContext = meetingContext;
}
public async Task<Unit> Handle(T command, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await this._decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
if (command is InternalCommandBase)
{
var internalCommand =
await _meetingContext.InternalCommands.FirstOrDefaultAsync(x => x.Id == command.Id,
cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
if (internalCommand != null)
{
internalCommand.ProcessedDate = DateTime.UtcNow;
}
}
await this._unitOfWork.CommitAsync(cancellationToken);
return Unit.Value;
}
}
2.7 模块集成
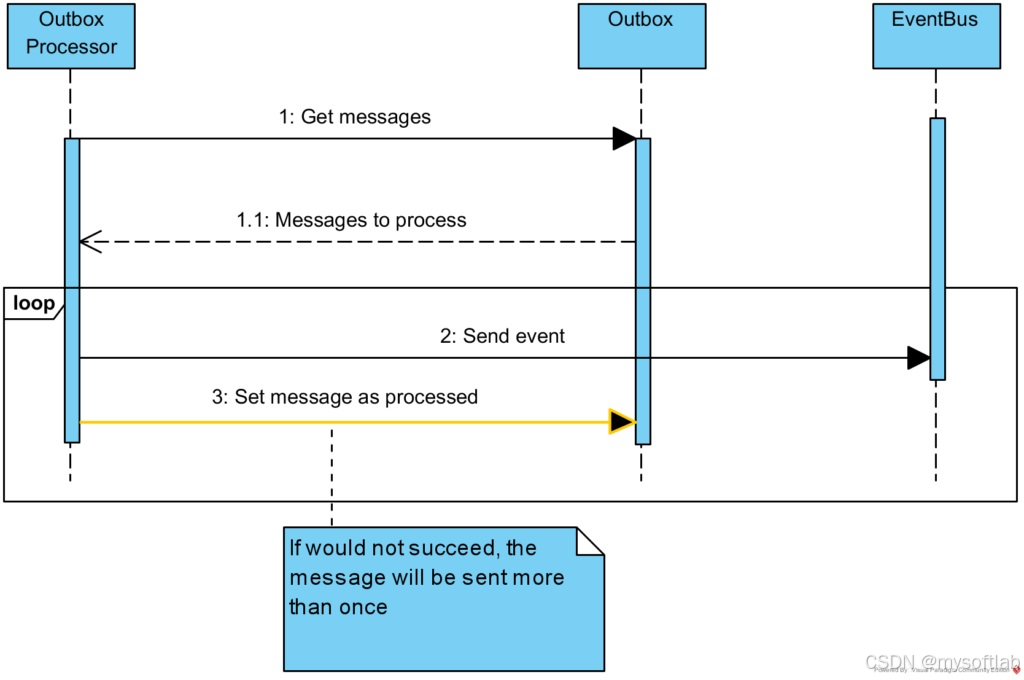
模块间集成只发生在使用异步方式进行事件传递,这种方式模块间的耦合度最小,模块间不共享数据,为了保证最大可靠性,使用了Outbox/Inbox模式,保证至少一次送到和至少一次处理。

Outbox和Inbox基于两个SQL表格和各个模块的后台工作线程实现。后台工作者线程基于Quartz.NET库。
保存到Outbox:

处理Outbox:
2.8 内部处理
系统的主要原则是只能通过指定的命令才能改变内部状态。有时候,命令的调用方可以不是API而是处理模块自身。使用这种机制是为了保证在不同线程和事务进行数据处理时的最终一致性。实现内部处理跟实现Outbox和Inbox非常相似,一个SQL表和一个工作者线程负责进行处理,每个内部处理命令必须继承InternalCommandBase类:
internal abstract class InternalCommandBase : ICommand
{
public Guid Id { get; }
protected InternalCommandBase(Guid id)
{
this.Id = id;
}
}
这非常重要因为UnitOfWorkCommandHandlerDecorator在提交的时候必须标记内部命令为已处理:
public async Task<Unit> Handle(T command, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await this._decorated.Handle(command, cancellationToken);
if (command is InternalCommandBase)
{
var internalCommand =
await _meetingContext.InternalCommands.FirstOrDefaultAsync(x => x.Id == command.Id,
cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
if (internalCommand != null)
{
internalCommand.ProcessedDate = DateTime.UtcNow;
}
}
await this._unitOfWork.CommitAsync(cancellationToken);
return Unit.Value;
}
2.9 安全
2.9.1 认证
认证基于IdentityServer的JWT token和Bearer实现。目前只有一个认证方式实现了,需要实现IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator接口:
public class ResourceOwnerPasswordValidator : IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator
{
private readonly IUserAccessModule _userAccessModule;
public ResourceOwnerPasswordValidator(IUserAccessModule userAccessModule)
{
_userAccessModule = userAccessModule;
}
public async Task ValidateAsync(ResourceOwnerPasswordValidationContext context)
{
var authenticationResult = await _userAccessModule.ExecuteCommandAsync(new AuthenticateCommand(context.UserName, context.Password));
if (!authenticationResult.IsAuthenticated)
{
context.Result = new GrantValidationResult(
TokenRequestErrors.InvalidGrant,
authenticationResult.AuthenticationError);
return;
}
context.Result = new GrantValidationResult(
authenticationResult.User.Id.ToString(),
"forms",
authenticationResult.User.Claims);
}
}
2.9.2 授权
授权机制基于权限实现了RBAC(基于角色的用户访问控制),权限比角色更好更安全。每个用户具有一系列角色,每个角色包含了一到多个权限。在Controller层经常需要检查用户权限:
[HttpPost]
[Route("")]
[HasPermission(MeetingsPermissions.ProposeMeetingGroup)]
public async Task<IActionResult> ProposeMeetingGroup(ProposeMeetingGroupRequest request)
{
await _meetingsModule.ExecuteCommandAsync(
new ProposeMeetingGroupCommand(
request.Name,
request.Description,
request.LocationCity,
request.LocationCountryCode));
return Ok();
}
2.10 单元测试
好的单元测试具有以下特点:
- 自动
- 可维护
- 运行快速
- 一致性,任何时候结果一致
- 与其他测试分离
- 可读性
- 可以被任何人执行
- 测试公共API,而不是内部行为
- 看起来像生产代码(production code)
- 当做生产代码
每个单元测试模块具有三个标准:Arrange、Act和Assert

①Arrange
准备测试公共方法的聚合,这个公共方法叫做SUT(system under test)。
- 只使用领域模型的公共API
- 不使用InternalsVisibleToAttribute类
- 不使用ConditionAttribute类
- 不创建只为测试提供的构造函数和工厂函数
- 不改变领域模型的封装,如将internal/private关键字改为public
- 不创建临时类继承自测试类来访问内部方法或属性
②Act
在SUT中只执行一个public方法。
③Assert - 方法执行完毕领域事件已经发布
- 业务规则破坏
简单实例:
[Test]
public void NewUserRegistration_WithUniqueLogin_IsSuccessful()
{
// Arrange
var usersCounter = Substitute.For<IUsersCounter>();
// Act
var userRegistration =
UserRegistration.RegisterNewUser(
"login", "password", "test@email",
"firstName", "lastName", usersCounter);
// Assert
var newUserRegisteredDomainEvent = AssertPublishedDomainEvent<NewUserRegisteredDomainEvent>(userRegistration);
Assert.That(newUserRegisteredDomainEvent.UserRegistrationId, Is.EqualTo(userRegistration.Id));
}
[Test]
public void NewUserRegistration_WithoutUniqueLogin_BreaksUserLoginMustBeUniqueRule()
{
// Arrange
var usersCounter = Substitute.For<IUsersCounter>();
usersCounter.CountUsersWithLogin("login").Returns(x => 1);
// Assert
AssertBrokenRule<UserLoginMustBeUniqueRule>(() =>
{
// Act
UserRegistration.RegisterNewUser(
"login", "password", "test@email",
"firstName", "lastName", usersCounter);
});
}
高级实例:
[Test]
public void AddAttendee_WhenMemberIsAlreadyAttendeeOfMeeting_IsNotPossible()
{
// Arrange
var creatorId = new MemberId(Guid.NewGuid());
var meetingTestData = CreateMeetingTestData(new MeetingTestDataOptions
{
CreatorId = creatorId
});
var newMemberId = new MemberId(Guid.NewGuid());
meetingTestData.MeetingGroup.JoinToGroupMember(newMemberId);
meetingTestData.Meeting.AddAttendee(meetingTestData.MeetingGroup, newMemberId, 0);
// Assert
AssertBrokenRule<MemberCannotBeAnAttendeeOfMeetingMoreThanOnceRule>(() =>
{
// Act
meetingTestData.Meeting.AddAttendee(meetingTestData.MeetingGroup, newMemberId, 0);
});
}
CreateMeetingTestData方法是SUT Factory的实现:
protected MeetingTestData CreateMeetingTestData(MeetingTestDataOptions options)
{
var proposalMemberId = options.CreatorId ?? new MemberId(Guid.NewGuid());
var meetingProposal = MeetingGroupProposal.ProposeNew(
"name", "description",
new MeetingGroupLocation("Warsaw", "PL"), proposalMemberId);
meetingProposal.Accept();
var meetingGroup = meetingProposal.CreateMeetingGroup();
meetingGroup.UpdatePaymentInfo(DateTime.Now.AddDays(1));
var meetingTerm = options.MeetingTerm ??
new MeetingTerm(DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(1), DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(2));
var rsvpTerm = options.RvspTerm ?? Term.NoTerm;
var meeting = meetingGroup.CreateMeeting("title",
meetingTerm,
"description",
new MeetingLocation("Name", "Address", "PostalCode", "City"),
options.AttendeesLimit,
options.GuestsLimit,
rsvpTerm,
MoneyValue.Zero,
new List<MemberId>(),
proposalMemberId);
DomainEventsTestHelper.ClearAllDomainEvents(meetingGroup);
return new MeetingTestData(meetingGroup, meeting);
}
























 1176
1176

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








