Linux VFS文件系统分析5(基于Linux6.6)---VFS与open接口介绍
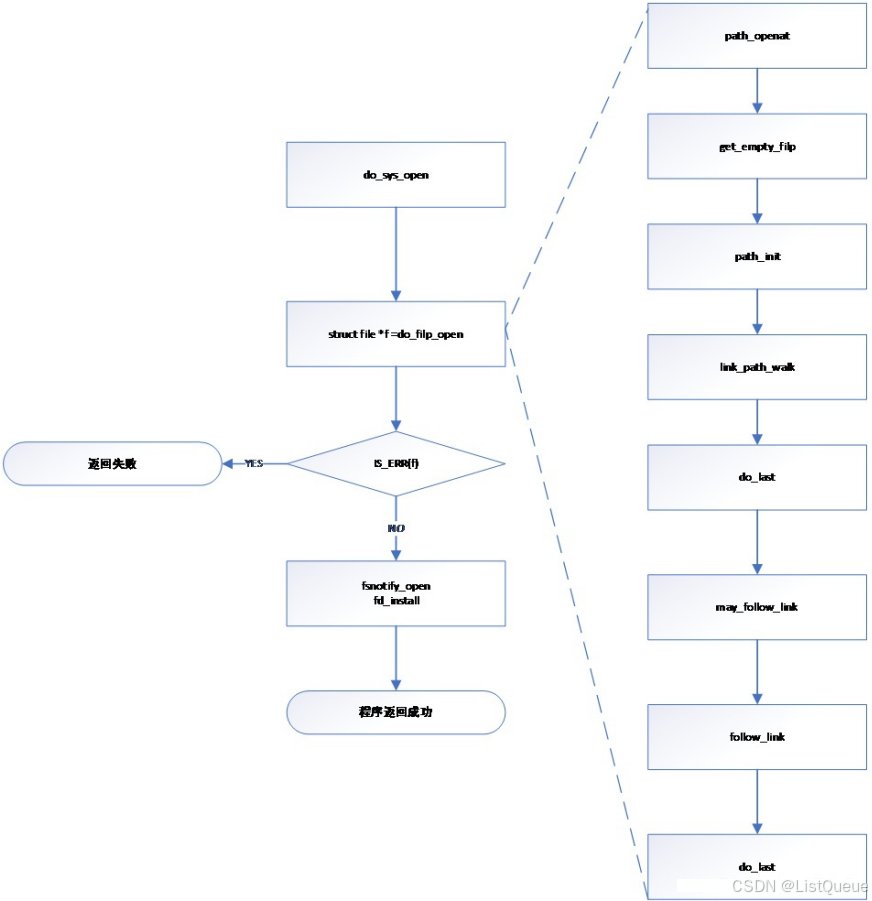
一、sys_open
sys_open实现功能的说明:
1.首先调用get_unused_fd_flags,在该进程空间中,获取一个尚未使用的fd,若获取成功,则继续向下执行,并确认是否需要扩展task->files->fdt的内存;若当前进程已打开的文件数超过限制,则返回失败。
2.若成功获取一个尚未使用的fd,则调用do_filp_open进行后续的操作,而do_filp_open则直接调用path_openat进行后续操作。
3.在path_openat中,主要包含如下几部分:
a.调用get_empty_filp接口,申请一个文件描述符指针。
b.进行路径查找时需要借助结构体struct nameidata类型的变量存储查找过程相关的dentry变量、路径名、inode节点等信息, 因此需要调用path_init接口用于初始化struct nameidata类型的变量,并设置路径查找的类型(根路径查找、当前路径查找等)。
c.调用link_path_walk接口,进行路径的查找,执行完该接口后,若查找成功,其返回打开文件的父目录的dentry、inode等变量值。
d.当查找路径成功后,则调用do_last进行文件的打开,若打开的文件为一个链接文件则do_last直接返回,由path_openat中的 接 下来的函数调用follow_link接口,对链接文件对应的target文件路径进行查找,并返回查找文件的父目录对应的dentry、inode,接着调用do_last进行文件的打开操作。
4.若第三步完成了文件的打开操作,则将该打开文件对应的文件描述符与fd进行关联,即
task->files->fdt[fd]=filep。
以上4步即为文件打开所需要执行的主要内容,通过这些操作,完成了文件描述符与dentry、inode、filesystem、进程描述符等变量的关联,即将文件与进程关联起来。接下来详细分析
二、get_unused_fd_flags接口分析
fs/file.c
get_unused_fd_flags获取一个未使用的fd。该接口的定义如下
int get_unused_fd_flags(unsigned flags)
{
return __get_unused_fd_flags(flags, rlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE));
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(get_unused_fd_flags);
int __get_unused_fd_flags(unsigned flags, unsigned long nofile)
{
return alloc_fd(0, nofile, flags);
}
主要是调用alloc_fd实现fd的申请。
alloc_fd接口
1.查找一个可用的fd(若没有可用fd,或者查找的fd值大于当前进程可打开的fd,则返回失败)
2.若查找到可用fd,则调用expand_files,确认是否需要扩展fdt
3.程序返回。
/*
* allocate a file descriptor, mark it busy.
*/
static int alloc_fd(unsigned start, unsigned end, unsigned flags)
{
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
unsigned int fd;
int error;
struct fdtable *fdt;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
repeat:
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
fd = start;
if (fd < files->next_fd)
fd = files->next_fd;
if (fd < fdt->max_fds)
fd = find_next_fd(fdt, fd);
/*
* N.B. For clone tasks sharing a files structure, this test
* will limit the total number of files that can be opened.
*/
error = -EMFILE;
if (fd >= end)
goto out;
error = expand_files(files, fd);
if (error < 0)
goto out;
/*
* If we needed to expand the fs array we
* might have blocked - try again.
*/
if (error)
goto repeat;
if (start <= files->next_fd)
files->next_fd = fd + 1;
__set_open_fd(fd, fdt);
if (flags & O_CLOEXEC)
__set_close_on_exec(fd, fdt);
else
__clear_close_on_exec(fd, fdt);
error = fd;
#if 1
/* Sanity check */
if (rcu_access_pointer(fdt->fd[fd]) != NULL) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "alloc_fd: slot %d not NULL!\n", fd);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], NULL);
}
#endif
out:
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
return error;
}
expand_files接口分析
expand_files的作用如下:
- 若nr小于fd->max_fds,则无需扩展fdt;
- 判断nr是否大于当前进程可打开的文件数;若大于则返回失败
- 若非以上两种情况,则需要扩展fdt,调用expand_fdtable扩展fdt
static int expand_files(struct files_struct *files, unsigned int nr)
__releases(files->file_lock)
__acquires(files->file_lock)
{
struct fdtable *fdt;
int expanded = 0;
repeat:
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
/* Do we need to expand? */
if (nr < fdt->max_fds)
return expanded;
/* Can we expand? */
if (nr >= sysctl_nr_open)
return -EMFILE;
if (unlikely(files->resize_in_progress)) {
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
expanded = 1;
wait_event(files->resize_wait, !files->resize_in_progress);
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
goto repeat;
}
/* All good, so we try */
files->resize_in_progress = true;
expanded = expand_fdtable(files, nr);
files->resize_in_progress = false;
wake_up_all(&files->resize_wait);
return expanded;
}
expand_fdtab主要是根据新的nr,重新申请进程描述符中的fdt指针变量及fdt->fd、fdt->open_fds等
static int expand_fdtable(struct files_struct *files, unsigned int nr)
__releases(files->file_lock)
__acquires(files->file_lock)
{
struct fdtable *new_fdt, *cur_fdt;
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
new_fdt = alloc_fdtable(nr);
/* make sure all fd_install() have seen resize_in_progress
* or have finished their rcu_read_lock_sched() section.
*/
if (atomic_read(&files->count) > 1)
synchronize_rcu();
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
if (!new_fdt)
return -ENOMEM;
/*
* extremely unlikely race - sysctl_nr_open decreased between the check in
* caller and alloc_fdtable(). Cheaper to catch it here...
*/
if (unlikely(new_fdt->max_fds <= nr)) {
__free_fdtable(new_fdt);
return -EMFILE;
}
cur_fdt = files_fdtable(files);
BUG_ON(nr < cur_fdt->max_fds);
copy_fdtable(new_fdt, cur_fdt);
rcu_assign_pointer(files->fdt, new_fdt);
if (cur_fdt != &files->fdtab)
call_rcu(&cur_fdt->rcu, free_fdtable_rcu);
/* coupled with smp_rmb() in fd_install() */
smp_wmb();
return 1;
}
alloc_fdtable接口分析
alloc_fdtable主要是根据nr值申请fdt,
当nr小于1024/sizeof(struct file*),则创建1024/sizeof(struct file *);否则,则创建nr最接近的2次幂的值作为需要申请的max_fds。
static struct fdtable * alloc_fdtable(unsigned int nr)
{
struct fdtable *fdt;
void *data;
/*
* Figure out how many fds we actually want to support in this fdtable.
* Allocation steps are keyed to the size of the fdarray, since it
* grows far faster than any of the other dynamic data. We try to fit
* the fdarray into comfortable page-tuned chunks: starting at 1024B
* and growing in powers of two from there on.
*/
nr /= (1024 / sizeof(struct file *));
nr = roundup_pow_of_two(nr + 1);
nr *= (1024 / sizeof(struct file *));
nr = ALIGN(nr, BITS_PER_LONG);
/*
* Note that this can drive nr *below* what we had passed if sysctl_nr_open
* had been set lower between the check in expand_files() and here. Deal
* with that in caller, it's cheaper that way.
*
* We make sure that nr remains a multiple of BITS_PER_LONG - otherwise
* bitmaps handling below becomes unpleasant, to put it mildly...
*/
if (unlikely(nr > sysctl_nr_open))
nr = ((sysctl_nr_open - 1) | (BITS_PER_LONG - 1)) + 1;
fdt = kmalloc(sizeof(struct fdtable), GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT);
if (!fdt)
goto out;
fdt->max_fds = nr;
data = kvmalloc_array(nr, sizeof(struct file *), GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT);
if (!data)
goto out_fdt;
fdt->fd = data;
data = kvmalloc(max_t(size_t,
2 * nr / BITS_PER_BYTE + BITBIT_SIZE(nr), L1_CACHE_BYTES),
GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT);
if (!data)
goto out_arr;
fdt->open_fds = data;
data += nr / BITS_PER_BYTE;
fdt->close_on_exec = data;
data += nr / BITS_PER_BYTE;
fdt->full_fds_bits = data;
return fdt;
out_arr:
kvfree(fdt->fd);
out_fdt:
kfree(fdt);
out:
return NULL;
}
三、alloc_empty_file接口分析
get_empty_filp在linux6.x已被alloc_empty_file替代,用于申请一个新的文件描述符,下面分析下这个接口函数,该接口主要实现如下功能:
1.申请一个struct file类型的指针变量;
2.获取当前进程相关的权限信息;
3.若当前进程不具备admin权限,且当前打开文件数大于max_files,则返回失败;
4.从缓存filp_cachep中申请sizeof(struct file)大小的内存,并初始化该类型变量对应的自旋锁、读写锁、链表等。
struct file *alloc_empty_file(int flags, const struct cred *cred)
{
static long old_max;
struct file *f;
int error;
/*
* Privileged users can go above max_files
*/
if (get_nr_files() >= files_stat.max_files && !capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN)) {
/*
* percpu_counters are inaccurate. Do an expensive check before
* we go and fail.
*/
if (percpu_counter_sum_positive(&nr_files) >= files_stat.max_files)
goto over;
}
f = kmem_cache_zalloc(filp_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (unlikely(!f))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
error = init_file(f, flags, cred);
if (unlikely(error)) {
kmem_cache_free(filp_cachep, f);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
percpu_counter_inc(&nr_files);
return f;
over:
/* Ran out of filps - report that */
if (get_nr_files() > old_max) {
pr_info("VFS: file-max limit %lu reached\n", get_max_files());
old_max = get_nr_files();
}
return ERR_PTR(-ENFILE);
}
四、路径查找模块分析
路径查找模块涉及路径查找初始化、路径查找、路径查找相关结构体定义等部分。
4.1、路径查找相关的结构体
在进行文件路径的查找时,需要用到结构体nameidata用于存储查找信息,该结构体的定义如下,包括查找路径、根路径、查找的inode节点等信息。
结构体nameidata的定义如下,
fs/namei.c
struct nameidata {
struct path path;
struct qstr last;
struct path root;
struct inode *inode; /* path.dentry.d_inode */
unsigned int flags, state;
unsigned seq, next_seq, m_seq, r_seq;
int last_type;
unsigned depth;
int total_link_count;
struct saved {
struct path link;
struct delayed_call done;
const char *name;
unsigned seq;
} *stack, internal[EMBEDDED_LEVELS];
struct filename *name;
struct nameidata *saved;
unsigned root_seq;
int dfd;
vfsuid_t dir_vfsuid;
umode_t dir_mode;
} __randomize_layout;
include/linux/path.h
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry;
} __randomize_layout;
结构体qstr的定义如下,主要包括name以及hash_len,该结构体主要包括要查找的下一级路径的名称,以便于用于路径对应的dentry以及inode变量的查找。
include/linux/dcache.h
struct qstr {
union {
struct {
HASH_LEN_DECLARE;
};
u64 hash_len;
};
const unsigned char *name;
};
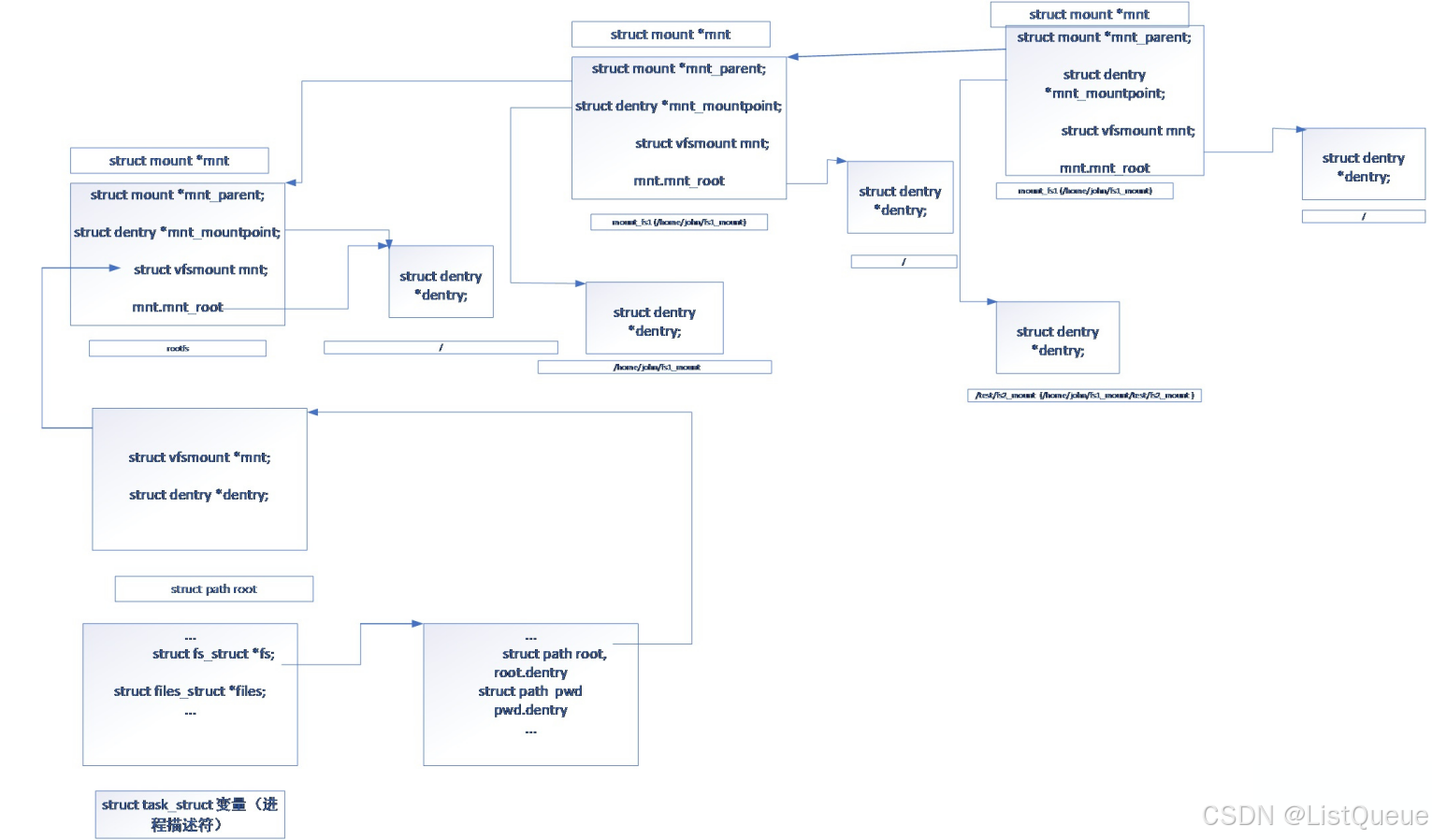
关于struct path、struct vfs_mount、struct fs_struct、struct task结构体变量的关联,可以用如下关联图表示
如下说明了一个进程描述符通过其fs指针变量,定义了该进程的根路径相关的root path,通过该root path,可以确定其
当前进程所在根目录的dentry、以及该目录对应文件系统相关的mount变量,根据mount变量,可以获取文件系统的挂载点以及根文件系统对应的根dentry。
而系统中所有的mount变量亦可以根据其mnt_parent实现关联。
4.2、路径查找初始化接口
路径查找相关的初始化接口为path_init,该接口实现对路径查找变量struct nameidate类型的变量初始化,并初始化路径查找的类型(从根路径查找/从当前路径查找/第一个查找变量即为文件)等内容,该接口主要是根据传递的查找路径内容,设置nd的path指针,主要包括根路径、当前路径、文件这三种case的处理。
fs/namei.c
/* must be paired with terminate_walk() */
static const char *path_init(struct nameidata *nd, unsigned flags)
{
int error;
const char *s = nd->name->name;
/* LOOKUP_CACHED requires RCU, ask caller to retry */
if ((flags & (LOOKUP_RCU | LOOKUP_CACHED)) == LOOKUP_CACHED)
return ERR_PTR(-EAGAIN);
if (!*s)
flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
rcu_read_lock();
else
nd->seq = nd->next_seq = 0;
nd->flags = flags;
nd->state |= ND_JUMPED;
nd->m_seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&mount_lock.seqcount);
nd->r_seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&rename_lock.seqcount);
smp_rmb();
if (nd->state & ND_ROOT_PRESET) {
struct dentry *root = nd->root.dentry;
struct inode *inode = root->d_inode;
if (*s && unlikely(!d_can_lookup(root)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
nd->path = nd->root;
nd->inode = inode;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
nd->root_seq = nd->seq;
} else {
path_get(&nd->path);
}
return s;
}
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
/* Absolute pathname -- fetch the root (LOOKUP_IN_ROOT uses nd->dfd). */
if (*s == '/' && !(flags & LOOKUP_IN_ROOT)) {
error = nd_jump_root(nd);
if (unlikely(error))
return ERR_PTR(error);
return s;
}
/* Relative pathname -- get the starting-point it is relative to. */
if (nd->dfd == AT_FDCWD) {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
unsigned seq;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&fs->seq);
nd->path = fs->pwd;
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&fs->seq, seq));
} else {
get_fs_pwd(current->fs, &nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
} else {
/* Caller must check execute permissions on the starting path component */
struct fd f = fdget_raw(nd->dfd);
struct dentry *dentry;
if (!f.file)
return ERR_PTR(-EBADF);
dentry = f.file->f_path.dentry;
if (*s && unlikely(!d_can_lookup(dentry))) {
fdput(f);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
}
nd->path = f.file->f_path;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} else {
path_get(&nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
fdput(f);
}
/* For scoped-lookups we need to set the root to the dirfd as well. */
if (flags & LOOKUP_IS_SCOPED) {
nd->root = nd->path;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
nd->root_seq = nd->seq;
} else {
path_get(&nd->root);
nd->state |= ND_ROOT_GRABBED;
}
}
return s;
}
4.3、路径查找接口
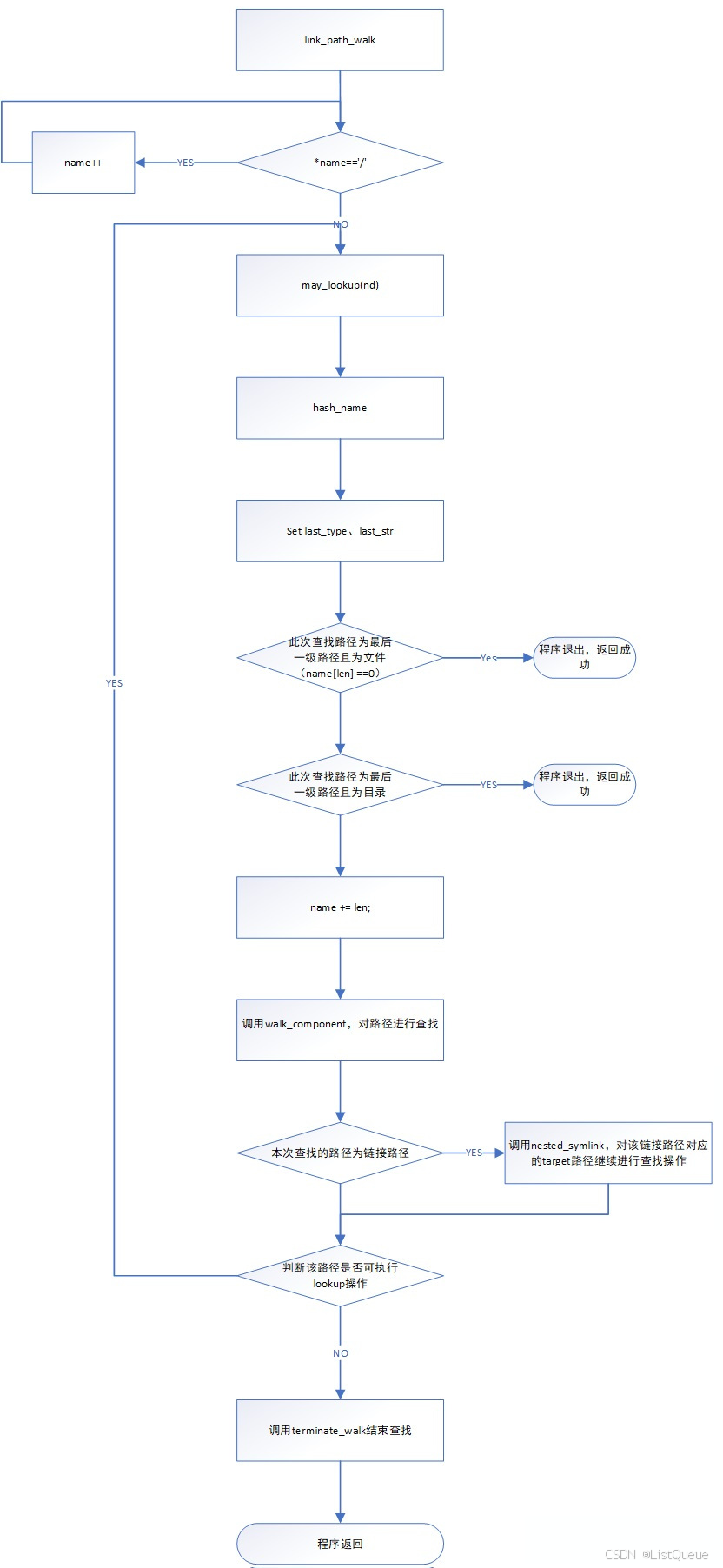
link_path_walk为路径查找接口,该接口对传入的文件路径,进行一级一级的查找,并对查找过程中遇到的链接目录进行进一步的查找,在路径查找的过程中,可能会跨越多个文件系统,因此在查找过程中,需要更新struct nameidate类型的变量中的root参数。
路径查找接口的主要功能如下流程图,主要分为如下几个主要步骤:
1.首先去除路径名称起始字符中所有的'/'字符(这也是我们在实际linux系统中进入执行"cd //home/"命令,可正常进入家目录的原因);
2.针对传入的路径名称,循环进行查找:
a.若需要查找的目录,没有执行权限或者不能执行lookup操作,则返回查找失败;
b.若当前目录为最后一级路径(最后一级路径为文件或者为目录),则更新last_type、last_str,该接口返回成功;
c.若不是以上情况,则更新name指针的位置,移植下一级目录的首地址处;
d.若不是上述b中的情况,则说明此处为一个目录项,则调用walk_component接口,查找本次目录对应的dentry以及inode:
>若查找失败,则返回路径查找失败;
>若查找成功且不是链接目录,则跳转至a,继续下一级路径的查找;
>若查找成功且是链接目录,则调用nested_symlink对链接路径对应的目标路径继续进行解析:
i.若解析失败,则返回查找失败;
Ii.若解析成功,则跳转至a,继续下一级路径的查找。
1.walk_component接口分析
该接口对当前的搜索路径进行搜索操作:
1.若last_type不是LAST_NORM,则调用handle_dots进行处理,针对'.' 、'..'的情形更新nd->path变量的值,程序退出;
2.若last_type是LAST_NORM,说明当前路径是正常的目录,则调用lookup_fast、lookup_slow进行查找。
a.首先调用lookup_fast,从nd->patn.dentry的hash链表中,根据nd->last.name查找子dentry:
若查找成功则返回0;
若没有查找到,则返回1,调用lookup_slow进行查找;
否则,则返回失败。
本次接口调用了三个主要的接口,handle_dots、lookup_fast、lookup_slow。这三个接口主要
对应于处理".."目录、从dcache中查找目录项、从子目录的dentry中查找目录项。
fs/namei.c
static const char *walk_component(struct nameidata *nd, int flags)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
/*
* "." and ".." are special - ".." especially so because it has
* to be able to know about the current root directory and
* parent relationships.
*/
if (unlikely(nd->last_type != LAST_NORM)) {
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
return handle_dots(nd, nd->last_type);
}
dentry = lookup_fast(nd);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
if (unlikely(!dentry)) {
dentry = lookup_slow(&nd->last, nd->path.dentry, nd->flags);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
}
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
return step_into(nd, flags, dentry);
}
handle_dots接口分析
该接口主要处理LAST_DOT、LAST_DOTDOT这两种类型:
1.对于LAST_DOTDOT,则需要跳转至父目录,具体调用follow_dotdot
2.对于LAST_DOT,则表示为当前目录,直接返回即可。
static const char *handle_dots(struct nameidata *nd, int type)
{
if (type == LAST_DOTDOT) {
const char *error = NULL;
struct dentry *parent;
if (!nd->root.mnt) {
error = ERR_PTR(set_root(nd));
if (error)
return error;
}
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
parent = follow_dotdot_rcu(nd);
else
parent = follow_dotdot(nd);
if (IS_ERR(parent))
return ERR_CAST(parent);
error = step_into(nd, WALK_NOFOLLOW, parent);
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
if (unlikely(nd->flags & LOOKUP_IS_SCOPED)) {
/*
* If there was a racing rename or mount along our
* path, then we can't be sure that ".." hasn't jumped
* above nd->root (and so userspace should retry or use
* some fallback).
*/
smp_rmb();
if (__read_seqcount_retry(&mount_lock.seqcount, nd->m_seq))
return ERR_PTR(-EAGAIN);
if (__read_seqcount_retry(&rename_lock.seqcount, nd->r_seq))
return ERR_PTR(-EAGAIN);
}
}
return NULL;
}
}
针对follow_dotdot接口,其定义如下:
该接口主要处理LAST_DOTDOT类型的路径变量,需要跳转至父目录,有如下几种情况
1.若当前搜索路径的dentry以及该dentry对应文件系统的mnt,即为当前进程的root路径及其mnt,则不能再往上查找,仍然以该目录作为查找路径。
2.若当前路径的dentry不是当前路径对应的文件系统的根dentry,则说明当前路径的父路径仍在相同的文件系统下,获取当前dentry的父节点即可。
3.若当前搜索路径的dentry即为其所在文件系统的根dentry,则调用follow_up进入其所挂载目录的上一级dentry,并修改nd->path中的mnt、dentry成员变量以及nd->inode的值。
fs/namei.c
static struct dentry *follow_dotdot(struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct dentry *parent;
if (path_equal(&nd->path, &nd->root))
goto in_root;
if (unlikely(nd->path.dentry == nd->path.mnt->mnt_root)) {
struct path path;
if (!choose_mountpoint(real_mount(nd->path.mnt),
&nd->root, &path))
goto in_root;
path_put(&nd->path);
nd->path = path;
nd->inode = path.dentry->d_inode;
if (unlikely(nd->flags & LOOKUP_NO_XDEV))
return ERR_PTR(-EXDEV);
}
/* rare case of legitimate dget_parent()... */
parent = dget_parent(nd->path.dentry);
if (unlikely(!path_connected(nd->path.mnt, parent))) {
dput(parent);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
}
return parent;
in_root:
if (unlikely(nd->flags & LOOKUP_BENEATH))
return ERR_PTR(-EXDEV);
return dget(nd->path.dentry);
}
针对其调用的follow_up接口,该接口为获取当前挂载点目录的dentry
1.通过path->mnt,获取该文件系统对应struct mount 类型的指针变量;
2.根据上述获取的struct mount类型的指针变量,获取挂载点对应目录的dentry以及其父mount的值,并赋值该struct path类型的指针变量中。
fs/namei.c
int follow_up(struct path *path)
{
struct mount *mnt = real_mount(path->mnt);
struct mount *parent;
struct dentry *mountpoint;
read_seqlock_excl(&mount_lock);
parent = mnt->mnt_parent;
if (parent == mnt) {
read_sequnlock_excl(&mount_lock);
return 0;
}
mntget(&parent->mnt);
mountpoint = dget(mnt->mnt_mountpoint);
read_sequnlock_excl(&mount_lock);
dput(path->dentry);
path->dentry = mountpoint;
mntput(path->mnt);
path->mnt = &parent->mnt;
return 1;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(follow_up);
lookup_fast接口分析
该接口的作用是在dentry的hash缓存链表中,查找名称为nd->last的dentry,且其parent dentry为nd->path.dentry。
fs/namei.c
static struct dentry *lookup_fast(struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct dentry *dentry, *parent = nd->path.dentry;
int status = 1;
/*
* Rename seqlock is not required here because in the off chance
* of a false negative due to a concurrent rename, the caller is
* going to fall back to non-racy lookup.
*/
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
dentry = __d_lookup_rcu(parent, &nd->last, &nd->next_seq);
if (unlikely(!dentry)) {
if (!try_to_unlazy(nd))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
return NULL;
}
/*
* This sequence count validates that the parent had no
* changes while we did the lookup of the dentry above.
*/
if (read_seqcount_retry(&parent->d_seq, nd->seq))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(status > 0))
return dentry;
if (!try_to_unlazy_next(nd, dentry))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
if (status == -ECHILD)
/* we'd been told to redo it in non-rcu mode */
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
} else {
dentry = __d_lookup(parent, &nd->last);
if (unlikely(!dentry))
return NULL;
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
}
if (unlikely(status <= 0)) {
if (!status)
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
return ERR_PTR(status);
}
return dentry;
}
lookup_slow接口分析
该接口实现的功能如下:
1.调用lookup查找符合要求的子dentry(该接口包括两种查找方式:1.从dcache中查找,成功则返回;2.若dcache中查找失败,则调用dentry的lookup接口进行查找);
2.若查找成功,则更新path的mnt、dentry变量,并调用follow_managed对查找到的dentry变量,确认是否进行autofs、mountpoint、 automountpoint的处理。
fs/namei.c
/* Fast lookup failed, do it the slow way */
static struct dentry *__lookup_slow(const struct qstr *name,
struct dentry *dir,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct dentry *dentry, *old;
struct inode *inode = dir->d_inode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
/* Don't go there if it's already dead */
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(inode)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
again:
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, name, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return dentry;
if (unlikely(!d_in_lookup(dentry))) {
int error = d_revalidate(dentry, flags);
if (unlikely(error <= 0)) {
if (!error) {
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
goto again;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = ERR_PTR(error);
}
} else {
old = inode->i_op->lookup(inode, dentry, flags);
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(old)) {
dput(dentry);
dentry = old;
}
}
return dentry;
}
2.symlink接口分析
该接口主要用于解析链接路径对应的目标路径,该接口的定义如下:
fs/namei.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(symlink, const char __user *, oldname, const char __user *, newname)
{
return do_symlinkat(getname(oldname), AT_FDCWD, getname(newname));
}
do_symlinkat接口分析
do_symlinkat 的作用是根据给定的目标路径(from)和符号链接路径(to)创建符号链接。它通过多步操作实现这一功能:
- 检查参数合法性。
- 调用
filename_create()创建符号链接的dentry。 - 进行安全检查(
security_path_symlink)。 - 调用
vfs_symlink()实际创建符号链接。 - 处理重试机制(如果操作失败且目录信息可能过时)。
- 清理资源并返回结果。
fs/namei.c
int do_symlinkat(struct filename *from, int newdfd, struct filename *to)
{
int error;
struct dentry *dentry;
struct path path;
unsigned int lookup_flags = 0;
if (IS_ERR(from)) {
error = PTR_ERR(from);
goto out_putnames;
}
retry:
dentry = filename_create(newdfd, to, &path, lookup_flags);
error = PTR_ERR(dentry);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
goto out_putnames;
error = security_path_symlink(&path, dentry, from->name);
if (!error)
error = vfs_symlink(mnt_idmap(path.mnt), path.dentry->d_inode,
dentry, from->name);
done_path_create(&path, dentry);
if (retry_estale(error, lookup_flags)) {
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_REVAL;
goto retry;
}
out_putnames:
putname(to);
putname(from);
return error;
}
至此完成路径查找的分析,主要包括普通路径的查找、链接路径的查找等信息。
4.4 文件打开接口open_last_lookups
open_last_lookups接口主要用于打开文件,包括文件创建等操作。
该接口主要用于打开或创建文件,具体实现如下内容:
1.若为目录(链接目录、根目录、当前目录、当前目录的父目录),则返回失败。
2.若为链接文件,返回1,由上层函数对链接文件进行查找操作。
3.若文件不存在且拥有创建文件权限,则创建文件对应的inode节点,并打开文件。
4.若文件不存在且不拥有创建文件权限,则返回失败。
5.若文件存在,则打开文件(若对该文件没有相应的权限,则返回失败)。
这个接口函数设置的函数调用比较多,不过其主要实现的功能即为上面说明的几个。
fs/namei.c
static const char *open_last_lookups(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool got_write = false;
struct dentry *dentry;
const char *res;
nd->flags |= op->intent;
if (nd->last_type != LAST_NORM) {
if (nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
return handle_dots(nd, nd->last_type);
}
if (!(open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
if (nd->last.name[nd->last.len])
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW | LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
/* we _can_ be in RCU mode here */
dentry = lookup_fast(nd);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
if (likely(dentry))
goto finish_lookup;
BUG_ON(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU);
} else {
/* create side of things */
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
if (!try_to_unlazy(nd))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
}
audit_inode(nd->name, dir, AUDIT_INODE_PARENT);
/* trailing slashes? */
if (unlikely(nd->last.name[nd->last.len]))
return ERR_PTR(-EISDIR);
}
if (open_flag & (O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY | O_RDWR)) {
got_write = !mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
/*
* do _not_ fail yet - we might not need that or fail with
* a different error; let lookup_open() decide; we'll be
* dropping this one anyway.
*/
}
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_lock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_lock_shared(dir->d_inode);
dentry = lookup_open(nd, file, op, got_write);
if (!IS_ERR(dentry) && (file->f_mode & FMODE_CREATED))
fsnotify_create(dir->d_inode, dentry);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_unlock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_unlock_shared(dir->d_inode);
if (got_write)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return ERR_CAST(dentry);
if (file->f_mode & (FMODE_OPENED | FMODE_CREATED)) {
dput(nd->path.dentry);
nd->path.dentry = dentry;
return NULL;
}
finish_lookup:
if (nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
res = step_into(nd, WALK_TRAILING, dentry);
if (unlikely(res))
nd->flags &= ~(LOOKUP_OPEN|LOOKUP_CREATE|LOOKUP_EXCL);
return res;
}
下面针对上面调用的lookup_open、may_open、finish_open这几个接口进行分析
1.lookup_open接口分析
该接口包括文件的查找以及文件创建等功能
该接口主要用于查找指定名称的文件,主要包括如下几种可能
1. 从dentry的dcache中查找文件,若查找成功,则更新path变量,返回成功;
2.若从dentry 的dcache中没有查找到文件,则调用dentry的looku接口,查找dentry的子dentry是否存在符合条件的子dentry。
若查找成功,更新path变量,返回成功;
若查找失败,则判断是否有创建文件的权限:
若有创建文件的权限,则调用vfs_create接口创建文件,更新path变量,返回成功;
若没有创建文件的权限,则更新path变量后,返回成功。
tatic struct dentry *lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct file *file,
const struct open_flags *op,
bool got_write)
{
struct mnt_idmap *idmap;
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
struct inode *dir_inode = dir->d_inode;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
struct dentry *dentry;
int error, create_error = 0;
umode_t mode = op->mode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(dir_inode)))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
file->f_mode &= ~FMODE_CREATED;
dentry = d_lookup(dir, &nd->last);
for (;;) {
if (!dentry) {
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, &nd->last, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return dentry;
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry))
break;
error = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(error > 0))
break;
if (error)
goto out_dput;
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
dentry = NULL;
}
if (dentry->d_inode) {
/* Cached positive dentry: will open in f_op->open */
return dentry;
}
/*
* Checking write permission is tricky, bacuse we don't know if we are
* going to actually need it: O_CREAT opens should work as long as the
* file exists. But checking existence breaks atomicity. The trick is
* to check access and if not granted clear O_CREAT from the flags.
*
* Another problem is returing the "right" error value (e.g. for an
* O_EXCL open we want to return EEXIST not EROFS).
*/
if (unlikely(!got_write))
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
idmap = mnt_idmap(nd->path.mnt);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if (open_flag & O_EXCL)
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
mode = vfs_prepare_mode(idmap, dir->d_inode, mode, mode, mode);
if (likely(got_write))
create_error = may_o_create(idmap, &nd->path,
dentry, mode);
else
create_error = -EROFS;
}
if (create_error)
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (dir_inode->i_op->atomic_open) {
dentry = atomic_open(nd, dentry, file, open_flag, mode);
if (unlikely(create_error) && dentry == ERR_PTR(-ENOENT))
dentry = ERR_PTR(create_error);
return dentry;
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry)) {
struct dentry *res = dir_inode->i_op->lookup(dir_inode, dentry,
nd->flags);
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (IS_ERR(res)) {
error = PTR_ERR(res);
goto out_dput;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = res;
}
}
/* Negative dentry, just create the file */
if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
file->f_mode |= FMODE_CREATED;
audit_inode_child(dir_inode, dentry, AUDIT_TYPE_CHILD_CREATE);
if (!dir_inode->i_op->create) {
error = -EACCES;
goto out_dput;
}
error = dir_inode->i_op->create(idmap, dir_inode, dentry,
mode, open_flag & O_EXCL);
if (error)
goto out_dput;
}
if (unlikely(create_error) && !dentry->d_inode) {
error = create_error;
goto out_dput;
}
return dentry;
out_dput:
dput(dentry);
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
2.may_open接口分析
该接口主要用于判断是否可以打开一个文件,主要涉及以下几个方面的判断:
1.若文件的flag设置了O_PATH标签,则返回可以;
2.若为链接文件,则返回失败;
3.若为字符或块设备,且该文件对应的文件系统不允许访问设备文件,则返回失败;
4.若打开文件的标签与超级块或者inode的权限不匹配,返回失败;
5.针对inode标记为S_APPEND或者打开文件标签为O_NOATIME时,做相应的合法性判断。
fs/namei.c
static int may_open(struct mnt_idmap *idmap, const struct path *path,
int acc_mode, int flag)
{
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry;
struct inode *inode = dentry->d_inode;
int error;
if (!inode)
return -ENOENT;
switch (inode->i_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFLNK:
return -ELOOP;
case S_IFDIR:
if (acc_mode & MAY_WRITE)
return -EISDIR;
if (acc_mode & MAY_EXEC)
return -EACCES;
break;
case S_IFBLK:
case S_IFCHR:
if (!may_open_dev(path))
return -EACCES;
fallthrough;
case S_IFIFO:
case S_IFSOCK:
if (acc_mode & MAY_EXEC)
return -EACCES;
flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
break;
case S_IFREG:
if ((acc_mode & MAY_EXEC) && path_noexec(path))
return -EACCES;
break;
}
error = inode_permission(idmap, inode, MAY_OPEN | acc_mode);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* An append-only file must be opened in append mode for writing.
*/
if (IS_APPEND(inode)) {
if ((flag & O_ACCMODE) != O_RDONLY && !(flag & O_APPEND))
return -EPERM;
if (flag & O_TRUNC)
return -EPERM;
}
/* O_NOATIME can only be set by the owner or superuser */
if (flag & O_NOATIME && !inode_owner_or_capable(idmap, inode))
return -EPERM;
return 0;
}
3.finish_open接口分析
该接口主要调用do_dentry_open接口,实现文件的打开操作。
fs/open.c
int finish_open(struct file *file, struct dentry *dentry,
int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *))
{
BUG_ON(file->f_mode & FMODE_OPENED); /* once it's opened, it's opened */
file->f_path.dentry = dentry;
return do_dentry_open(file, d_backing_inode(dentry), open);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(finish_open);
do_dentry_open接口的定义如下,该接口通过调用inode->i_fop获取文件操作的接口函数指针。
fs/open.c
static int do_dentry_open(struct file *f,
struct inode *inode,
int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *))
{
static const struct file_operations empty_fops = {};
int error;
path_get(&f->f_path);
f->f_inode = inode;
f->f_mapping = inode->i_mapping;
f->f_wb_err = filemap_sample_wb_err(f->f_mapping);
f->f_sb_err = file_sample_sb_err(f);
if (unlikely(f->f_flags & O_PATH)) {
f->f_mode = FMODE_PATH | FMODE_OPENED;
f->f_op = &empty_fops;
return 0;
}
if ((f->f_mode & (FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE)) == FMODE_READ) {
i_readcount_inc(inode);
} else if (f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE && !special_file(inode->i_mode)) {
error = get_write_access(inode);
if (unlikely(error))
goto cleanup_file;
error = __mnt_want_write(f->f_path.mnt);
if (unlikely(error)) {
put_write_access(inode);
goto cleanup_file;
}
f->f_mode |= FMODE_WRITER;
}
/* POSIX.1-2008/SUSv4 Section XSI 2.9.7 */
if (S_ISREG(inode->i_mode) || S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_ATOMIC_POS;
f->f_op = fops_get(inode->i_fop);
if (WARN_ON(!f->f_op)) {
error = -ENODEV;
goto cleanup_all;
}
error = security_file_open(f);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
error = break_lease(file_inode(f), f->f_flags);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
/* normally all 3 are set; ->open() can clear them if needed */
f->f_mode |= FMODE_LSEEK | FMODE_PREAD | FMODE_PWRITE;
if (!open)
open = f->f_op->open;
if (open) {
error = open(inode, f);
if (error)
goto cleanup_all;
}
f->f_mode |= FMODE_OPENED;
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_READ) &&
likely(f->f_op->read || f->f_op->read_iter))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_READ;
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE) &&
likely(f->f_op->write || f->f_op->write_iter))
f->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_WRITE;
if ((f->f_mode & FMODE_LSEEK) && !f->f_op->llseek)
f->f_mode &= ~FMODE_LSEEK;
if (f->f_mapping->a_ops && f->f_mapping->a_ops->direct_IO)
f->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_ODIRECT;
f->f_flags &= ~(O_CREAT | O_EXCL | O_NOCTTY | O_TRUNC);
f->f_iocb_flags = iocb_flags(f);
file_ra_state_init(&f->f_ra, f->f_mapping->host->i_mapping);
if ((f->f_flags & O_DIRECT) && !(f->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_ODIRECT))
return -EINVAL;
/*
* XXX: Huge page cache doesn't support writing yet. Drop all page
* cache for this file before processing writes.
*/
if (f->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE) {
/*
* Paired with smp_mb() in collapse_file() to ensure nr_thps
* is up to date and the update to i_writecount by
* get_write_access() is visible. Ensures subsequent insertion
* of THPs into the page cache will fail.
*/
smp_mb();
if (filemap_nr_thps(inode->i_mapping)) {
struct address_space *mapping = inode->i_mapping;
filemap_invalidate_lock(inode->i_mapping);
/*
* unmap_mapping_range just need to be called once
* here, because the private pages is not need to be
* unmapped mapping (e.g. data segment of dynamic
* shared libraries here).
*/
unmap_mapping_range(mapping, 0, 0, 0);
truncate_inode_pages(mapping, 0);
filemap_invalidate_unlock(inode->i_mapping);
}
}
/*
* Once we return a file with FMODE_OPENED, __fput() will call
* fsnotify_close(), so we need fsnotify_open() here for symmetry.
*/
fsnotify_open(f);
return 0;
cleanup_all:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(error > 0))
error = -EINVAL;
fops_put(f->f_op);
put_file_access(f);
cleanup_file:
path_put(&f->f_path);
f->f_path.mnt = NULL;
f->f_path.dentry = NULL;
f->f_inode = NULL;
return error;
}
以上即为do_sys_open接口的分析,主要涉及路径查找、链接目录、链接文件的查找、文件的打开等操作,简单来说就是实现了将文件系统相关的结构体(dentry、inode、task、fs_struct、file等结构体的关联)。
五、举例应用
5.1、示例 1:使用 open 系统调用打开一个文件
假设我们有一个简单的应用程序,使用 open 系统调用打开一个文件,读取文件内容并输出到标准输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *file_path = "/tmp/testfile.txt"; // 要打开的文件路径
char buffer[128];
ssize_t bytes_read;
// 使用 open 系统调用打开文件
int fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 读取文件内容
bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出文件内容
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
printf("File content:\n%s\n", buffer);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
分析:
open调用通过 VFS 层查找文件路径/tmp/testfile.txt所在的文件系统。- VFS 会通过与文件系统相关的
vfs_open接口,最终将open操作转发到具体文件系统的open函数。 - 由于
/tmp/testfile.txt是一个常见的文件路径,通常使用ext4或tmpfs文件系统,vfs_open会通过具体的文件系统驱动来打开文件并返回文件描述符。
文件系统与 VFS 交互:
- 对于
ext4文件系统,vfs_open会调用ext4_file_open来处理文件的打开操作。 - VFS 负责文件路径解析和文件系统选择,具体的文件操作则由文件系统的驱动函数来实现。
5.2、示例 2:使用 open 打开设备文件
Linux 中设备文件(如 /dev/sda 或 /dev/null)是特殊的文件,通常与硬件或虚拟设备相关。打开设备文件时,VFS 也会通过相应的设备驱动来处理操作。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *dev_path = "/dev/null"; // 打开设备文件
int fd;
// 打开设备文件
fd = open(dev_path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 向设备写入数据
const char *data = "Hello, /dev/null!";
if (write(fd, data, 17) == -1) {
perror("write");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
printf("Data written to /dev/null successfully.\n");
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
分析:
- 打开
/dev/null设备文件时,open系统调用通过 VFS 层查找设备文件路径。 - VFS 层会调用相应的设备驱动来处理设备文件的打开操作。对于
/dev/null,VFS 会找到对应的设备驱动并执行相应的设备打开操作。 - 对于设备文件的写入,数据会被丢弃,因为
/dev/null是一个特殊的设备,它会丢弃所有写入的数据。
设备文件与 VFS 交互:
/dev/null通常由一个名为null的字符设备驱动处理。VFS 会将open请求转发给字符设备的驱动程序,在驱动程序中实现具体的文件打开操作。
5.3、示例 3:使用 open 系统调用访问网络文件系统
在 Linux 中,网络文件系统(如 NFS 或 CIFS)允许用户访问远程主机上的文件。open 系统调用同样可以用来打开网络文件系统中的文件。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
const char *remote_file_path = "/mnt/nfs/share/testfile.txt"; // NFS 挂载点路径
int fd;
// 使用 open 打开 NFS 文件
fd = open(remote_file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// 读取文件内容
char buffer[128];
ssize_t bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
// 输出文件内容
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0';
printf("File content from NFS:\n%s\n", buffer);
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
return 0;
}
分析:
- 假设
/mnt/nfs/share/是一个 NFS 网络文件系统的挂载点,open调用会通过 VFS 层定位文件路径。 - VFS 会查找挂载的文件系统,并根据 NFS 协议转发操作到 NFS 客户端的代码中,完成文件的打开和读取。
- NFS 文件系统的操作会通过特定的协议处理,从远程服务器加载文件内容。
网络文件系统与 VFS 交互:
- VFS 会根据挂载点的类型选择文件系统类型(如 NFS、CIFS 等)。
- 对于 NFS 文件系统,VFS 会调用 NFS 客户端的实现来处理文件的打开、读取等操作。





















 1287
1287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








