希尔排序
- 原理:
因为插入排序在(1):序列基本有序的情况下;(2)数据较少的情况下;效率较高,对于乱序的大数据效率不高。所以希尔排序对此进行优化,先分组进行插入排序,完成之后序列基本有序,再进行最后总的插入排序。
代码
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
//对插入排序的改进
void Shell_Sorting(int array[10], int length)
{
int increase = length;
int tmp;
int i,j,k;
do
{
increase = increase / 3 + 1; //循环到最后肯定是1, 1执行下面代码意味着总的插入排序,但是经过前面几次分组之后,序列基本有序,效率会高很多
for ( i = 0; i < increase; i++) //进行的是第几组
{
for ( j = i + increase; j < length; j += increase) //下面代码对每组进行插入排序
{
if (array[j] < array[j - increase])
{
tmp = array[j];
for ( k = j - increase; k >= 0 && tmp < array[k]; k -= increase)
{
array[k+increase] = array[k];
}
array[k + increase] = tmp;
}
}
}
} while (increase > 1); //进行最后一次总的插入排序,increase==1,那么条件不成立,结束了
}
void Insert_Sorting(int array[], int length)
{
int tmp, j;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
if (array[i] < array[i - 1])
{
tmp = array[i];
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && tmp < array[j]; j--)
{
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
array[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int array[10];
int length = sizeof(array) / sizeof(int);
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
cout << "排序前:";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
array[i] = rand() % 10;
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
Shell_Sorting(array, length);
cout << "排序后:";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
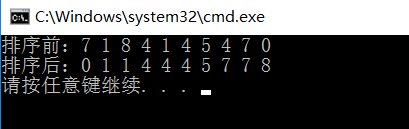
和插入排序对比效率
int main()
{
int array1[100000];
int array2[100000];
int length = sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int);
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
array1[i] = rand() ;
}
memcpy(array2,array1,length);
cout << "希尔排序" << " :";
double start1 = GetTickCount();
Shell_Sorting(array1, length);
double end1 = GetTickCount();
cout << end1 - start1 << " ms"<<endl;
cout << "插入排序" << " :";
double start2 = GetTickCount();
Insert_Sorting(array2, length);
double end2 = GetTickCount();
cout << end2 - start2 << " ms" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:可见希尔排序比插入排序的效率高得多
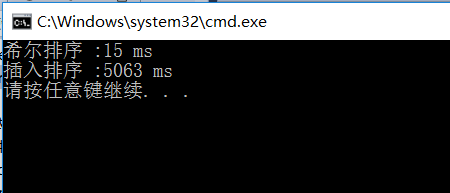





















 18万+
18万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








