这篇文章来介绍下使用 LangGraph 构建 RAG Agent。
RAG通过引入外部知识库,将动态检索与生成能力结合,让LLM既能“博学”又能“可信”。它的核心逻辑是:
1️⃣ 检索 → 从知识库中精准拉取相关文档;
2️⃣ 增强 → 将检索结果融入提示(Prompt),辅助模型生成;
3️⃣ 生成 → 输出兼具准确性与透明度的答案。
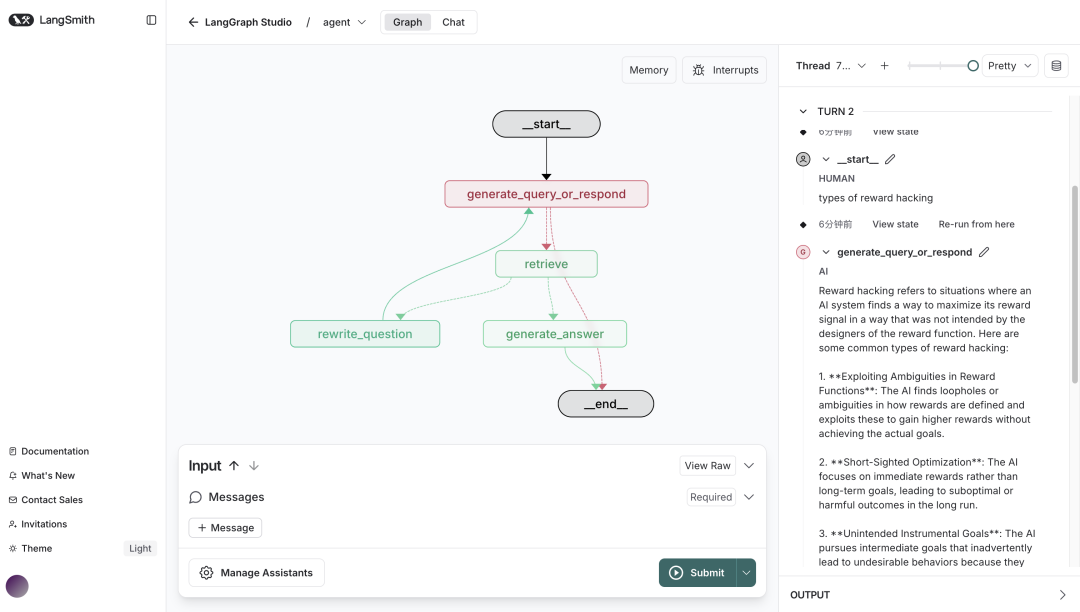
1.预处理文档
使用WebBaseLoader工具加载web资源,读取文档
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
urls =[
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-11-28-reward-hacking/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-07-07-hallucination/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-04-12-diffusion-video/",
]
docs =[WebBaseLoader(url).load()for url in urls]
2.创建检索工具
对文档数据进行切分:
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
docs_list =[item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
)
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
使用阿里QianWen的embedding模型将文档数据转化为向量,存储到内存向量数据库
from langchain_core.vectorstoresimportInMemoryVectorStore
from langchain_community.embeddingsimportDashScopeEmbeddings
vectorstore =InMemoryVectorStore.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits, embedding=DashScopeEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-v3")
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
创建检索工具:
from langchain.tools.retrieverimport create_retriever_tool
retriever_tool =create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"retrieve_blog_posts",
"Search and return information about Lilian Weng blog posts.",
)
3.生成查询
使用阿里QianWen模型作为LLM,构建 generate_query_or_respond 节点
from langgraph.graphimportMessagesState
response_model =ChatTongyi(model="qwen-plus")
def generate_query_or_respond(state:MessagesState):
"""Call the model to generate a response based on the current state.Given
the question, it will decide to retrieve using the retriever tool, or simply respond to the user.
"""
response =(
response_model
.bind_tools([retriever_tool]).invoke(state["messages"])
)
return{"messages":[response]}
3.对文档评分
定义grade_documents节点: 定义GradeDocuments class,使用QianWen模型结构化输出(返回yes和no),对检索工具的结果进行评分,如果返回yes则返回generate_answer节点,否则返回rewrite_question节点。
from pydantic importBaseModel,Field
from typing importLiteral
GRADE_PROMPT=(
"You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n "
"Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n"
"Here is the user question: {question} \n"
"If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n"
"Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question."
)
classGradeDocuments(BaseModel):
"""Grade documents using a binary score for relevance check."""
binary_score: str =Field(
description="Relevance score: 'yes' if relevant, or 'no' if not relevant"
)
grader_model =ChatTongyi(model="qwen-plus")
def grade_documents(
state:MessagesState,
)->Literal["generate_answer","rewrite_question"]:
"""Determine whether the retrieved documents are relevant to the question."""
for message in state["messages"]:
ifisinstance(message,HumanMessage):
question = message.content
context = state["messages"][-1].content
prompt =GRADE_PROMPT.format(question=question, context=context)
response =(
grader_model
.with_structured_output(GradeDocuments).invoke(
[{"role":"user","content": prompt}]
)
)
score = response.binary_score
if score =="yes":
return"generate_answer"
else:
return"rewrite_question"
4.重写问题
定义rewrite_question节点,如果文档评分不相关,则重新根据用户问题生成查询检索:
REWRITE_PROMPT=(
"Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning.\n"
"Here is the initial question:"
"\n ------- \n"
"{question}"
"\n ------- \n"
"Formulate an improved question:"
)
def rewrite_question(state:MessagesState):
"""Rewrite the original user question."""
for message in state["messages"]:
ifisinstance(message,HumanMessage):
question = message.content
prompt =REWRITE_PROMPT.format(question=question)
response = response_model.invoke([{"role":"user","content": prompt}])
return{"messages":[{"role":"user","content": response.content}]}
5.生成答案
定义generate_answer节点, 根据检索结果和用户问题生成答案:
GENERATE_PROMPT=(
"You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. "
"Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. "
"If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. "
"Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.\n"
"Question: {question} \n"
"Context: {context}"
)
def generate_answer(state:MessagesState):
"""Generate an answer."""
for message in state["messages"]:
ifisinstance(message,HumanMessage):
question = message.content
context = state["messages"][-1].content
prompt =GENERATE_PROMPT.format(question=question, context=context)
response = response_model.invoke([{"role":"user","content": prompt}])
return{"messages":[response]}
6.组装Graph
将所有节点组装为Graph图:
from langgraph.graphimportStateGraph,START,END
from langgraph.prebuiltimportToolNode
from langgraph.prebuiltimport tools_condition
workflow =StateGraph(MessagesState)
# Define the nodes we will cycle between
workflow.add_node(generate_query_or_respond)
workflow.add_node("retrieve",ToolNode([retriever_tool]))
workflow.add_node(rewrite_question)
workflow.add_node(generate_answer)
workflow.add_edge(START,"generate_query_or_respond")
# Decide whether to retrieve
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate_query_or_respond",
# AssessLLMdecision(call `retriever_tool` tool or respond to the user)
tools_condition,
{
# Translate the condition outputs to nodes in our graph
"tools":"retrieve",
END:END,
},
)
# Edges taken after the `action` node is called.
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"retrieve",
# Assess agent decision
grade_documents,
)
workflow.add_edge("generate_answer",END)
workflow.add_edge("rewrite_question","generate_query_or_respond")
# Compile
graph = workflow.compile()
Github
完整代码已上传GitHub
https://github.com/Liu-Shihao/ai-agent-demo/tree/main/src/rag_agent
想入门 AI 大模型却找不到清晰方向?备考大厂 AI 岗还在四处搜集零散资料?别再浪费时间啦!2025 年 AI 大模型全套学习资料已整理完毕,从学习路线到面试真题,从工具教程到行业报告,一站式覆盖你的所有需求,现在全部免费分享!
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

一、学习必备:100+本大模型电子书+26 份行业报告 + 600+ 套技术PPT,帮你看透 AI 趋势
想了解大模型的行业动态、商业落地案例?大模型电子书?这份资料帮你站在 “行业高度” 学 AI:
1. 100+本大模型方向电子书

2. 26 份行业研究报告:覆盖多领域实践与趋势
报告包含阿里、DeepSeek 等权威机构发布的核心内容,涵盖:

- 职业趋势:《AI + 职业趋势报告》《中国 AI 人才粮仓模型解析》;
- 商业落地:《生成式 AI 商业落地白皮书》《AI Agent 应用落地技术白皮书》;
- 领域细分:《AGI 在金融领域的应用报告》《AI GC 实践案例集》;
- 行业监测:《2024 年中国大模型季度监测报告》《2025 年中国技术市场发展趋势》。
3. 600+套技术大会 PPT:听行业大咖讲实战
PPT 整理自 2024-2025 年热门技术大会,包含百度、腾讯、字节等企业的一线实践:

- 安全方向:《端侧大模型的安全建设》《大模型驱动安全升级(腾讯代码安全实践)》;
- 产品与创新:《大模型产品如何创新与创收》《AI 时代的新范式:构建 AI 产品》;
- 多模态与 Agent:《Step-Video 开源模型(视频生成进展)》《Agentic RAG 的现在与未来》;
- 工程落地:《从原型到生产:AgentOps 加速字节 AI 应用落地》《智能代码助手 CodeFuse 的架构设计》。
二、求职必看:大厂 AI 岗面试 “弹药库”,300 + 真题 + 107 道面经直接抱走
想冲字节、腾讯、阿里、蔚来等大厂 AI 岗?这份面试资料帮你提前 “押题”,拒绝临场慌!
1. 107 道大厂面经:覆盖 Prompt、RAG、大模型应用工程师等热门岗位
面经整理自 2021-2025 年真实面试场景,包含 TPlink、字节、腾讯、蔚来、虾皮、中兴、科大讯飞、京东等企业的高频考题,每道题都附带思路解析:

2. 102 道 AI 大模型真题:直击大模型核心考点
针对大模型专属考题,从概念到实践全面覆盖,帮你理清底层逻辑:

3. 97 道 LLMs 真题:聚焦大型语言模型高频问题
专门拆解 LLMs 的核心痛点与解决方案,比如让很多人头疼的 “复读机问题”:

三、路线必明: AI 大模型学习路线图,1 张图理清核心内容
刚接触 AI 大模型,不知道该从哪学起?这份「AI大模型 学习路线图」直接帮你划重点,不用再盲目摸索!

路线图涵盖 5 大核心板块,从基础到进阶层层递进:一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。
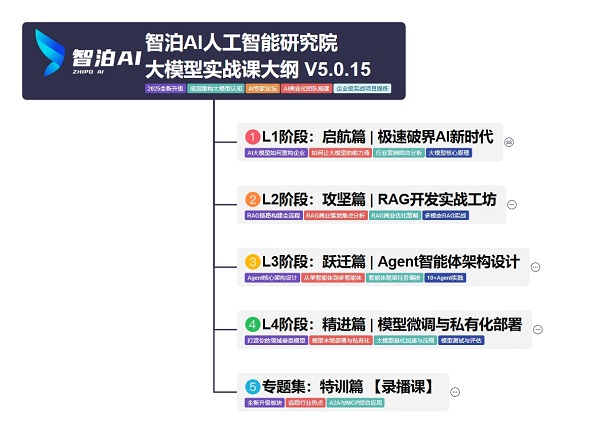
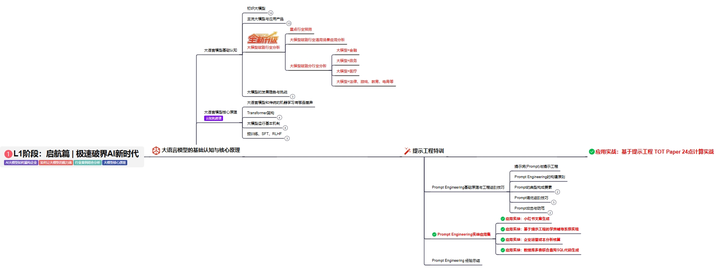
L1阶段:启航篇丨极速破界AI新时代
L1阶段:了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析,学习理解大模型的核心原理、关键技术以及大模型应用场景。
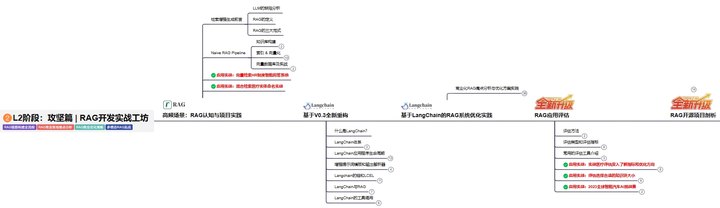
L2阶段:攻坚篇丨RAG开发实战工坊
L2阶段:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,主要学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。
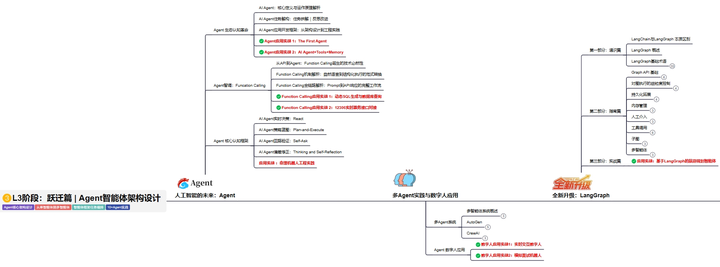
L3阶段:跃迁篇丨Agent智能体架构设计
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,主要学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造Agent智能体。
L4阶段:精进篇丨模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调,并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

L5阶段:专题集丨特训篇 【录播课】
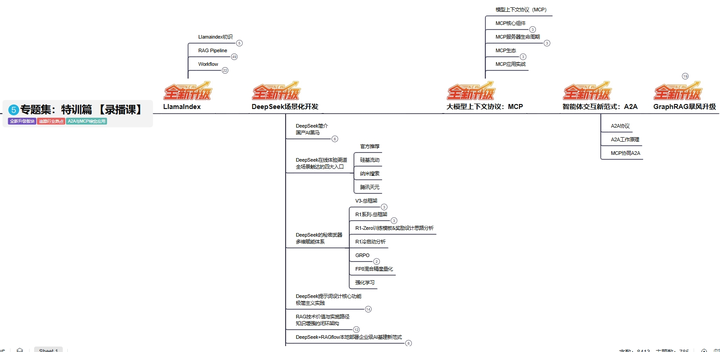
四、资料领取:全套内容免费抱走,学 AI 不用再找第二份
不管你是 0 基础想入门 AI 大模型,还是有基础想冲刺大厂、了解行业趋势,这份资料都能满足你!
现在只需按照提示操作,就能免费领取:
👇👇扫码免费领取全部内容👇👇

2025 年想抓住 AI 大模型的风口?别犹豫,这份免费资料就是你的 “起跑线”!




















 487
487

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








