前言
[感谢博主](https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/lixiaoweimashixiao/article/details/102061182?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522160730848519724838515036%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fall.%2522%257D&request_id=160730848519724838515036&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~first_rank_v2~rank_v29-3-102061182.first_rank_v2_pc_rank_v29&utm_term=Ardupilot%20GpS%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE&spm=1018.2118.3001.4449) 本节主要学习ardupilot的GPS数据更新过程,欢迎批评指正。
1.GPS信息简介
GPS(Global Positioning System),即全球定位系统,利用24颗GPS的测距和测时功能进行全球定位,在许多系统中,如现代船载(或车载)导航系统、机场导航系统、江河流域的灾害信息管理和预测系统中,GPS得到了广泛的应用。
GPS主要有3大组成部分,即空间星座部分、地面监控部分和用户设备部分。其中空间星座部分、地面监控部分均为美国所控制。GPS的用户设备主要有接收机硬件和处理软件组成。用户通过用户设备接收GPS卫星信号,经信号处理而获得用户位置、速度等信息,最终实现GPS进行导航和定位的目的。
对于通用GPS应用软件,需要一个统一格式的数据标准,以解决与任意一台GPS的接口问题。NMEA-0183数据标准就是解决这类问题的方案之一。NMEA协议是为了在不同的GPS导航设备中建立统一的RTCM(海事无线电技术委员会)标准,它最初是由美国国家海洋电子协会(NMEA—The NationalMarine Electronics Association)制定的。NMEA协议有0180、0182和0183这3种,0183可以认为是前两种的升级,也是目前使用最为广泛的一种。
一般GPS模块采用串口方式与外部模块进行通信,输出的GPS定位数据采用NMEA-0183协议,控制协议为为UBX协议。
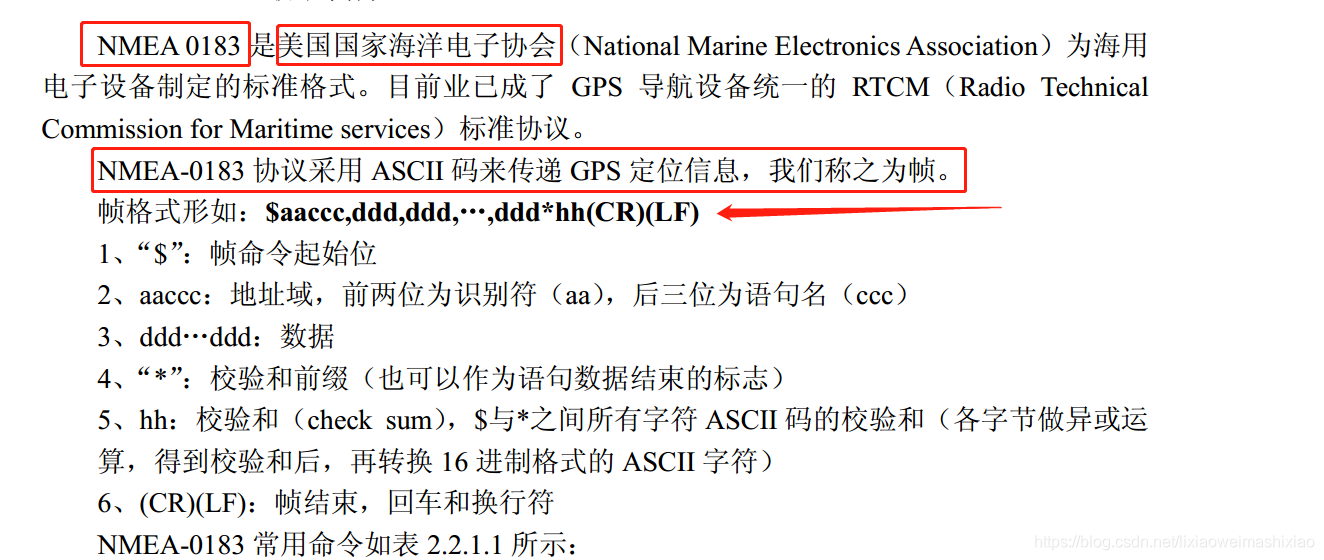
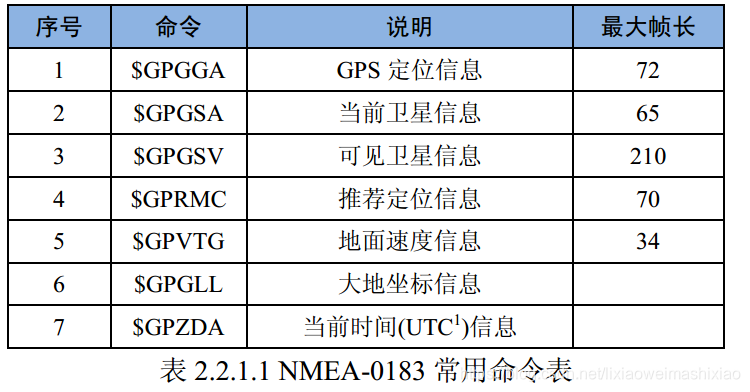
注 1: 即协调世界时,相当于本初子午线(0 度经线)上的时间,北京时间比 UTC 早 8 个小时。
1. GPGGA(gps定位信息)
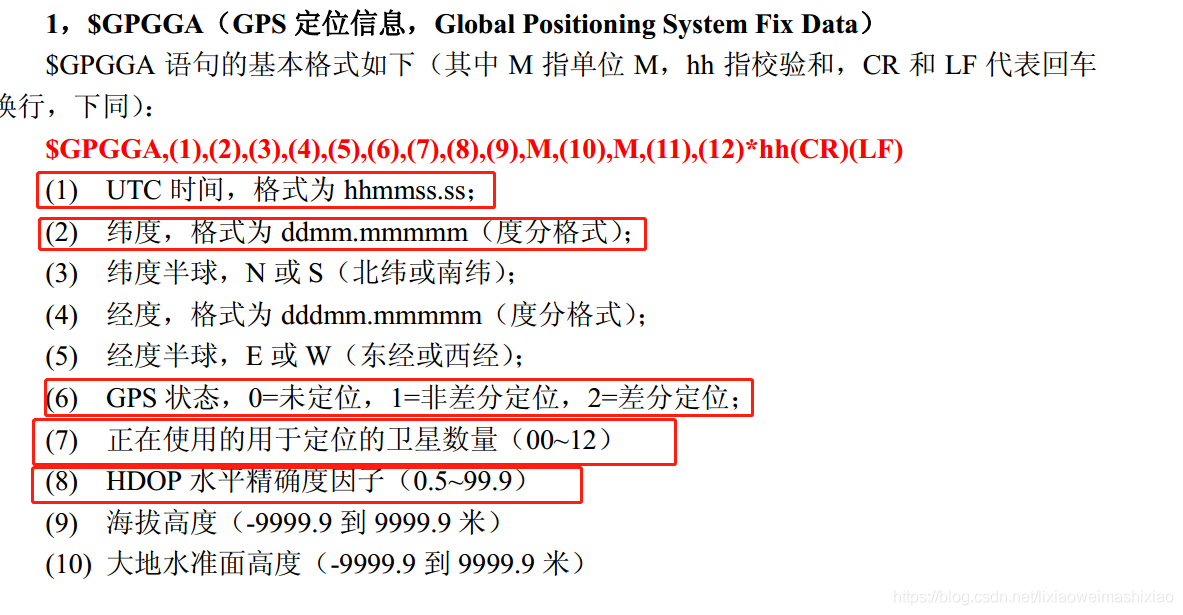

2. GPGSA(当前卫星信息)

3. GPGSV(可见卫星信息)

4. GPRMC (推荐定位信息)


5. GPVTG (地面速度信息)

6. GPG LL(定位地理信息)

7. GPZDA (当前时间信息)

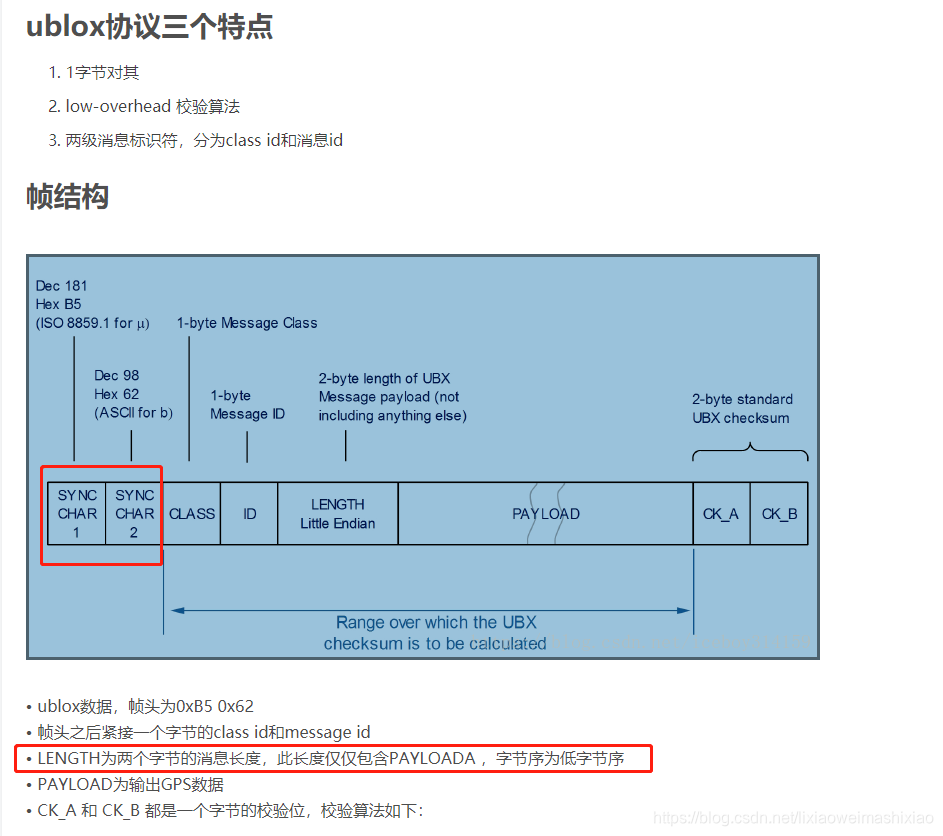
8.GPS的UBLOX协议
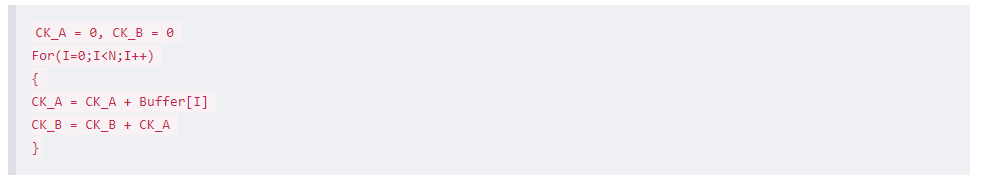
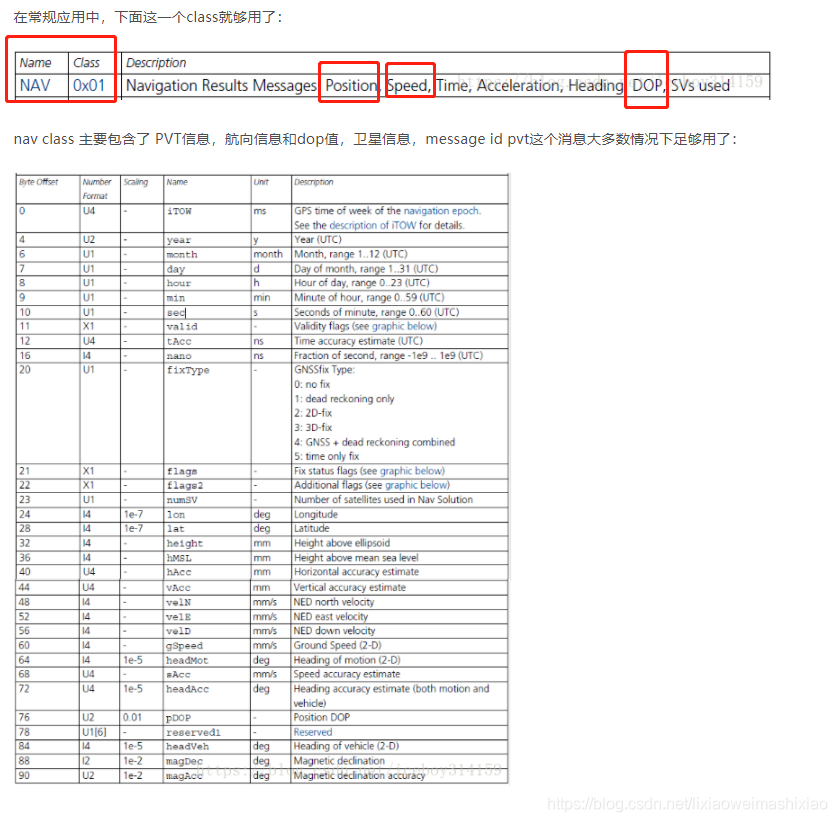
–>> 20201216更新:
UBLX协议补充:NAV_PVT协议
(1)carrSoln:载波相位距离信息状态(这里直接翻译,可能翻译不够精准):有3种状态:

0:没有定位时候的载波相位范围解决方案
1:float时候的载波相位范围解决方案
2: fixed时候的载波相位范围解决方案
(2) fixType:GNSSfix Type
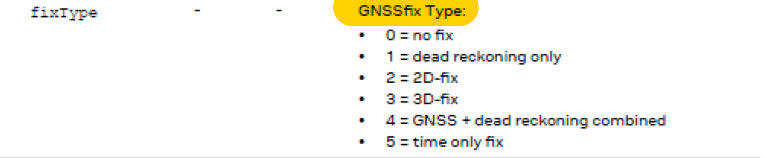
0:没有定位
1:只推算
2: 2D定位
3:3D定位
4:GNSS和推算结合
5:fix状态
(3)sAcc 速度精度 一般此值越低越好

–<<end
2.GPS传感器初始化
//执行init_ardupilot();这一部分,在上一篇文章中已经进行了讲解,请点[这里](https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhangfengmei1987/article/details/110469601)
/*
setup is called when the sketch starts
*/
void AP_Vehicle::setup()
{
...
// initialise serial ports
serial_manager.init();
...
// init_ardupilot is where the vehicle does most of its initialisation.
init_ardupilot();
}
void Copter::init_ardupilot()
{
...
// Do GPS init
gps.init(serial_manager);
}
1.执行 GPS的串口协议初始化:serial_manager.init();
// init - // init - initialise serial ports
void AP_SerialManager::init()
{
...
// initialise serial ports
for (uint8_t i=1; i<SERIALMANAGER_NUM_PORTS; i++) {
...
case SerialProtocol_GPS:
case SerialProtocol_GPS2:
state[i].uart->begin(map_baudrate(state[i].baud),
AP_SERIALMANAGER_GPS_BUFSIZE_RX,
AP_SERIALMANAGER_GPS_BUFSIZE_TX);
break;
...}
在libraries/AP_SerialManager/AP_SerialManager.cpp中从swatch函数中可以看出,init函数重点是配置实现相应的串口协议和波特率。而对应的协议和波特率已经通过如下定义实现。
#if SERIALMANAGER_NUM_PORTS > 3
// @Param: 3_PROTOCOL
// @DisplayName: Serial 3 (GPS) protocol selection
// @Description: Control what protocol Serial 3 (GPS) should be used for. Note that the Frsky options require external converter hardware. See the wiki for details.
// @Values: -1:None, 1:MAVLink1, 2:MAVLink2, 3:Frsky D, 4:Frsky SPort, 5:GPS, 7:Alexmos Gimbal Serial, 8:SToRM32 Gimbal Serial, 9:Rangefinder, 10:FrSky SPort Passthrough (OpenTX), 11:Lidar360, 13:Beacon, 14:Volz servo out, 15:SBus servo out, 16:ESC Telemetry, 17:Devo Telemetry, 18:OpticalFlow, 19:RobotisServo, 20:NMEA Output, 21:WindVane, 22:SLCAN, 23:RCIN, 24:MegaSquirt EFI, 25:LTM, 26:RunCam, 27:HottTelem, 28:Scripting, 29:Crossfire, 30:Generator, 31:Winch, 32:MSP, 33:DJI FPV
// @User: Standard
// @RebootRequired: True
AP_GROUPINFO("3_PROTOCOL", 5, AP_SerialManager, state[3].protocol, SERIAL3_PROTOCOL),
// @Param: 3_BAUD
// @DisplayName: Serial 3 (GPS) Baud Rate
// @Description: The baud rate used for the Serial 3 (GPS). Most stm32-based boards can support rates of up to 1500. If you setup a rate you cannot support and then can't connect to your board you should load a firmware from a different vehicle type. That will reset all your parameters to defaults.
// @Values: 1:1200,2:2400,4:4800,9:9600,19:19200,38:38400,57:57600,111:111100,115:115200,230:230400,256:256000,460:460800,500:500000,921:921600,1500:1500000
// @User: Standard
AP_GROUPINFO("3_BAUD", 6, AP_SerialManager, state[3].baud, AP_SERIALMANAGER_GPS_BAUD/1000),
#endif
2.GPS函数初始化
由于在AP_Vehicle.h中gps来源如下,所以可以追溯 gps.init的来源为AP_GPS::init // sensor drivers
AP_GPS gps;
/// Startup initialisation.
void AP_GPS::init(const AP_SerialManager& serial_manager)
{
primary_instance = 0;
// search for serial ports with gps protocol
uint8_t uart_idx = 0;
for (uint8_t i=0; i<GPS_MAX_RECEIVERS; i++) {
if (needs_uart((GPS_Type)_type[i].get())) {
_port[i] = serial_manager.find_serial(AP_SerialManager::SerialProtocol_GPS, uart_idx);
uart_idx++;
}
}
_last_instance_swap_ms = 0;
// Initialise class variables used to do GPS blending
_omega_lpf = 1.0f / constrain_float(_blend_tc, 5.0f, 30.0f);
// prep the state instance fields
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < GPS_MAX_INSTANCES; i++) {
state[i].instance = i;
}
// sanity check update rate
for (uint8_t i=0; i<GPS_MAX_RECEIVERS; i++) {
if (_rate_ms[i] <= 0 || _rate_ms[i] > GPS_MAX_RATE_MS) {
_rate_ms[i] = GPS_MAX_RATE_MS;
}
}
}
3.更新GPS数据
3.1 AP_GPS::update
/*
scheduler table for fast CPUs - all regular tasks apart from the fast_loop()
should be listed here, along with how often they should be called (in hz)
and the maximum time they are expected to take (in microseconds)
*/
const AP_Scheduler::Task Copter::scheduler_tasks[] = {
SCHED_TASK(rc_loop, 100, 130),
SCHED_TASK(throttle_loop, 50, 75),
SCHED_TASK_CLASS(AP_GPS, &copter.gps, update, 50, 200),
在ArduCopter/Copter.cpp中可知任务调度GPS更新采用的是50Hz。
/*
update all GPS instances
*/
void AP_GPS::update(void)
{
WITH_SEMAPHORE(rsem);
for (uint8_t i=0; i<GPS_MAX_RECEIVERS; i++) {
update_instance(i);
}
// calculate number of instances
for (uint8_t i=0; i<GPS_MAX_RECEIVERS; i++) {
if (drivers[i] != nullptr) {
num_instances = i+1;
}
}
update_primary();
#ifndef HAL_BUILD_AP_PERIPH
// update notify with gps status. We always base this on the primary_instance
AP_Notify::flags.gps_status = state[primary_instance].status;
AP_Notify::flags.gps_num_sats = state[primary_instance].num_sats;
#endif
}
GPS更新函数中主要是完成update_instance和update_primary。
3.2 AP_GPS::update_instance
由于AP_GPS::update_instance代码较长,这里不copy代码了。这个函数主要是更新GPS实例的个数。内部detect_instance实例化选择配置不同的GPS。 以下是detect_instance函数中比较关键的地方。 //我们已经激活GPS驱动实例,这里进行了数据的读取----we have an active driver for this instance
bool result = drivers[instance]->read(); //读取数据
uint32_t tnow = AP_HAL::millis();
bool data_should_be_logged = false;
if (!result) {
if (tnow - timing[instance].last_message_time_ms > GPS_TIMEOUT_MS) {
...
send_blob_start(instance, _initialisation_blob, sizeof(_initialisation_blob));
...
send_blob_update(instance);
}
else{
...
}
}
整体代码较长
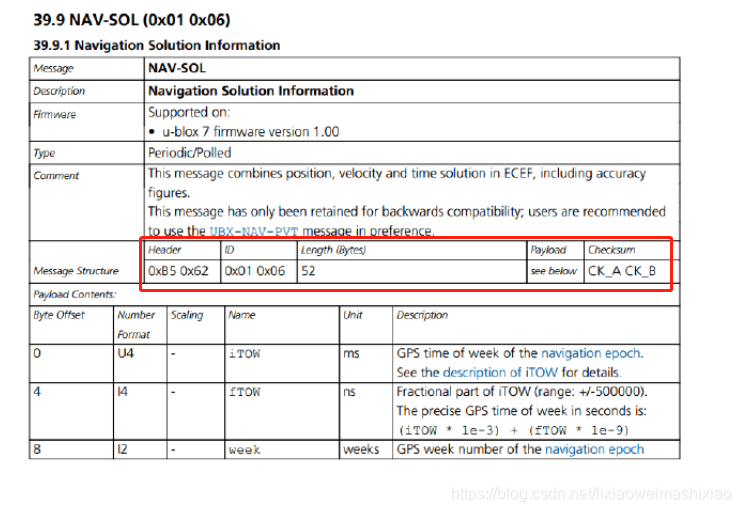
下面是UBLOX的Class信息
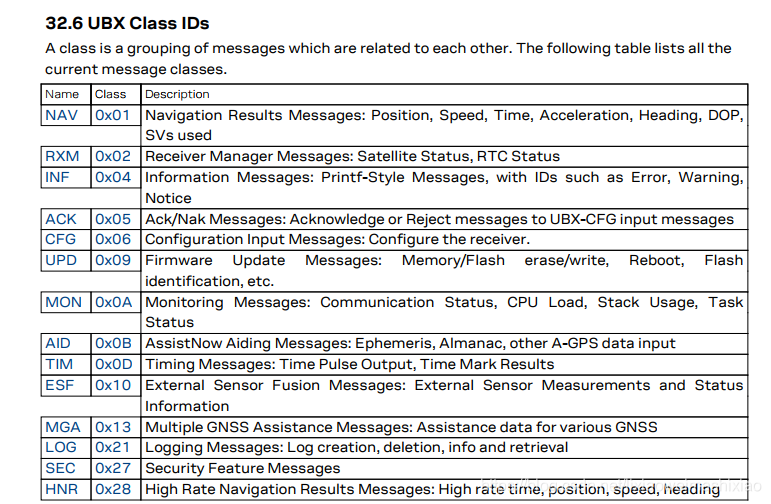
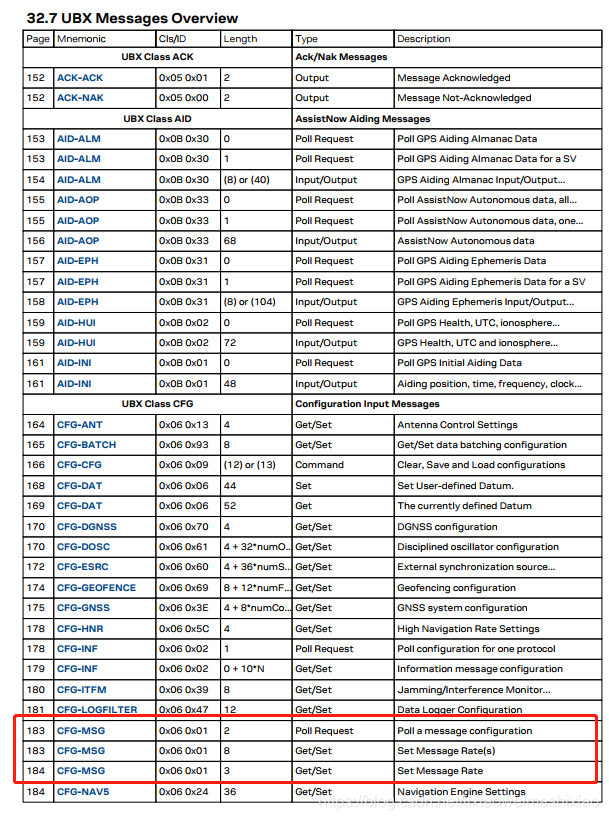
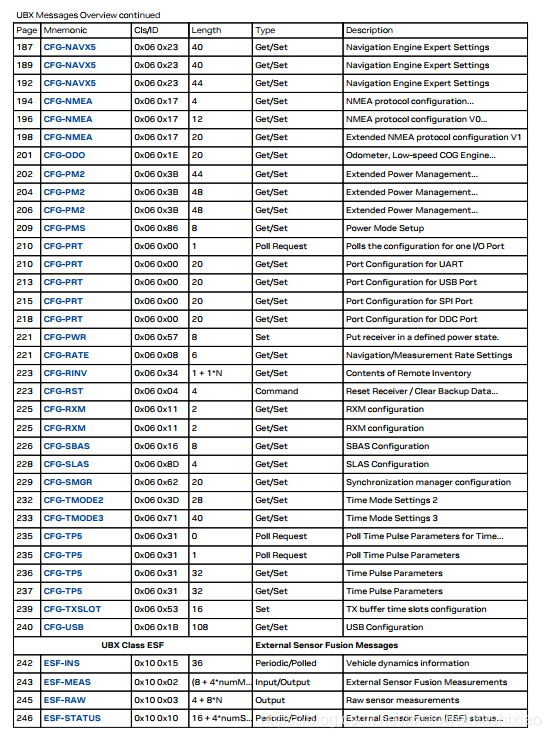
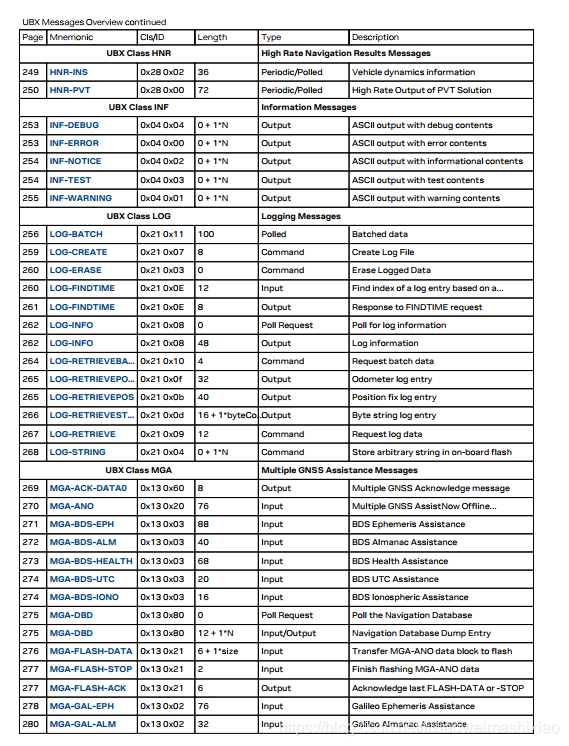
具体的UBLOX协议信息可以去这里下载:UBLOX协议
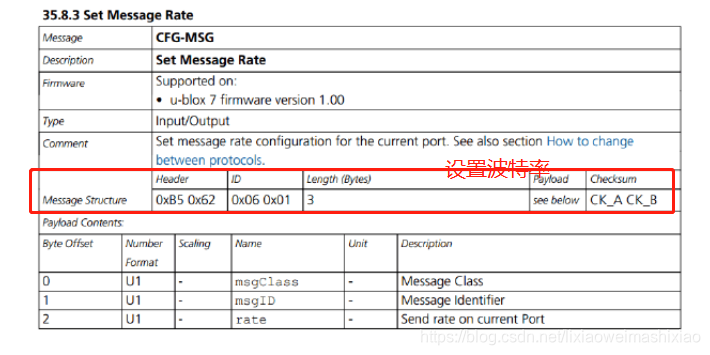

void AP_GPS::send_blob_start(uint8_t instance, const char *_blob, uint16_t size)
{
initblob_state[instance].blob = _blob;
initblob_state[instance].remaining = size;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
send_blob_update(instance);
/*
send some more initialisation string bytes if there is room in the
UART transmit buffer
*/
void AP_GPS::send_blob_update(uint8_t instance)
{
// exit immediately if no uart for this instance
if (_port[instance] == nullptr) {
return;
}
// see if we can write some more of the initialisation blob
if (initblob_state[instance].remaining > 0) {
int16_t space = _port[instance]->txspace();
if (space > (int16_t)initblob_state[instance].remaining) {
space = initblob_state[instance].remaining;
}
while (space > 0) {
_port[instance]->write(*initblob_state[instance].blob);
initblob_state[instance].blob++;
space--;
initblob_state[instance].remaining--;
}
}
}
在update_instance()函数中出现的send_blob_start()和send_blob_update()这两个函数中的作用并不是很理解,但通过注释的功能可以看出主要是完成数据的发送部分。
2. bool result = drivers[instance]->read(); //读取数据
这里我们主要选择UBLOX进行GPS数据解析,当然你可以选择NMEA等等。这个函数在update_instance()中。
1.UBLOX数据读取
AP_GPS_Backend *drivers[GPS_MAX_RECEIVERS];
由上述部分可以知道drivers[instance]是AP_GPS_Backend 的实体对象。
在AP_GPS/GPS_Backend.h中定义的AP_GPS_Backend类中可以看出read函数纯虚函数,所以会在子类中进行实现。所以找到AP_GPS/AP_GPS_UBLOX.h中,可以找到read函数的实现。
virtual bool read() = 0;
// Ensure there is enough space for the largest possible outgoing message
// Process bytes available from the stream
//
// The stream is assumed to contain only messages we recognise. If it
// contains other messages, and those messages contain the preamble
// bytes, it is possible for this code to fail to synchronise to the
// stream immediately. Without buffering the entire message and
// re-processing it from the top, this is unavoidable. The parser
// attempts to avoid this when possible.
//
bool
AP_GPS_UBLOX::read(void)
{
uint8_t data;
int16_t numc;
bool parsed = false;
uint32_t millis_now = AP_HAL::millis();
// walk through the gps configuration at 1 message per second
if (millis_now - _last_config_time >= _delay_time) {
_request_next_config();
_last_config_time = millis_now;
if (_unconfigured_messages) { // send the updates faster until fully configured
if (!havePvtMsg && (_unconfigured_messages & CONFIG_REQUIRED_INITIAL)) {
_delay_time = 300;
} else {
_delay_time = 750;
}
} else {
_delay_time = 2000;
}
}
if(!_unconfigured_messages && gps._save_config && !_cfg_saved &&
_num_cfg_save_tries < 5 && (millis_now - _last_cfg_sent_time) > 5000 &&
!hal.util->get_soft_armed()) {
//save the configuration sent until now
if (gps._save_config == 1 ||
(gps._save_config == 2 && _cfg_needs_save)) {
_save_cfg();
}
}
numc = port->available();
for (int16_t i = 0; i < numc; i++) { // Process bytes received
// read the next byte
data = port->read();
#if GPS_UBLOX_MOVING_BASELINE
if (rtcm3_parser) {
if (rtcm3_parser->read(data)) {
// we've found a RTCMv3 packet. We stop parsing at
// this point and reset u-blox parse state. We need to
// stop parsing to give the higher level driver a
// chance to send the RTCMv3 packet to another (rover)
// GPS
_step = 0;
break;
}
}
#endif
reset:
switch(_step) {
// Message preamble detection
//
// If we fail to match any of the expected bytes, we reset
// the state machine and re-consider the failed byte as
// the first byte of the preamble. This improves our
// chances of recovering from a mismatch and makes it less
// likely that we will be fooled by the preamble appearing
// as data in some other message.
//
case 1:
if (PREAMBLE2 == data) {
_step++;
break;
}
_step = 0;
Debug("reset %u", __LINE__);
FALLTHROUGH;
case 0:
if(PREAMBLE1 == data)
_step++;
break;
// Message header processing
//
// We sniff the class and message ID to decide whether we
// are going to gather the message bytes or just discard
// them.
//
// We always collect the length so that we can avoid being
// fooled by preamble bytes in messages.
//
case 2:
_step++;
_class = data;
_ck_b = _ck_a = data; // reset the checksum accumulators
break;
case 3:
_step++;
_ck_b += (_ck_a += data); // checksum byte
_msg_id = data;
break;
case 4:
_step++;
_ck_b += (_ck_a += data); // checksum byte
_payload_length = data; // payload length low byte
break;
case 5:
_step++;
_ck_b += (_ck_a += data); // checksum byte
_payload_length += (uint16_t)(data<<8);
if (_payload_length > sizeof(_buffer)) {
Debug("large payload %u", (unsigned)_payload_length);
// assume any payload bigger then what we know about is noise
_payload_length = 0;
_step = 0;
goto reset;
}
_payload_counter = 0; // prepare to receive payload
if (_payload_length == 0) {
// bypass payload and go straight to checksum
_step++;
}
break;
// Receive message data
//
case 6:
_ck_b += (_ck_a += data); // checksum byte
if (_payload_counter < sizeof(_buffer)) {
_buffer[_payload_counter] = data;
}
if (++_payload_counter == _payload_length)
_step++;
break;
// Checksum and message processing
//
case 7:
_step++;
if (_ck_a != data) {
Debug("bad cka %x should be %x", data, _ck_a);
_step = 0;
goto reset;
}
break;
case 8:
_step = 0;
if (_ck_b != data) {
Debug("bad ckb %x should be %x", data, _ck_b);
break; // bad checksum
}
#if GPS_UBLOX_MOVING_BASELINE
if (rtcm3_parser) {
// this is a uBlox packet, discard any partial RTCMv3 state
rtcm3_parser->reset();
}
#endif
if (_parse_gps()) {
parsed = true;
}
break;
}
}
return parsed;
}
2.NMEA数据读取
bool AP_GPS_NMEA::read(void)
{
int16_t numc;
bool parsed = false;
numc = port->available();
while (numc--) {
char c = port->read();
#ifdef NMEA_LOG_PATH
static FILE *logf = nullptr;
if (logf == nullptr) {
logf = fopen(NMEA_LOG_PATH, "wb");
}
if (logf != nullptr) {
::fwrite(&c, 1, 1, logf);
}
#endif
if (_decode(c)) {
parsed = true;
}
}
return parsed;
}
进行GPS数据解析
bool AP_GPS_NMEA::_decode(char c)
{
bool valid_sentence = false;
_sentence_length++;
switch (c) {
case ',': // term terminators
_parity ^= c;
FALLTHROUGH;
case '\r':
case '\n':
case '*':
if (_sentence_done) {
return false;
}
if (_term_offset < sizeof(_term)) {
_term[_term_offset] = 0;
valid_sentence = _term_complete();
}
++_term_number;
_term_offset = 0;
_is_checksum_term = c == '*';
return valid_sentence;
case '$': // sentence begin
_term_number = _term_offset = 0;
_parity = 0;
_sentence_type = _GPS_SENTENCE_OTHER;
_is_checksum_term = false;
_gps_data_good = false;
_sentence_length = 1;
_sentence_done = false;
return valid_sentence;
}
// ordinary characters
if (_term_offset < sizeof(_term) - 1)
_term[_term_offset++] = c;
if (!_is_checksum_term)
_parity ^= c;
return valid_sentence;
}
4.GPS数据异常判定bool AP_GPS::is_healthy(uint8_t instance) const
通过上面的讲解,并没有给出GPS数据异常等判定。所以这里进行初步分析bool AP_GPS::is_healthy(uint8_t instance) const
{
if (instance >= GPS_MAX__INSTANCES) {
return false;
}
/*
allow two lost frames before declaring the GPS unhealthy, but
require the average frame rate to be close to 5Hz. We allow for
a bit higher average for a rover due to the packet loss that
happens with the RTCMv3 data
*/
const uint8_t delay_threshold = 2;
const float delay_avg_max = _type[instance] == GPS_TYPE_UBLOX_RTK_ROVER?245:215;
const GPS_timing &t = timing[instance];
bool delay_ok = (t.delayed_count < delay_threshold) &&
t.average_delta_ms < delay_avg_max &&
state[instance].lagged_sample_count < 5;
#if defined(GPS_BLENDED_INSTANCE)
if (instance == GPS_BLENDED_INSTANCE) {
return delay_ok && blend_health_check();
}
#endif
return delay_ok && drivers[instance] != nullptr &&
drivers[instance]->is_healthy();
}
通过上述代码可以看出判定GPS健康的状态主要是通过数据丢帧计数和是否接受到有效数据两部分组成。
现在对drivers[instance]->is_healthy();这个函数也没有什么特别的理解,就是表示串口接收正常吧。
感觉有点乱了,后面再补充吧。20201207
~~ 20201223更新








 本文详细介绍了ArduPilot中GPS数据的初始化、更新及解析过程,包括GPS传感器初始化步骤、不同协议(NMEA与UBLOX)下的数据读取与解析方法。
本文详细介绍了ArduPilot中GPS数据的初始化、更新及解析过程,包括GPS传感器初始化步骤、不同协议(NMEA与UBLOX)下的数据读取与解析方法。
















 3154
3154

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








