由题目(也是基础知识),二叉树的遍历如下:
二叉树遍历:
对一棵二叉树进行遍历,我们可以采取3中顺序进行遍历,分别是前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。这三种方式是以访问父节点的顺序来进行命名的。假设父节点是N,左节点是L,右节点是R,那么对应的访问遍历顺序如下:
前序遍历 N->L->R
中序遍历 L->N->R
后序遍历 L->R->N
所以,对于以下这棵树,三种遍历方式的结果是:
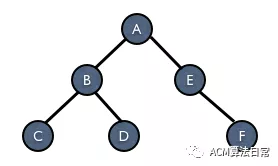
::: 前序遍历 ABCDEF
::: 中序遍历 CBDAEF
::: 后序遍历 CDBFEA
思路:
题目里给了前序和中序,我们可以知道,前序的第一个肯定是根,在中序中找到根的位置n,n左边的就是左子树,右边的就是右子树(根据上面说的中序遍历),那么再由前序遍历的定义,我们得知2-n+1就是左子树(前序),剩下的就是右子树,再分析前序里的左子树,左子树最左面的肯定又是一个根(只不过他不是最上面的根儿,叫他分根),再像上面一样操作,你会发现,这不就是递归嘛,我们就按上面的步骤进行递归
递归方程:
int build(int L1,int R1,int L2,int R2)//L1,R1是前序左右范围,L2,R2中序
{
if(L1 > R1) return 0;
int root = pre_order[L1];//前序第一个为根
int p = L2;
while(in_order[p] != root) p++;//找到中序的根
int cnt = p-L2;
lch[root] = build(L1+1,L1+cnt,L2,L2+cnt-1);//构建左子树
rch[root] = build(L1+cnt+1,R1,p+1,R2);//构建右子树
return root;
}
然后用lch,rch数组构建二叉树,最后用递归求后序遍历
先左边,再右边,后中间
void dfs(int l)
{
if(lch[l]) dfs(lch[l]); //左边
if(rch[l]) dfs(rch[l]);//右边
a.push_back(l);//中间
return;
}
最后ac代码是:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000+8;
int N;
int pre_order[maxn],in_order[maxn];
int lch[maxn],rch[maxn];
vector<int> a;
int build(int L1,int R1,int L2,int R2)
{
if(L1 > R1) return 0;
int root = pre_order[L1];
int p = L2;
while(in_order[p] != root) p++;
int cnt = p-L2;
lch[root] = build(L1+1,L1+cnt,L2,L2+cnt-1);
rch[root] = build(L1+cnt+1,R1,p+1,R2);
return root;
}
void dfs(int l)
{
if(lch[l]) dfs(lch[l]);
if(rch[l]) dfs(rch[l]);
a.push_back(l);
return;
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>N)
{
memset(lch,0,sizeof(lch));
memset(rch,0,sizeof(rch));
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) cin>>pre_order[i];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) cin>>in_order[i];
int root = build(0,N-1,0,N-1);
a.clear();
dfs(root);
for(int cnt = 0; cnt < a.size(); cnt++)
{
if(cnt == 0) cout<<a[cnt];
else cout<<" "<<a[cnt];
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
奥利给,干了兄弟们!








 本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序和后序遍历,并通过递归算法,利用前序和中序遍历结果重构二叉树,最后实现后序遍历的输出。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序和后序遍历,并通过递归算法,利用前序和中序遍历结果重构二叉树,最后实现后序遍历的输出。
















 1088
1088

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








