Linux VFS文件系统分析6(基于Linux6.6)---VFS与read接口介绍
一、read接口
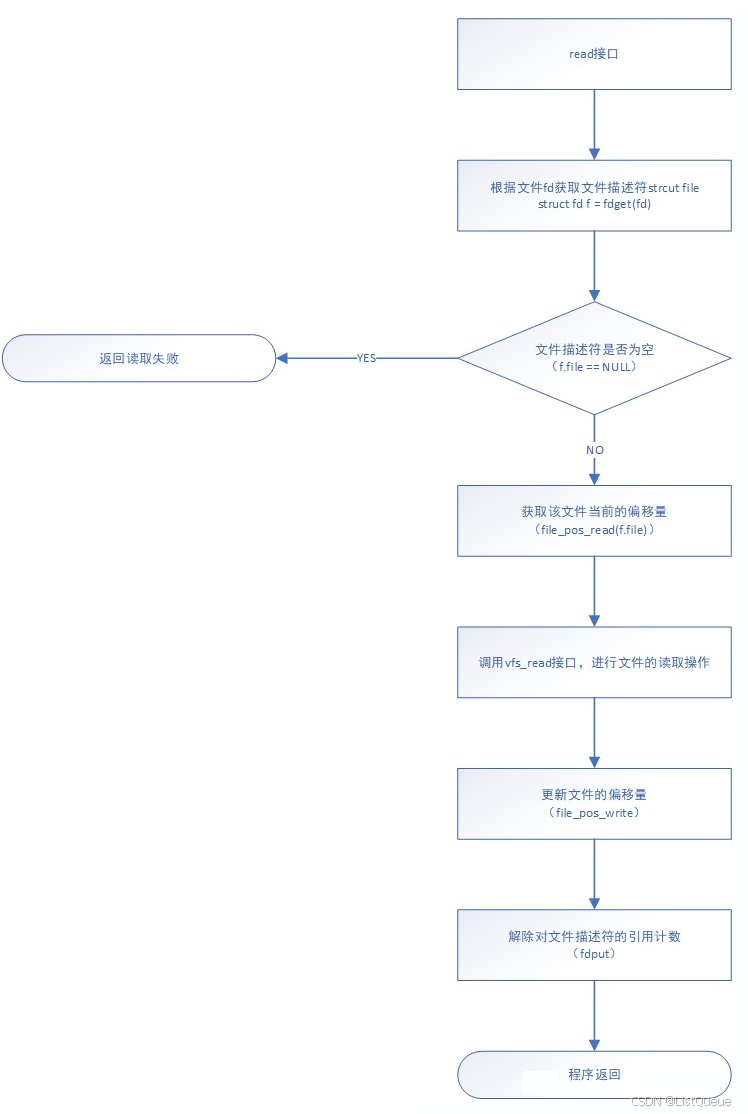
首先根据fd,获取文件描述符,接着判断文件描述符是否合法;若合法则获取当前文件的偏移量,并调用vfs_read读取文件内容,最后更新文件偏移量。
事实上该接口的实现内容也大致如此,该接口实现的内容如下:
1.该接口首先从当前进程的files指针中获取fd对应的文件描述符;
2.若获取文件描述符成功,则调用file_pos_read获取当前文件的offset;
3.调用vfs_read接口,从而调用该文件对应inode节点提供的read接口,实现read操作;
4.调用file_pos_write更新当前文件的offset;
5.调用fdput解除对文件描述符的引用计数。
该接口的实现流程图如下所示,该流程图说明了read接口的实现逻辑。
fs/read_write.c
ssize_t ksys_read(unsigned int fd, char __user *buf, size_t count)
{
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
if (f.file) {
loff_t pos, *ppos = file_ppos(f.file);
if (ppos) {
pos = *ppos;
ppos = &pos;
}
ret = vfs_read(f.file, buf, count, ppos);
if (ret >= 0 && ppos)
f.file->f_pos = pos;
fdput_pos(f);
}
return ret;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, unsigned int, fd, char __user *, buf, size_t, count)
{
return ksys_read(fd, buf, count);
}
二、fdget_pos接口分析
fs/file.c
static inline struct fd fdget_pos(int fd)
{
return __to_fd(__fdget_pos(fd));
}
unsigned long __fdget_pos(unsigned int fd)
{
unsigned long v = __fdget(fd);
struct file *file = (struct file *)(v & ~3);
if (file && file_needs_f_pos_lock(file)) {
v |= FDPUT_POS_UNLOCK;
mutex_lock(&file->f_pos_lock);
}
return v;
}
unsigned long __fdget(unsigned int fd)
{
return __fget_light(fd, FMODE_PATH);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__fdget);
static unsigned long __fget_light(unsigned int fd, fmode_t mask)
{
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
struct file *file;
/*
* If another thread is concurrently calling close_fd() followed
* by put_files_struct(), we must not observe the old table
* entry combined with the new refcount - otherwise we could
* return a file that is concurrently being freed.
*
* atomic_read_acquire() pairs with atomic_dec_and_test() in
* put_files_struct().
*/
if (atomic_read_acquire(&files->count) == 1) {
file = files_lookup_fd_raw(files, fd);
if (!file || unlikely(file->f_mode & mask))
return 0;
return (unsigned long)file;
} else {
file = __fget(fd, mask);
if (!file)
return 0;
return FDPUT_FPUT | (unsigned long)file;
}
}
2.1、file_ppos接口分析
/* file_ppos returns &file->f_pos or NULL if file is stream */
static inline loff_t *file_ppos(struct file *file)
{
return file->f_mode & FMODE_STREAM ? NULL : &file->f_pos;
}
2.2、vfs_read接口分析
该接口主要用于读取文件内容,其实现功能如下:
1.若文件描述符不存在读取权限,返回失败;
2.若应用层传递的内存指针没有写权限,返回失败;
3.若该文件描述符没有read或aio_read接口,则返回失败;
4.调用rw_verify_area检测是否可对文件进行读取操作(如是否别的进程对文件加锁、要读取的大小是否合法等);
5.若file->f_op->read接口存在,则调用文件inode的read接口,进行文件读取操作;若不存在,则调用do_sync_read,调用aio_read;
6.调用fsnotify_access,发送文件被读取的通知。
fs/read_write.c
ssize_t vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_READ))
return -EBADF;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_READ))
return -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!access_ok(buf, count)))
return -EFAULT;
ret = rw_verify_area(READ, file, pos, count);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (count > MAX_RW_COUNT)
count = MAX_RW_COUNT;
if (file->f_op->read)
ret = file->f_op->read(file, buf, count, pos);
else if (file->f_op->read_iter)
ret = new_sync_read(file, buf, count, pos);
else
ret = -EINVAL;
if (ret > 0) {
fsnotify_access(file);
add_rchar(current, ret);
}
inc_syscr(current);
return ret;
}
三、举例应用
3.1、VFS 与 read 接口的工作原理
当应用程序调用 read 系统调用时,VFS 会根据文件描述符确定文件类型,并通过相应的文件操作方法(如文件系统的 read 操作)来完成实际的读取操作。
- 文件描述符:
read操作会依赖于一个已经打开的文件描述符,该描述符由open系统调用返回。 - VFS 层:VFS 层会将
read调用转发给底层的文件系统实现,例如ext4、ntfs、nfs或设备文件。 - 具体实现:不同类型的文件(普通文件、设备文件、网络文件等)会有不同的
read处理方法,VFS 会根据文件描述符指向的文件类型调用相应的实现。
3.2、read 示例
1.示例 1:读取本地普通文件
可以使用 read 系统调用从本地普通文件中读取内容。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
const char *file_path = "/tmp/testfile.txt"; // 假设这是一个已存在的文件
int fd;
char buffer[128];
ssize_t bytes_read;
// 打开文件
fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 读取文件内容
bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出读取的内容
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
printf("File content:\n%s\n", buffer);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
工作流程:
open系统调用通过 VFS 层查找文件路径/tmp/testfile.txt所在的文件系统。- VFS 层会通过文件系统的
open操作将文件描述符返回给应用程序。 - 在
read系统调用时,VFS 会通过file_operations结构体的read操作方法,调用具体文件系统(如ext4、tmpfs)的read函数。 - 最终,
read系统调用从文件中读取数据,并返回读取的字节数。
2.示例 2:读取设备文件(如 /dev/null)
设备文件是 Linux 中的特殊文件,像 /dev/null 这样的文件不存储数据,而是丢弃所有写入的数据,并且从中读取数据时总是返回特定的值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *dev_path = "/dev/null"; // 设备文件
int fd;
char buffer[128];
ssize_t bytes_read;
// 打开设备文件
fd = open(dev_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 尝试从设备文件读取数据
bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出读取的数据
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
printf("Read from /dev/null: '%s'\n", buffer);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
工作流程:
open系统调用通过 VFS 层查找/dev/null文件。- VFS 会识别这是一个设备文件,并将操作传递给设备驱动(
null驱动)。 - 当调用
read时,由于/dev/null是一个特殊的设备,它总是返回一个“空”值。因此,read返回的数据会是空的。
3.示例 3:读取 NFS 网络文件
假设你已经将远程的 NFS 共享目录挂载到本地文件系统上。你可以像访问本地文件一样,使用 read 操作读取网络文件系统(NFS)中的文件。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *remote_file_path = "/mnt/nfs/share/testfile.txt"; // NFS 挂载点路径
int fd;
char buffer[128];
ssize_t bytes_read;
// 打开远程 NFS 文件
fd = open(remote_file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 读取 NFS 文件内容
bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出读取的内容
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0';
printf("File content from NFS:\n%s\n", buffer);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
工作流程:
open系统调用通过 VFS 层查找/mnt/nfs/share/testfile.txt所在的文件系统,识别它是一个 NFS 文件。- VFS 会通过 NFS 客户端实现的
read操作与远程服务器进行通信,读取远程文件的内容。 read系统调用返回读取到的内容。
4.示例 4:读取随机数设备文件(/dev/random)
/dev/random 是一个伪设备文件,用于提供高质量的随机数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *dev_path = "/dev/random"; // 随机数设备
int fd;
unsigned char buffer[16];
ssize_t bytes_read;
// 打开随机数设备
fd = open(dev_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 从设备文件读取随机数
bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出读取到的随机数
printf("Random bytes:\n");
for (ssize_t i = 0; i < bytes_read; i++) {
printf("%02x ", buffer[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
工作流程:
open系统调用通过 VFS 层打开/dev/random文件。- VFS 识别该文件是一个字符设备文件,并将
read请求传递给随机数生成设备的驱动程序。 - 设备驱动程序生成随机数并返回给应用程序。





















 6255
6255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








