Linux文件系统4(基于6.1内核)---VFS数据读取vfs_read和写入vfs_write
一、vfs调用流程图
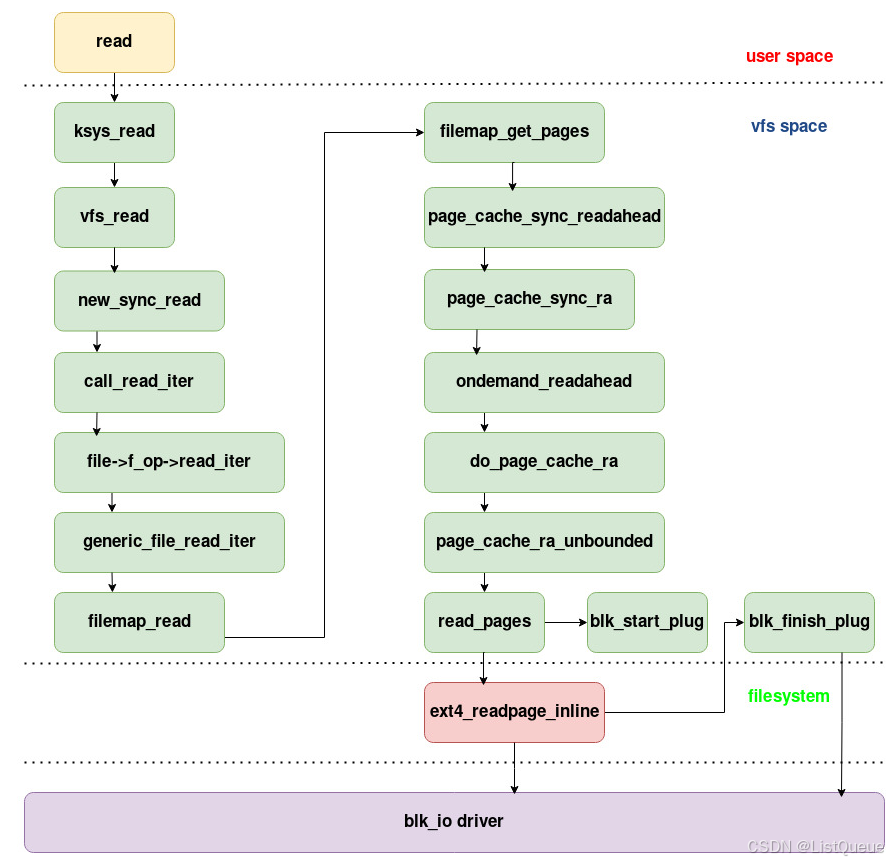
1.1 vfs_read的调用流程
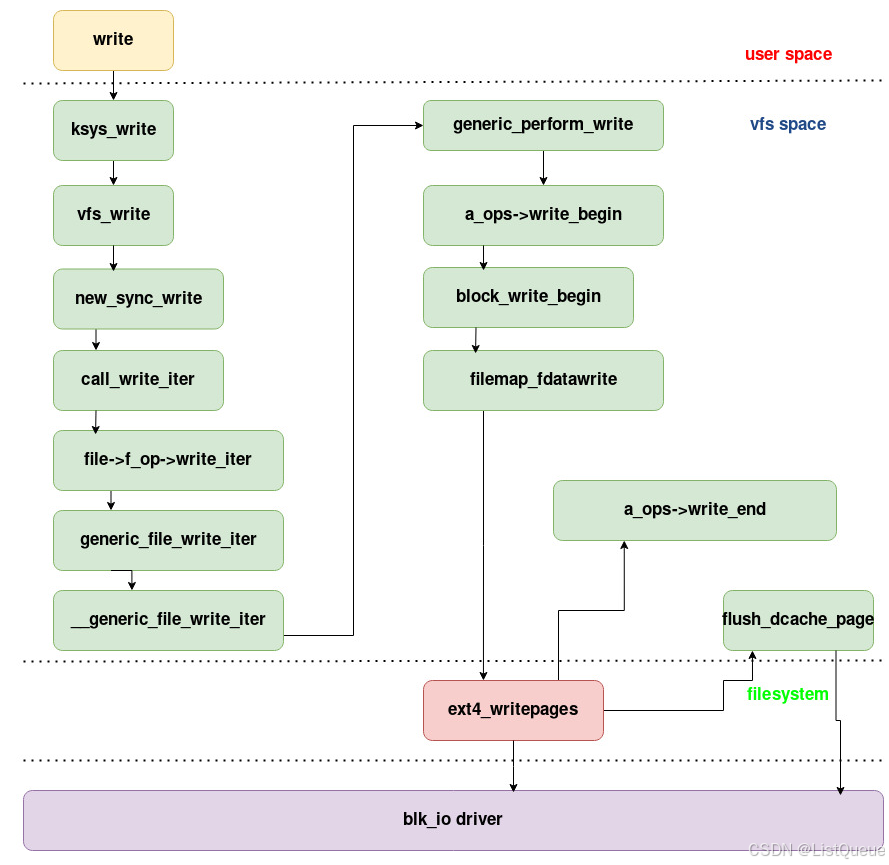
1.2 vfs_write的调用流程
二、VFS层调用流程
2.1 vfs_read调用流程
fs/read_write.c
ssize_t ksys_read(unsigned int fd, char __user *buf, size_t count)
{
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
if (f.file) {
loff_t pos, *ppos = file_ppos(f.file);
if (ppos) {
pos = *ppos;
ppos = &pos;
}
ret = vfs_read(f.file, buf, count, ppos);
if (ret >= 0 && ppos)
f.file->f_pos = pos;
fdput_pos(f);
}
return ret;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, unsigned int, fd, char __user *, buf, size_t, count)
{
return ksys_read(fd, buf, count);
}
ssize_t vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_READ))
return -EBADF;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_READ))
return -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!access_ok(buf, count)))
return -EFAULT;
ret = rw_verify_area(READ, file, pos, count);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (count > MAX_RW_COUNT)
count = MAX_RW_COUNT;
if (file->f_op->read)
ret = file->f_op->read(file, buf, count, pos);
else if (file->f_op->read_iter)
ret = new_sync_read(file, buf, count, pos);
else
ret = -EINVAL;
if (ret > 0) {
fsnotify_access(file);
add_rchar(current, ret);
}
inc_syscr(current);
return ret;
}
static ssize_t new_sync_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct kiocb kiocb;
struct iov_iter iter;
ssize_t ret;
init_sync_kiocb(&kiocb, filp);
kiocb.ki_pos = (ppos ? *ppos : 0);
iov_iter_ubuf(&iter, ITER_DEST, buf, len);
ret = call_read_iter(filp, &kiocb, &iter);
BUG_ON(ret == -EIOCBQUEUED);
if (ppos)
*ppos = kiocb.ki_pos;
return ret;
}
include/linux/fs.h
static inline ssize_t call_read_iter(struct file *file, struct kiocb *kio,
struct iov_iter *iter)
{
return file->f_op->read_iter(kio, iter);
}
mm/filemap.c
ssize_t
generic_file_read_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *iter)
{
size_t count = iov_iter_count(iter);
ssize_t retval = 0;
if (!count)
return 0; /* skip atime */
if (iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_DIRECT) {
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;
struct inode *inode = mapping->host;
retval = kiocb_write_and_wait(iocb, count);
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
file_accessed(file);
retval = mapping->a_ops->direct_IO(iocb, iter);
if (retval >= 0) {
iocb->ki_pos += retval;
count -= retval;
}
if (retval != -EIOCBQUEUED)
iov_iter_revert(iter, count - iov_iter_count(iter));
/*
* Btrfs can have a short DIO read if we encounter
* compressed extents, so if there was an error, or if
* we've already read everything we wanted to, or if
* there was a short read because we hit EOF, go ahead
* and return. Otherwise fallthrough to buffered io for
* the rest of the read. Buffered reads will not work for
* DAX files, so don't bother trying.
*/
if (retval < 0 || !count || IS_DAX(inode))
return retval;
if (iocb->ki_pos >= i_size_read(inode))
return retval;
}
return filemap_read(iocb, iter, retval);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_file_read_iter);
ssize_t filemap_read(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *iter,
ssize_t already_read)
{
struct file *filp = iocb->ki_filp;
struct file_ra_state *ra = &filp->f_ra;
struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
struct inode *inode = mapping->host;
struct folio_batch fbatch;
int i, error = 0;
bool writably_mapped;
loff_t isize, end_offset;
loff_t last_pos = ra->prev_pos;
if (unlikely(iocb->ki_pos >= inode->i_sb->s_maxbytes))
return 0;
if (unlikely(!iov_iter_count(iter)))
return 0;
iov_iter_truncate(iter, inode->i_sb->s_maxbytes);
folio_batch_init(&fbatch);
do {
cond_resched();
/*
* If we've already successfully copied some data, then we
* can no longer safely return -EIOCBQUEUED. Hence mark
* an async read NOWAIT at that point.
*/
if ((iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_WAITQ) && already_read)
iocb->ki_flags |= IOCB_NOWAIT;
if (unlikely(iocb->ki_pos >= i_size_read(inode)))
break;
error = filemap_get_pages(iocb, iter->count, &fbatch, false);
if (error < 0)
break;
/*
* i_size must be checked after we know the pages are Uptodate.
*
* Checking i_size after the check allows us to calculate
* the correct value for "nr", which means the zero-filled
* part of the page is not copied back to userspace (unless
* another truncate extends the file - this is desired though).
*/
isize = i_size_read(inode);
if (unlikely(iocb->ki_pos >= isize))
goto put_folios;
end_offset = min_t(loff_t, isize, iocb->ki_pos + iter->count);
/*
* Pairs with a barrier in
* block_write_end()->mark_buffer_dirty() or other page
* dirtying routines like iomap_write_end() to ensure
* changes to page contents are visible before we see
* increased inode size.
*/
smp_rmb();
/*
* Once we start copying data, we don't want to be touching any
* cachelines that might be contended:
*/
writably_mapped = mapping_writably_mapped(mapping);
/*
* When a read accesses the same folio several times, only
* mark it as accessed the first time.
*/
if (!pos_same_folio(iocb->ki_pos, last_pos - 1,
fbatch.folios[0]))
folio_mark_accessed(fbatch.folios[0]);
for (i = 0; i < folio_batch_count(&fbatch); i++) {
struct folio *folio = fbatch.folios[i];
size_t fsize = folio_size(folio);
size_t offset = iocb->ki_pos & (fsize - 1);
size_t bytes = min_t(loff_t, end_offset - iocb->ki_pos,
fsize - offset);
size_t copied;
if (end_offset < folio_pos(folio))
break;
if (i > 0)
folio_mark_accessed(folio);
/*
* If users can be writing to this folio using arbitrary
* virtual addresses, take care of potential aliasing
* before reading the folio on the kernel side.
*/
if (writably_mapped)
flush_dcache_folio(folio);
copied = copy_folio_to_iter(folio, offset, bytes, iter);
already_read += copied;
iocb->ki_pos += copied;
last_pos = iocb->ki_pos;
if (copied < bytes) {
error = -EFAULT;
break;
}
}
put_folios:
for (i = 0; i < folio_batch_count(&fbatch); i++)
folio_put(fbatch.folios[i]);
folio_batch_init(&fbatch);
} while (iov_iter_count(iter) && iocb->ki_pos < isize && !error);
file_accessed(filp);
ra->prev_pos = last_pos;
return already_read ? already_read : error;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(filemap_read);
static int filemap_get_pages(struct kiocb *iocb, size_t count,
struct folio_batch *fbatch, bool need_uptodate)
{
struct file *filp = iocb->ki_filp;
struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
struct file_ra_state *ra = &filp->f_ra;
pgoff_t index = iocb->ki_pos >> PAGE_SHIFT;
pgoff_t last_index;
struct folio *folio;
int err = 0;
/* "last_index" is the index of the page beyond the end of the read */
last_index = DIV_ROUND_UP(iocb->ki_pos + count, PAGE_SIZE);
retry:
if (fatal_signal_pending(current))
return -EINTR;
filemap_get_read_batch(mapping, index, last_index - 1, fbatch);
if (!folio_batch_count(fbatch)) {
if (iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_NOIO)
return -EAGAIN;
page_cache_sync_readahead(mapping, ra, filp, index,
last_index - index);
filemap_get_read_batch(mapping, index, last_index - 1, fbatch);
}
if (!folio_batch_count(fbatch)) {
if (iocb->ki_flags & (IOCB_NOWAIT | IOCB_WAITQ))
return -EAGAIN;
err = filemap_create_folio(filp, mapping,
iocb->ki_pos >> PAGE_SHIFT, fbatch);
if (err == AOP_TRUNCATED_PAGE)
goto retry;
return err;
}
folio = fbatch->folios[folio_batch_count(fbatch) - 1];
if (folio_test_readahead(folio)) {
err = filemap_readahead(iocb, filp, mapping, folio, last_index);
if (err)
goto err;
}
if (!folio_test_uptodate(folio)) {
if ((iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_WAITQ) &&
folio_batch_count(fbatch) > 1)
iocb->ki_flags |= IOCB_NOWAIT;
err = filemap_update_page(iocb, mapping, count, folio,
need_uptodate);
if (err)
goto err;
}
return 0;
err:
if (err < 0)
folio_put(folio);
if (likely(--fbatch->nr))
return 0;
if (err == AOP_TRUNCATED_PAGE)
goto retry;
return err;
}
include/linux/pagemap.h
static inline
void page_cache_sync_readahead(struct address_space *mapping,
struct file_ra_state *ra, struct file *file, pgoff_t index,
unsigned long req_count)
{
DEFINE_READAHEAD(ractl, file, ra, mapping, index);
page_cache_sync_ra(&ractl, req_count);
}
mm/readahead.c
void page_cache_sync_ra(struct readahead_control *ractl,
unsigned long req_count)
{
bool do_forced_ra = ractl->file && (ractl->file->f_mode & FMODE_RANDOM);
/*
* Even if readahead is disabled, issue this request as readahead
* as we'll need it to satisfy the requested range. The forced
* readahead will do the right thing and limit the read to just the
* requested range, which we'll set to 1 page for this case.
*/
if (!ractl->ra->ra_pages || blk_cgroup_congested()) {
if (!ractl->file)
return;
req_count = 1;
do_forced_ra = true;
}
/* be dumb */
if (do_forced_ra) {
force_page_cache_ra(ractl, req_count);
return;
}
ondemand_readahead(ractl, NULL, req_count);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(page_cache_sync_ra);
/*
* A minimal readahead algorithm for trivial sequential/random reads.
*/
static void ondemand_readahead(struct readahead_control *ractl,
struct folio *folio, unsigned long req_size)
{
struct backing_dev_info *bdi = inode_to_bdi(ractl->mapping->host);
struct file_ra_state *ra = ractl->ra;
unsigned long max_pages = ra->ra_pages;
unsigned long add_pages;
pgoff_t index = readahead_index(ractl);
pgoff_t expected, prev_index;
unsigned int order = folio ? folio_order(folio) : 0;
/*
* If the request exceeds the readahead window, allow the read to
* be up to the optimal hardware IO size
*/
if (req_size > max_pages && bdi->io_pages > max_pages)
max_pages = min(req_size, bdi->io_pages);
/*
* start of file
*/
if (!index)
goto initial_readahead;
/*
* It's the expected callback index, assume sequential access.
* Ramp up sizes, and push forward the readahead window.
*/
expected = round_down(ra->start + ra->size - ra->async_size,
1UL << order);
if (index == expected || index == (ra->start + ra->size)) {
ra->start += ra->size;
ra->size = get_next_ra_size(ra, max_pages);
ra->async_size = ra->size;
goto readit;
}
/*
* Hit a marked folio without valid readahead state.
* E.g. interleaved reads.
* Query the pagecache for async_size, which normally equals to
* readahead size. Ramp it up and use it as the new readahead size.
*/
if (folio) {
pgoff_t start;
rcu_read_lock();
start = page_cache_next_miss(ractl->mapping, index + 1,
max_pages);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (!start || start - index > max_pages)
return;
ra->start = start;
ra->size = start - index; /* old async_size */
ra->size += req_size;
ra->size = get_next_ra_size(ra, max_pages);
ra->async_size = ra->size;
goto readit;
}
/*
* oversize read
*/
if (req_size > max_pages)
goto initial_readahead;
/*
* sequential cache miss
* trivial case: (index - prev_index) == 1
* unaligned reads: (index - prev_index) == 0
*/
prev_index = (unsigned long long)ra->prev_pos >> PAGE_SHIFT;
if (index - prev_index <= 1UL)
goto initial_readahead;
/*
* Query the page cache and look for the traces(cached history pages)
* that a sequential stream would leave behind.
*/
if (sysctl_enable_context_readahead &&
try_context_readahead(ractl->mapping, ra, index, req_size,
max_pages)) {
goto readit;
}
/*
* standalone, small random read
* Read as is, and do not pollute the readahead state.
*/
do_page_cache_ra(ractl, req_size, 0);
return;
initial_readahead:
ra->start = index;
ra->size = get_init_ra_size(req_size, max_pages);
ra->async_size = ra->size > req_size ? ra->size - req_size : ra->size;
readit:
/*
* Will this read hit the readahead marker made by itself?
* If so, trigger the readahead marker hit now, and merge
* the resulted next readahead window into the current one.
* Take care of maximum IO pages as above.
*/
if (index == ra->start && ra->size == ra->async_size) {
add_pages = get_next_ra_size(ra, max_pages);
if (ra->size + add_pages <= max_pages) {
ra->async_size = add_pages;
ra->size += add_pages;
} else {
ra->size = max_pages;
ra->async_size = max_pages >> 1;
}
}
ractl->_index = ra->start;
page_cache_ra_order(ractl, ra, order);
}
static void do_page_cache_ra(struct readahead_control *ractl,
unsigned long nr_to_read, unsigned long lookahead_size)
{
struct inode *inode = ractl->mapping->host;
unsigned long index = readahead_index(ractl);
loff_t isize = i_size_read(inode);
pgoff_t end_index; /* The last page we want to read */
if (isize == 0)
return;
end_index = (isize - 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
if (index > end_index)
return;
/* Don't read past the page containing the last byte of the file */
if (nr_to_read > end_index - index)
nr_to_read = end_index - index + 1;
page_cache_ra_unbounded(ractl, nr_to_read, lookahead_size);
}
void page_cache_ra_unbounded(struct readahead_control *ractl,
unsigned long nr_to_read, unsigned long lookahead_size)
{
struct address_space *mapping = ractl->mapping;
unsigned long index = readahead_index(ractl);
gfp_t gfp_mask = readahead_gfp_mask(mapping);
unsigned long i;
/*
* Partway through the readahead operation, we will have added
* locked pages to the page cache, but will not yet have submitted
* them for I/O. Adding another page may need to allocate memory,
* which can trigger memory reclaim. Telling the VM we're in
* the middle of a filesystem operation will cause it to not
* touch file-backed pages, preventing a deadlock. Most (all?)
* filesystems already specify __GFP_NOFS in their mapping's
* gfp_mask, but let's be explicit here.
*/
unsigned int nofs = memalloc_nofs_save();
filemap_invalidate_lock_shared(mapping);
/*
* Preallocate as many pages as we will need.
*/
for (i = 0; i < nr_to_read; i++) {
struct folio *folio = xa_load(&mapping->i_pages, index + i);
if (folio && !xa_is_value(folio)) {
/*
* Page already present? Kick off the current batch
* of contiguous pages before continuing with the
* next batch. This page may be the one we would
* have intended to mark as Readahead, but we don't
* have a stable reference to this page, and it's
* not worth getting one just for that.
*/
read_pages(ractl);
ractl->_index++;
i = ractl->_index + ractl->_nr_pages - index - 1;
continue;
}
folio = filemap_alloc_folio(gfp_mask, 0);
if (!folio)
break;
if (filemap_add_folio(mapping, folio, index + i,
gfp_mask) < 0) {
folio_put(folio);
read_pages(ractl);
ractl->_index++;
i = ractl->_index + ractl->_nr_pages - index - 1;
continue;
}
if (i == nr_to_read - lookahead_size)
folio_set_readahead(folio);
ractl->_workingset |= folio_test_workingset(folio);
ractl->_nr_pages++;
}
/*
* Now start the IO. We ignore I/O errors - if the folio is not
* uptodate then the caller will launch read_folio again, and
* will then handle the error.
*/
read_pages(ractl);
filemap_invalidate_unlock_shared(mapping);
memalloc_nofs_restore(nofs);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(page_cache_ra_unbounded);
static void read_pages(struct readahead_control *rac)
{
const struct address_space_operations *aops = rac->mapping->a_ops;
struct folio *folio;
struct blk_plug plug;
if (!readahead_count(rac))
return;
if (unlikely(rac->_workingset))
psi_memstall_enter(&rac->_pflags);
blk_start_plug(&plug);
if (aops->readahead) {
aops->readahead(rac);
/*
* Clean up the remaining folios. The sizes in ->ra
* may be used to size the next readahead, so make sure
* they accurately reflect what happened.
*/
while ((folio = readahead_folio(rac)) != NULL) {
unsigned long nr = folio_nr_pages(folio);
folio_get(folio);
rac->ra->size -= nr;
if (rac->ra->async_size >= nr) {
rac->ra->async_size -= nr;
filemap_remove_folio(folio);
}
folio_unlock(folio);
folio_put(folio);
}
} else {
while ((folio = readahead_folio(rac)) != NULL)
aops->read_folio(rac->file, folio);
}
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
if (unlikely(rac->_workingset))
psi_memstall_leave(&rac->_pflags);
rac->_workingset = false;
BUG_ON(readahead_count(rac));
}
block/blk-core.c
/**
* blk_finish_plug - mark the end of a batch of submitted I/O
* @plug: The &struct blk_plug passed to blk_start_plug()
*
* Description:
* Indicate that a batch of I/O submissions is complete. This function
* must be paired with an initial call to blk_start_plug(). The intent
* is to allow the block layer to optimize I/O submission. See the
* documentation for blk_start_plug() for more information.
*/
void blk_finish_plug(struct blk_plug *plug)
{
if (plug == current->plug) {
__blk_flush_plug(plug, false);
current->plug = NULL;
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(blk_finish_plug);
2.2 vfs_write调用流程
fs/read_write.c
ssize_t ksys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user *buf, size_t count)
{
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
if (f.file) {
loff_t pos, *ppos = file_ppos(f.file);
if (ppos) {
pos = *ppos;
ppos = &pos;
}
ret = vfs_write(f.file, buf, count, ppos);
if (ret >= 0 && ppos)
f.file->f_pos = pos;
fdput_pos(f);
}
return ret;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
size_t, count)
{
return ksys_write(fd, buf, count);
}
ssize_t vfs_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))
return -EBADF;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_WRITE))
return -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!access_ok(buf, count)))
return -EFAULT;
ret = rw_verify_area(WRITE, file, pos, count);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (count > MAX_RW_COUNT)
count = MAX_RW_COUNT;
file_start_write(file);
if (file->f_op->write)
ret = file->f_op->write(file, buf, count, pos);
else if (file->f_op->write_iter)
ret = new_sync_write(file, buf, count, pos);
else
ret = -EINVAL;
if (ret > 0) {
fsnotify_modify(file);
add_wchar(current, ret);
}
inc_syscw(current);
file_end_write(file);
return ret;
}
static ssize_t new_sync_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct kiocb kiocb;
struct iov_iter iter;
ssize_t ret;
init_sync_kiocb(&kiocb, filp);
kiocb.ki_pos = (ppos ? *ppos : 0);
iov_iter_ubuf(&iter, ITER_SOURCE, (void __user *)buf, len);
ret = call_write_iter(filp, &kiocb, &iter);
BUG_ON(ret == -EIOCBQUEUED);
if (ret > 0 && ppos)
*ppos = kiocb.ki_pos;
return ret;
}
include/linux/fs.h
static inline ssize_t call_write_iter(struct file *file, struct kiocb *kio,
struct iov_iter *iter)
{
return file->f_op->write_iter(kio, iter);
}
mm/filemap.c
ssize_t generic_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
{
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
struct inode *inode = file->f_mapping->host;
ssize_t ret;
inode_lock(inode);
ret = generic_write_checks(iocb, from);
if (ret > 0)
ret = __generic_file_write_iter(iocb, from);
inode_unlock(inode);
if (ret > 0)
ret = generic_write_sync(iocb, ret);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_file_write_iter);
ssize_t __generic_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
{
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;
struct inode *inode = mapping->host;
ssize_t ret;
ret = file_remove_privs(file);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = file_update_time(file);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_DIRECT) {
ret = generic_file_direct_write(iocb, from);
/*
* If the write stopped short of completing, fall back to
* buffered writes. Some filesystems do this for writes to
* holes, for example. For DAX files, a buffered write will
* not succeed (even if it did, DAX does not handle dirty
* page-cache pages correctly).
*/
if (ret < 0 || !iov_iter_count(from) || IS_DAX(inode))
return ret;
return direct_write_fallback(iocb, from, ret,
generic_perform_write(iocb, from));
}
return generic_perform_write(iocb, from);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__generic_file_write_iter);
ssize_t generic_perform_write(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *i)
{
struct file *file = iocb->ki_filp;
loff_t pos = iocb->ki_pos;
struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;
const struct address_space_operations *a_ops = mapping->a_ops;
long status = 0;
ssize_t written = 0;
do {
struct page *page;
unsigned long offset; /* Offset into pagecache page */
unsigned long bytes; /* Bytes to write to page */
size_t copied; /* Bytes copied from user */
void *fsdata = NULL;
offset = (pos & (PAGE_SIZE - 1));
bytes = min_t(unsigned long, PAGE_SIZE - offset,
iov_iter_count(i));
again:
/*
* Bring in the user page that we will copy from _first_.
* Otherwise there's a nasty deadlock on copying from the
* same page as we're writing to, without it being marked
* up-to-date.
*/
if (unlikely(fault_in_iov_iter_readable(i, bytes) == bytes)) {
status = -EFAULT;
break;
}
if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {
status = -EINTR;
break;
}
status = a_ops->write_begin(file, mapping, pos, bytes,
&page, &fsdata);
if (unlikely(status < 0))
break;
if (mapping_writably_mapped(mapping))
flush_dcache_page(page);
copied = copy_page_from_iter_atomic(page, offset, bytes, i);
flush_dcache_page(page);
status = a_ops->write_end(file, mapping, pos, bytes, copied,
page, fsdata);
if (unlikely(status != copied)) {
iov_iter_revert(i, copied - max(status, 0L));
if (unlikely(status < 0))
break;
}
cond_resched();
if (unlikely(status == 0)) {
/*
* A short copy made ->write_end() reject the
* thing entirely. Might be memory poisoning
* halfway through, might be a race with munmap,
* might be severe memory pressure.
*/
if (copied)
bytes = copied;
goto again;
}
pos += status;
written += status;
balance_dirty_pages_ratelimited(mapping);
} while (iov_iter_count(i));
if (!written)
return status;
iocb->ki_pos += written;
return written;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_perform_write);
fs/buffer.c
int block_write_begin(struct address_space *mapping, loff_t pos, unsigned len,
struct page **pagep, get_block_t *get_block)
{
pgoff_t index = pos >> PAGE_SHIFT;
struct page *page;
int status;
page = grab_cache_page_write_begin(mapping, index);
if (!page)
return -ENOMEM;
status = __block_write_begin(page, pos, len, get_block);
if (unlikely(status)) {
unlock_page(page);
put_page(page);
page = NULL;
}
*pagep = page;
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(block_write_begin);
int __block_write_begin(struct page *page, loff_t pos, unsigned len,
get_block_t *get_block)
{
return __block_write_begin_int(page_folio(page), pos, len, get_block,
NULL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__block_write_begin);
int __block_write_begin_int(struct folio *folio, loff_t pos, unsigned len,
get_block_t *get_block, const struct iomap *iomap)
{
unsigned from = pos & (PAGE_SIZE - 1);
unsigned to = from + len;
struct inode *inode = folio->mapping->host;
unsigned block_start, block_end;
sector_t block;
int err = 0;
unsigned blocksize, bbits;
struct buffer_head *bh, *head, *wait[2], **wait_bh=wait;
BUG_ON(!folio_test_locked(folio));
BUG_ON(from > PAGE_SIZE);
BUG_ON(to > PAGE_SIZE);
BUG_ON(from > to);
head = folio_create_buffers(folio, inode, 0);
blocksize = head->b_size;
bbits = block_size_bits(blocksize);
block = (sector_t)folio->index << (PAGE_SHIFT - bbits);
for(bh = head, block_start = 0; bh != head || !block_start;
block++, block_start=block_end, bh = bh->b_this_page) {
block_end = block_start + blocksize;
if (block_end <= from || block_start >= to) {
if (folio_test_uptodate(folio)) {
if (!buffer_uptodate(bh))
set_buffer_uptodate(bh);
}
continue;
}
if (buffer_new(bh))
clear_buffer_new(bh);
if (!buffer_mapped(bh)) {
WARN_ON(bh->b_size != blocksize);
if (get_block)
err = get_block(inode, block, bh, 1);
else
err = iomap_to_bh(inode, block, bh, iomap);
if (err)
break;
if (buffer_new(bh)) {
clean_bdev_bh_alias(bh);
if (folio_test_uptodate(folio)) {
clear_buffer_new(bh);
set_buffer_uptodate(bh);
mark_buffer_dirty(bh);
continue;
}
if (block_end > to || block_start < from)
folio_zero_segments(folio,
to, block_end,
block_start, from);
continue;
}
}
if (folio_test_uptodate(folio)) {
if (!buffer_uptodate(bh))
set_buffer_uptodate(bh);
continue;
}
if (!buffer_uptodate(bh) && !buffer_delay(bh) &&
!buffer_unwritten(bh) &&
(block_start < from || block_end > to)) {
bh_read_nowait(bh, 0);
*wait_bh++=bh;
}
}
/*
* If we issued read requests - let them complete.
*/
while(wait_bh > wait) {
wait_on_buffer(*--wait_bh);
if (!buffer_uptodate(*wait_bh))
err = -EIO;
}
if (unlikely(err))
folio_zero_new_buffers(folio, from, to);
return err;
}
mm/filemap.c
int __filemap_fdatawrite_range(struct address_space *mapping, loff_t start,
loff_t end, int sync_mode)
{
struct writeback_control wbc = {
.sync_mode = sync_mode,
.nr_to_write = LONG_MAX,
.range_start = start,
.range_end = end,
};
return filemap_fdatawrite_wbc(mapping, &wbc);
}
static inline int __filemap_fdatawrite(struct address_space *mapping,
int sync_mode)
{
return __filemap_fdatawrite_range(mapping, 0, LLONG_MAX, sync_mode);
}
int filemap_fdatawrite(struct address_space *mapping)
{
return __filemap_fdatawrite(mapping, WB_SYNC_ALL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(filemap_fdatawrite);
三、ext4文件系统调用流程
3.1 ext4文件系统readpages
fs/ext4/inode.c
static const struct address_space_operations ext4_aops = {
.read_folio = ext4_read_folio,
.readahead = ext4_readahead,
.writepages = ext4_writepages,
.write_begin = ext4_write_begin,
.write_end = ext4_write_end,
.dirty_folio = ext4_dirty_folio,
.bmap = ext4_bmap,
.invalidate_folio = ext4_invalidate_folio,
.release_folio = ext4_release_folio,
.direct_IO = noop_direct_IO,
.migrate_folio = buffer_migrate_folio,
.is_partially_uptodate = block_is_partially_uptodate,
.error_remove_page = generic_error_remove_page,
.swap_activate = ext4_iomap_swap_activate,
};
static void ext4_readahead(struct readahead_control *rac)
{
struct inode *inode = rac->mapping->host;
/* If the file has inline data, no need to do readahead. */
if (ext4_has_inline_data(inode))
return;
ext4_mpage_readpages(inode, rac, NULL);
}
在ext4_mpage_readpages中,会构造一个bio,不通的page请求保存在bio的bio_vec不同元素(段)中。
当然很多时候,mpage_readpages多个page会产生多个bio,这个时候read_pages的start/stop plug组合就起作用了:fs/ext4/readpage.c
int ext4_mpage_readpages(struct inode *inode,
struct readahead_control *rac, struct folio *folio)
{
struct bio *bio = NULL;
sector_t last_block_in_bio = 0;
const unsigned blkbits = inode->i_blkbits;
const unsigned blocks_per_page = PAGE_SIZE >> blkbits;
const unsigned blocksize = 1 << blkbits;
sector_t next_block;
sector_t block_in_file;
sector_t last_block;
sector_t last_block_in_file;
sector_t blocks[MAX_BUF_PER_PAGE];
unsigned page_block;
struct block_device *bdev = inode->i_sb->s_bdev;
int length;
unsigned relative_block = 0;
struct ext4_map_blocks map;
unsigned int nr_pages = rac ? readahead_count(rac) : 1;
map.m_pblk = 0;
map.m_lblk = 0;
map.m_len = 0;
map.m_flags = 0;
for (; nr_pages; nr_pages--) {
int fully_mapped = 1;
unsigned first_hole = blocks_per_page;
if (rac)
folio = readahead_folio(rac);
prefetchw(&folio->flags);
if (folio_buffers(folio))
goto confused;
block_in_file = next_block =
(sector_t)folio->index << (PAGE_SHIFT - blkbits);
last_block = block_in_file + nr_pages * blocks_per_page;
last_block_in_file = (ext4_readpage_limit(inode) +
blocksize - 1) >> blkbits;
if (last_block > last_block_in_file)
last_block = last_block_in_file;
page_block = 0;
/*
* Map blocks using the previous result first.
*/
if ((map.m_flags & EXT4_MAP_MAPPED) &&
block_in_file > map.m_lblk &&
block_in_file < (map.m_lblk + map.m_len)) {
unsigned map_offset = block_in_file - map.m_lblk;
unsigned last = map.m_len - map_offset;
for (relative_block = 0; ; relative_block++) {
if (relative_block == last) {
/* needed? */
map.m_flags &= ~EXT4_MAP_MAPPED;
break;
}
if (page_block == blocks_per_page)
break;
blocks[page_block] = map.m_pblk + map_offset +
relative_block;
page_block++;
block_in_file++;
}
}
/*
* Then do more ext4_map_blocks() calls until we are
* done with this folio.
*/
while (page_block < blocks_per_page) {
if (block_in_file < last_block) {
map.m_lblk = block_in_file;
map.m_len = last_block - block_in_file;
if (ext4_map_blocks(NULL, inode, &map, 0) < 0) {
set_error_page:
folio_set_error(folio);
folio_zero_segment(folio, 0,
folio_size(folio));
folio_unlock(folio);
goto next_page;
}
}
if ((map.m_flags & EXT4_MAP_MAPPED) == 0) {
fully_mapped = 0;
if (first_hole == blocks_per_page)
first_hole = page_block;
page_block++;
block_in_file++;
continue;
}
if (first_hole != blocks_per_page)
goto confused; /* hole -> non-hole */
/* Contiguous blocks? */
if (page_block && blocks[page_block-1] != map.m_pblk-1)
goto confused;
for (relative_block = 0; ; relative_block++) {
if (relative_block == map.m_len) {
/* needed? */
map.m_flags &= ~EXT4_MAP_MAPPED;
break;
} else if (page_block == blocks_per_page)
break;
blocks[page_block] = map.m_pblk+relative_block;
page_block++;
block_in_file++;
}
}
if (first_hole != blocks_per_page) {
folio_zero_segment(folio, first_hole << blkbits,
folio_size(folio));
if (first_hole == 0) {
if (ext4_need_verity(inode, folio->index) &&
!fsverity_verify_folio(folio))
goto set_error_page;
folio_mark_uptodate(folio);
folio_unlock(folio);
continue;
}
} else if (fully_mapped) {
folio_set_mappedtodisk(folio);
}
/*
* This folio will go to BIO. Do we need to send this
* BIO off first?
*/
if (bio && (last_block_in_bio != blocks[0] - 1 ||
!fscrypt_mergeable_bio(bio, inode, next_block))) {
submit_and_realloc:
submit_bio(bio);
bio = NULL;
}
if (bio == NULL) {
/*
* bio_alloc will _always_ be able to allocate a bio if
* __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM is set, see bio_alloc_bioset().
*/
bio = bio_alloc(bdev, bio_max_segs(nr_pages),
REQ_OP_READ, GFP_KERNEL);
fscrypt_set_bio_crypt_ctx(bio, inode, next_block,
GFP_KERNEL);
ext4_set_bio_post_read_ctx(bio, inode, folio->index);
bio->bi_iter.bi_sector = blocks[0] << (blkbits - 9);
bio->bi_end_io = mpage_end_io;
if (rac)
bio->bi_opf |= REQ_RAHEAD;
}
length = first_hole << blkbits;
if (!bio_add_folio(bio, folio, length, 0))
goto submit_and_realloc;
if (((map.m_flags & EXT4_MAP_BOUNDARY) &&
(relative_block == map.m_len)) ||
(first_hole != blocks_per_page)) {
submit_bio(bio);
bio = NULL;
} else
last_block_in_bio = blocks[blocks_per_page - 1];
continue;
confused:
if (bio) {
submit_bio(bio);
bio = NULL;
}
if (!folio_test_uptodate(folio))
block_read_full_folio(folio, ext4_get_block);
else
folio_unlock(folio);
next_page:
; /* A label shall be followed by a statement until C23 */
}
if (bio)
submit_bio(bio);
return 0;
}
ext4_mpage_readpages会调用submit_bio向blk层申请request。
3.2 ext4文件系统writepages
fs/ext4/inode.c
static const struct address_space_operations ext4_journalled_aops = {
.read_folio = ext4_read_folio,
.readahead = ext4_readahead,
.writepages = ext4_writepages,
.write_begin = ext4_write_begin,
.write_end = ext4_journalled_write_end,
.dirty_folio = ext4_journalled_dirty_folio,
.bmap = ext4_bmap,
.invalidate_folio = ext4_journalled_invalidate_folio,
.release_folio = ext4_release_folio,
.direct_IO = noop_direct_IO,
.migrate_folio = buffer_migrate_folio_norefs,
.is_partially_uptodate = block_is_partially_uptodate,
.error_remove_page = generic_error_remove_page,
.swap_activate = ext4_iomap_swap_activate,
};
static int ext4_writepages(struct address_space *mapping,
struct writeback_control *wbc)
{
struct super_block *sb = mapping->host->i_sb;
struct mpage_da_data mpd = {
.inode = mapping->host,
.wbc = wbc,
.can_map = 1,
};
int ret;
int alloc_ctx;
if (unlikely(ext4_forced_shutdown(sb)))
return -EIO;
alloc_ctx = ext4_writepages_down_read(sb);
ret = ext4_do_writepages(&mpd);
/*
* For data=journal writeback we could have come across pages marked
* for delayed dirtying (PageChecked) which were just added to the
* running transaction. Try once more to get them to stable storage.
*/
if (!ret && mpd.journalled_more_data)
ret = ext4_do_writepages(&mpd);
ext4_writepages_up_read(sb, alloc_ctx);
return ret;
}
static int ext4_do_writepages(struct mpage_da_data *mpd)
{
struct writeback_control *wbc = mpd->wbc;
pgoff_t writeback_index = 0;
long nr_to_write = wbc->nr_to_write;
int range_whole = 0;
int cycled = 1;
handle_t *handle = NULL;
struct inode *inode = mpd->inode;
struct address_space *mapping = inode->i_mapping;
int needed_blocks, rsv_blocks = 0, ret = 0;
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi = EXT4_SB(mapping->host->i_sb);
struct blk_plug plug;
bool give_up_on_write = false;
trace_ext4_writepages(inode, wbc);
/*
* No pages to write? This is mainly a kludge to avoid starting
* a transaction for special inodes like journal inode on last iput()
* because that could violate lock ordering on umount
*/
if (!mapping->nrpages || !mapping_tagged(mapping, PAGECACHE_TAG_DIRTY))
goto out_writepages;
/*
* If the filesystem has aborted, it is read-only, so return
* right away instead of dumping stack traces later on that
* will obscure the real source of the problem. We test
* fs shutdown state instead of sb->s_flag's SB_RDONLY because
* the latter could be true if the filesystem is mounted
* read-only, and in that case, ext4_writepages should
* *never* be called, so if that ever happens, we would want
* the stack trace.
*/
if (unlikely(ext4_forced_shutdown(mapping->host->i_sb))) {
ret = -EROFS;
goto out_writepages;
}
/*
* If we have inline data and arrive here, it means that
* we will soon create the block for the 1st page, so
* we'd better clear the inline data here.
*/
if (ext4_has_inline_data(inode)) {
/* Just inode will be modified... */
handle = ext4_journal_start(inode, EXT4_HT_INODE, 1);
if (IS_ERR(handle)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(handle);
goto out_writepages;
}
BUG_ON(ext4_test_inode_state(inode,
EXT4_STATE_MAY_INLINE_DATA));
ext4_destroy_inline_data(handle, inode);
ext4_journal_stop(handle);
}
/*
* data=journal mode does not do delalloc so we just need to writeout /
* journal already mapped buffers. On the other hand we need to commit
* transaction to make data stable. We expect all the data to be
* already in the journal (the only exception are DMA pinned pages
* dirtied behind our back) so we commit transaction here and run the
* writeback loop to checkpoint them. The checkpointing is not actually
* necessary to make data persistent *but* quite a few places (extent
* shifting operations, fsverity, ...) depend on being able to drop
* pagecache pages after calling filemap_write_and_wait() and for that
* checkpointing needs to happen.
*/
if (ext4_should_journal_data(inode)) {
mpd->can_map = 0;
if (wbc->sync_mode == WB_SYNC_ALL)
ext4_fc_commit(sbi->s_journal,
EXT4_I(inode)->i_datasync_tid);
}
mpd->journalled_more_data = 0;
if (ext4_should_dioread_nolock(inode)) {
/*
* We may need to convert up to one extent per block in
* the page and we may dirty the inode.
*/
rsv_blocks = 1 + ext4_chunk_trans_blocks(inode,
PAGE_SIZE >> inode->i_blkbits);
}
if (wbc->range_start == 0 && wbc->range_end == LLONG_MAX)
range_whole = 1;
if (wbc->range_cyclic) {
writeback_index = mapping->writeback_index;
if (writeback_index)
cycled = 0;
mpd->first_page = writeback_index;
mpd->last_page = -1;
} else {
mpd->first_page = wbc->range_start >> PAGE_SHIFT;
mpd->last_page = wbc->range_end >> PAGE_SHIFT;
}
ext4_io_submit_init(&mpd->io_submit, wbc);
retry:
if (wbc->sync_mode == WB_SYNC_ALL || wbc->tagged_writepages)
tag_pages_for_writeback(mapping, mpd->first_page,
mpd->last_page);
blk_start_plug(&plug);
/*
* First writeback pages that don't need mapping - we can avoid
* starting a transaction unnecessarily and also avoid being blocked
* in the block layer on device congestion while having transaction
* started.
*/
mpd->do_map = 0;
mpd->scanned_until_end = 0;
mpd->io_submit.io_end = ext4_init_io_end(inode, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mpd->io_submit.io_end) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto unplug;
}
ret = mpage_prepare_extent_to_map(mpd);
/* Unlock pages we didn't use */
mpage_release_unused_pages(mpd, false);
/* Submit prepared bio */
ext4_io_submit(&mpd->io_submit);
ext4_put_io_end_defer(mpd->io_submit.io_end);
mpd->io_submit.io_end = NULL;
if (ret < 0)
goto unplug;
while (!mpd->scanned_until_end && wbc->nr_to_write > 0) {
/* For each extent of pages we use new io_end */
mpd->io_submit.io_end = ext4_init_io_end(inode, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mpd->io_submit.io_end) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
break;
}
WARN_ON_ONCE(!mpd->can_map);
/*
* We have two constraints: We find one extent to map and we
* must always write out whole page (makes a difference when
* blocksize < pagesize) so that we don't block on IO when we
* try to write out the rest of the page. Journalled mode is
* not supported by delalloc.
*/
BUG_ON(ext4_should_journal_data(inode));
needed_blocks = ext4_da_writepages_trans_blocks(inode);
/* start a new transaction */
handle = ext4_journal_start_with_reserve(inode,
EXT4_HT_WRITE_PAGE, needed_blocks, rsv_blocks);
if (IS_ERR(handle)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(handle);
ext4_msg(inode->i_sb, KERN_CRIT, "%s: jbd2_start: "
"%ld pages, ino %lu; err %d", __func__,
wbc->nr_to_write, inode->i_ino, ret);
/* Release allocated io_end */
ext4_put_io_end(mpd->io_submit.io_end);
mpd->io_submit.io_end = NULL;
break;
}
mpd->do_map = 1;
trace_ext4_da_write_pages(inode, mpd->first_page, wbc);
ret = mpage_prepare_extent_to_map(mpd);
if (!ret && mpd->map.m_len)
ret = mpage_map_and_submit_extent(handle, mpd,
&give_up_on_write);
/*
* Caution: If the handle is synchronous,
* ext4_journal_stop() can wait for transaction commit
* to finish which may depend on writeback of pages to
* complete or on page lock to be released. In that
* case, we have to wait until after we have
* submitted all the IO, released page locks we hold,
* and dropped io_end reference (for extent conversion
* to be able to complete) before stopping the handle.
*/
if (!ext4_handle_valid(handle) || handle->h_sync == 0) {
ext4_journal_stop(handle);
handle = NULL;
mpd->do_map = 0;
}
/* Unlock pages we didn't use */
mpage_release_unused_pages(mpd, give_up_on_write);
/* Submit prepared bio */
ext4_io_submit(&mpd->io_submit);
/*
* Drop our io_end reference we got from init. We have
* to be careful and use deferred io_end finishing if
* we are still holding the transaction as we can
* release the last reference to io_end which may end
* up doing unwritten extent conversion.
*/
if (handle) {
ext4_put_io_end_defer(mpd->io_submit.io_end);
ext4_journal_stop(handle);
} else
ext4_put_io_end(mpd->io_submit.io_end);
mpd->io_submit.io_end = NULL;
if (ret == -ENOSPC && sbi->s_journal) {
/*
* Commit the transaction which would
* free blocks released in the transaction
* and try again
*/
jbd2_journal_force_commit_nested(sbi->s_journal);
ret = 0;
continue;
}
/* Fatal error - ENOMEM, EIO... */
if (ret)
break;
}
unplug:
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
if (!ret && !cycled && wbc->nr_to_write > 0) {
cycled = 1;
mpd->last_page = writeback_index - 1;
mpd->first_page = 0;
goto retry;
}
/* Update index */
if (wbc->range_cyclic || (range_whole && wbc->nr_to_write > 0))
/*
* Set the writeback_index so that range_cyclic
* mode will write it back later
*/
mapping->writeback_index = mpd->first_page;
out_writepages:
trace_ext4_writepages_result(inode, wbc, ret,
nr_to_write - wbc->nr_to_write);
return ret;
}
fs/ext4/page-io.c
ext4_do_writepages会调用ext4_io_submit --> submit_bio向blk层申请request。
void ext4_io_submit(struct ext4_io_submit *io)
{
struct bio *bio = io->io_bio;
if (bio) {
if (io->io_wbc->sync_mode == WB_SYNC_ALL)
io->io_bio->bi_opf |= REQ_SYNC;
submit_bio(io->io_bio);
}
io->io_bio = NULL;
}
四、blk块设备驱动层
submit_bio是内核标准的提交request方法,基本会调用到submit_bio_noacct
block/blk-core.c
/**
* submit_bio - submit a bio to the block device layer for I/O
* @bio: The &struct bio which describes the I/O
*
* submit_bio() is used to submit I/O requests to block devices. It is passed a
* fully set up &struct bio that describes the I/O that needs to be done. The
* bio will be send to the device described by the bi_bdev field.
*
* The success/failure status of the request, along with notification of
* completion, is delivered asynchronously through the ->bi_end_io() callback
* in @bio. The bio must NOT be touched by the caller until ->bi_end_io() has
* been called.
*/
void submit_bio(struct bio *bio)
{
if (bio_op(bio) == REQ_OP_READ) {
task_io_account_read(bio->bi_iter.bi_size);
count_vm_events(PGPGIN, bio_sectors(bio));
} else if (bio_op(bio) == REQ_OP_WRITE) {
count_vm_events(PGPGOUT, bio_sectors(bio));
}
submit_bio_noacct(bio);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(submit_bio);
在submit_bio_noacct中会向bio层申请request请求:
/**
* submit_bio_noacct - re-submit a bio to the block device layer for I/O
* @bio: The bio describing the location in memory and on the device.
*
* This is a version of submit_bio() that shall only be used for I/O that is
* resubmitted to lower level drivers by stacking block drivers. All file
* systems and other upper level users of the block layer should use
* submit_bio() instead.
*/
void submit_bio_noacct(struct bio *bio)
{
struct block_device *bdev = bio->bi_bdev;
struct request_queue *q = bdev_get_queue(bdev);
blk_status_t status = BLK_STS_IOERR;
DEFINE_WAIT(wait);
wait_queue_head_t *wait_head = NULL;
bool throtl;
might_sleep();
/*
* For a REQ_NOWAIT based request, return -EOPNOTSUPP
* if queue does not support NOWAIT.
*/
if ((bio->bi_opf & REQ_NOWAIT) && !bdev_nowait(bdev))
goto not_supported;
if (should_fail_bio(bio))
goto end_io;
bio_check_ro(bio);
if (!bio_flagged(bio, BIO_REMAPPED)) {
if (unlikely(bio_check_eod(bio)))
goto end_io;
if (bdev->bd_partno && unlikely(blk_partition_remap(bio)))
goto end_io;
}
/*
* Filter flush bio's early so that bio based drivers without flush
* support don't have to worry about them.
*/
if (op_is_flush(bio->bi_opf)) {
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(bio_op(bio) != REQ_OP_WRITE &&
bio_op(bio) != REQ_OP_ZONE_APPEND))
goto end_io;
if (!test_bit(QUEUE_FLAG_WC, &q->queue_flags)) {
bio->bi_opf &= ~(REQ_PREFLUSH | REQ_FUA);
if (!bio_sectors(bio)) {
status = BLK_STS_OK;
goto end_io;
}
}
}
if (!test_bit(QUEUE_FLAG_POLL, &q->queue_flags))
bio_clear_polled(bio);
switch (bio_op(bio)) {
case REQ_OP_DISCARD:
if (!bdev_max_discard_sectors(bdev))
goto not_supported;
break;
case REQ_OP_SECURE_ERASE:
if (!bdev_max_secure_erase_sectors(bdev))
goto not_supported;
break;
case REQ_OP_ZONE_APPEND:
status = blk_check_zone_append(q, bio);
if (status != BLK_STS_OK)
goto end_io;
break;
case REQ_OP_ZONE_RESET:
case REQ_OP_ZONE_OPEN:
case REQ_OP_ZONE_CLOSE:
case REQ_OP_ZONE_FINISH:
if (!bdev_is_zoned(bio->bi_bdev))
goto not_supported;
break;
case REQ_OP_ZONE_RESET_ALL:
if (!bdev_is_zoned(bio->bi_bdev) || !blk_queue_zone_resetall(q))
goto not_supported;
break;
case REQ_OP_WRITE_ZEROES:
if (!q->limits.max_write_zeroes_sectors)
goto not_supported;
break;
default:
break;
}
throtl = blk_throtl_bio(bio, &wait_head, &wait);
if (wait_head) {
io_schedule();
finish_wait(wait_head, &wait);
}
if (throtl)
return;
submit_bio_noacct_nocheck(bio);
return;
not_supported:
status = BLK_STS_NOTSUPP;
end_io:
bio->bi_status = status;
bio_endio(bio);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(submit_bio_noacct);
调用queue的request_fn方法把request提交给磁盘驱动进行真正的处理。当前进程是plug的,在read_pages之后会调用stop plug,将所有request集中交给磁盘驱动处理。





















 6255
6255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








